link: API Architectures
SOAP API (Simple Object Access Protocol)
Diagram
Overview
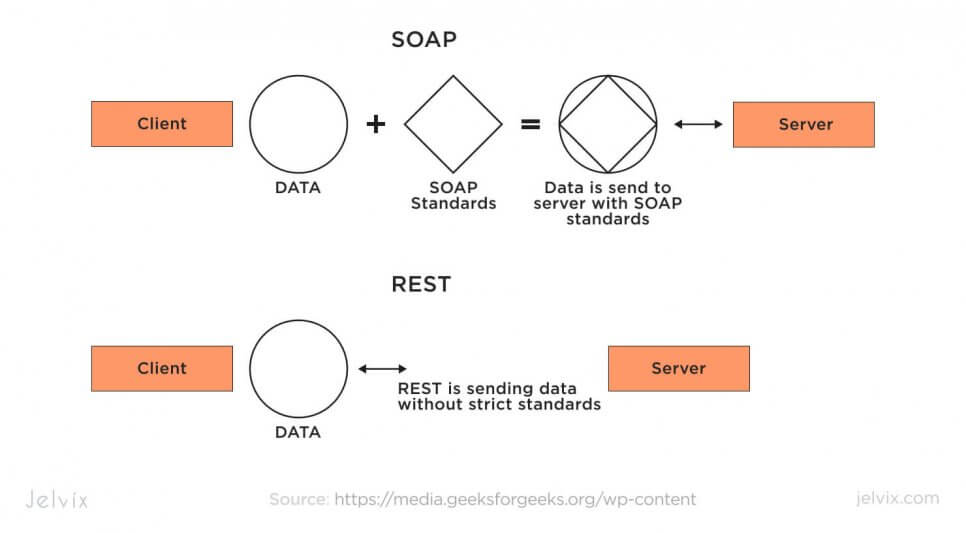
SOAP, or Simple Object Access Protocol, is a protocol standard for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. It relies on XML (Extensible Markup Language) for its message format and usually relies on other application layer protocols, most notably HTTP or SMTP, for message negotiation and transmission.
Characteristics of SOAP
SOAP defines a set of rules for structuring messages that can be processed by any operating system. SOAP APIs are highly standardized and provide robust mechanisms for ensuring that messages are delivered correctly and securely.
Info
- Protocol: SOAP can operate over any transport protocol such as HTTP, SMTP, TCP, or JMS.
- Enveloping: SOAP messages are encapsulated in an envelope. They can contain a header (optional) and a body, which is the main part of the message.
- Encoding Rules: Defines a serialization mechanism that can be used to exchange instances of application-defined datatypes.
- Convention: Uses a specific convention for representing procedure calls and responses.
Pros/Cons
Pros
- Standardization: SOAP ensures strict compliance with standards, making it suitable for formal enterprise environments.
- Security: Features comprehensive security protocols like WS-Security for authentication, authorization, and encryption.
- Extensibility: Can be extended with protocols such as WS-ReliableMessaging for enhanced capabilities.
- Stateful Operations: Supports operations that require the server to maintain client session state.
- Language and Platform Independence: Uses XML, allowing use across different platforms and programming languages.
- ACID Compliance: Facilitates reliable transaction processing by supporting ACID-compliant transactions.
Cons
- Complexity: The complexity of SOAP can be daunting for new developers due to its detailed standards and features.
- Performance Overhead: SOAP’s use of XML can increase message size and reduce performance relative to simpler protocols like REST.
- Limited Flexibility: The strict standards can restrict how data is handled and result in verbose messages.
- Steep Learning Curve: Learning SOAP’s various standards and protocols requires significant time and effort.
- Browser Compatibility: Setting up SOAP calls is more complex than using REST, which can be easily managed in modern web browsers.
Common Use Cases
SOAP is widely used in enterprise environments and integrated large-scale systems:
Example
- Financial Services: Banks and other financial institutions use SOAP for secure and reliable communication of transactional data.
- Telecommunications: Used for billing services and customer relationship management.
- Health Care: Exchanges patient information, billing data, and scheduling between facilities.
Conclusion
SOAP APIs are particularly well-suited for business-critical applications requiring high security, transactional reliability, and standardized operations across different networks and domains. While SOAP can be more complex and resource-intensive than other approaches, its robustness makes it ideal for certain use cases in enterprise environments.