link: Web
Session Management
Diagrams
Diagrams
Overview
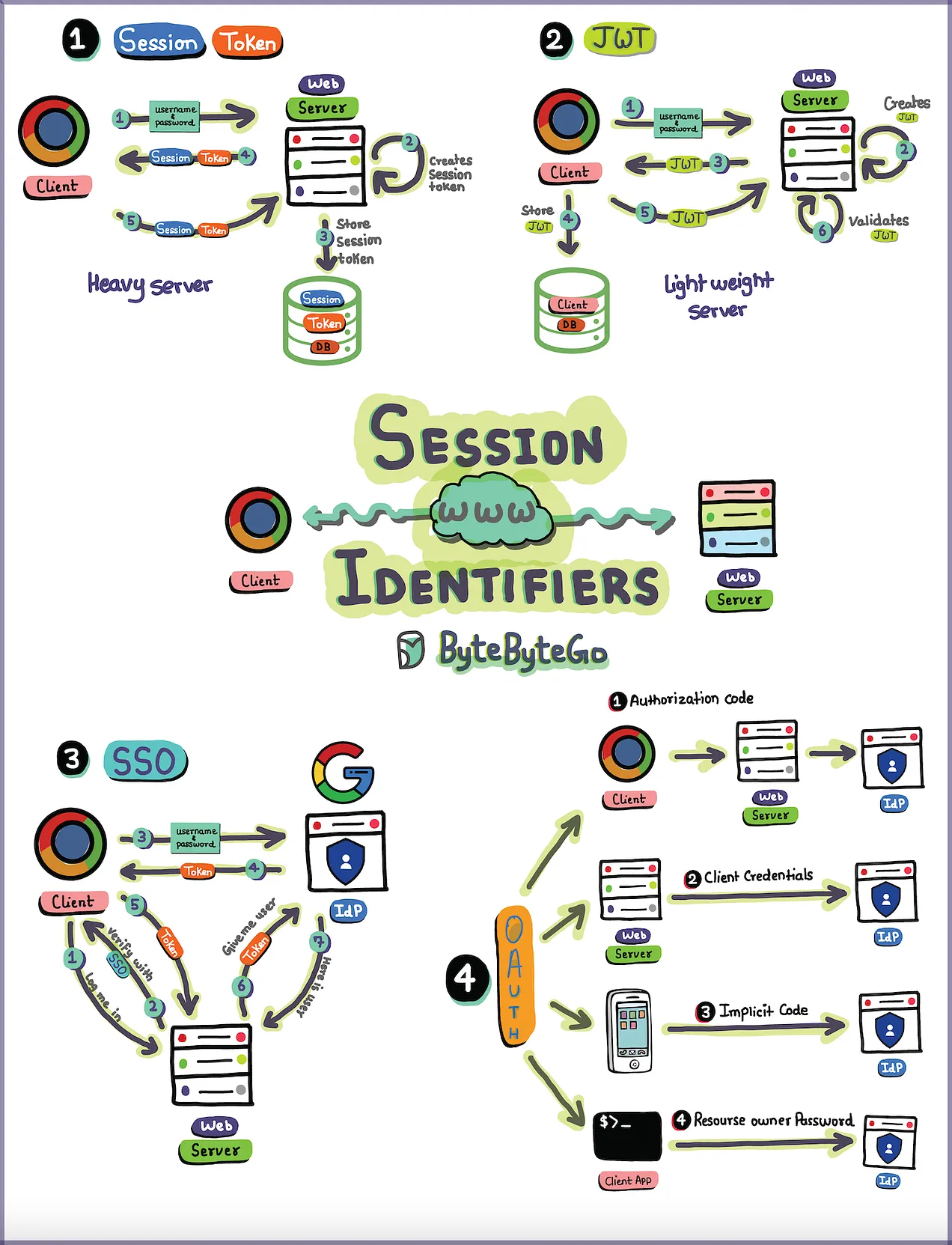
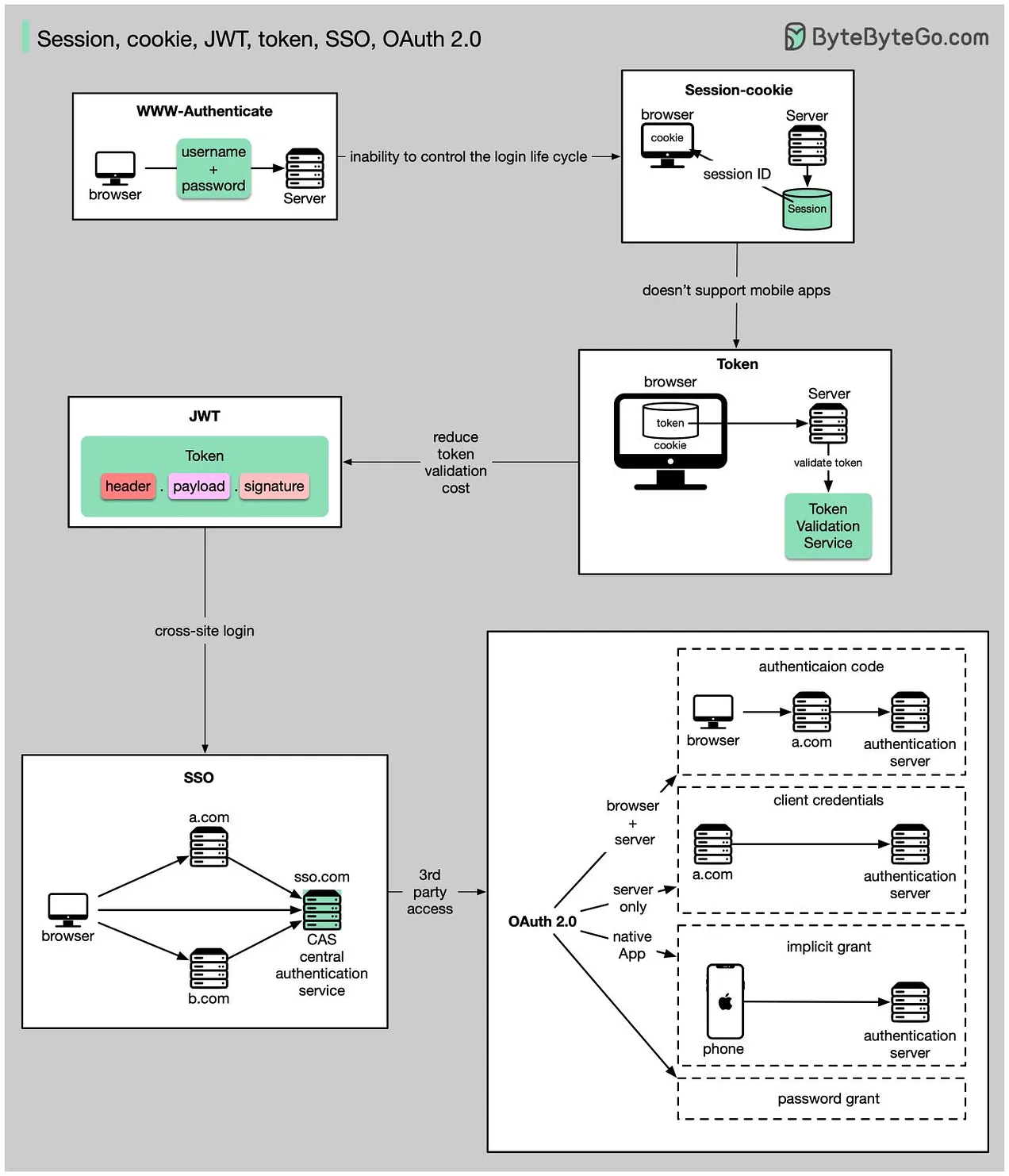
Web session management is essential for maintaining user state and session information across multiple requests in web applications. Given that HTTP is a stateless protocol, session management techniques are employed to persist user interactions and data across multiple requests, ensuring a seamless and personalized user experience.
Key Session Management Techniques
Techniques
- Web Cookies: Used to store session data on the client side.
- Web Server-Side Sessions: Stores session data on the server, with a session ID stored in a client-side cookie.
- Web Local Storage: HTML5 feature for storing data on the client side with no expiration date.
- Web Session Storage: HTML5 feature similar to local storage, but data is cleared when the page session ends.
- Web Tokens: Encrypted tokens like JSON Web Tokens (JWT) used for maintaining user sessions.
How Session Management Works
How It Works
- User Authentication: When a user logs in, the server generates a session and assigns a unique session ID.
- Session ID Storage: The session ID is stored on the client-side, typically in a cookie.
- Request Handling: For each subsequent request, the client sends the session ID to the server.
- Session Validation: The server validates the session ID and retrieves the corresponding session data.
- Session Termination: Sessions can be terminated explicitly (e.g., user logs out) or implicitly (e.g., session timeout).
Best Practices
Recommendations
- Use Secure Cookies: Mark cookies as secure to ensure they are only sent over HTTPS.
- Set HttpOnly Flag: Use the HttpOnly flag to prevent client-side scripts from accessing cookies.
- Implement Session Expiration: Set expiration times for sessions to minimize security risks.
- Regenerate Session IDs: Regenerate session IDs upon login to prevent session fixation attacks.
- Use Strong Encryption: Encrypt session data and tokens to protect against unauthorized access.
Related Topics
Summary
- Authentication: The process of verifying user identity, which often leads to the creation of a session.
- Authorization: Determines what authenticated users are allowed to do, often managed through session data.
- Security Policies: Guidelines and practices for maintaining secure session management and protecting user data.
- Encryption: Essential for protecting session data, especially in tokens and cookies, to prevent unauthorized access.