link: Web Communication Protocols
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
Overview
SMTP, or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, is the standard protocol used on the Internet for sending emails from clients to mail servers and between servers. It’s a part of the TCP/IP protocol suite and operates on port 25. SMTP is used primarily for sending messages but also has mechanisms for relaying and forwarding messages from one server to another.
Key Features of SMTP
- Text-Based Protocol: SMTP commands are human-readable text.
- Reliable Delivery: Ensures that emails are properly transmitted between servers using a process of requests and responses.
- Simple Mechanism: Focuses solely on sending out emails without the capabilities to fetch or store received emails, which is handled by other protocols like IMAP or POP.
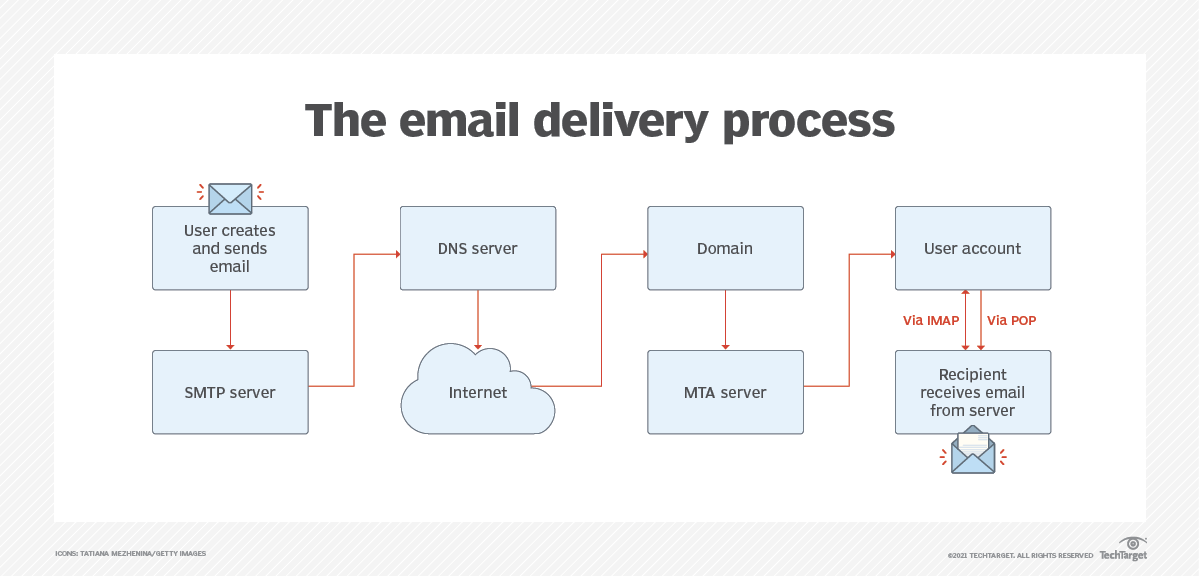
SMTP Flow
The SMTP communication process involves several key stages, typically beginning with an SMTP client initiating a connection to an SMTP server:
- Connection Establishment: The client requests a connection to the SMTP server.
- SMTP Handshake: Once connected, the SMTP server and client exchange greetings, and the server identifies itself.
- Mail Transmission: The client begins the mail transmission process using SMTP commands.
- Queue and Forward: The server queues the email for delivery. If the recipient is outside the server’s domain, the email is forwarded to another SMTP server.
- Session Termination: After emails are queued or sent, the session is terminated with a QUIT command.
SMTP Commands
SMTP operates using a series of text-based commands sent from the client to the server. Here are some of the fundamental SMTP commands:
- HELO/EHLO: Initiates the SMTP session and identifies the sender’s domain.
- MAIL FROM: Specifies the email address of the sender.
- RCPT TO: Specifies the recipient’s email address.
- DATA: Begins the transfer of the message content, ending with a single period (.) on a line by itself.
- QUIT: Ends the SMTP session.
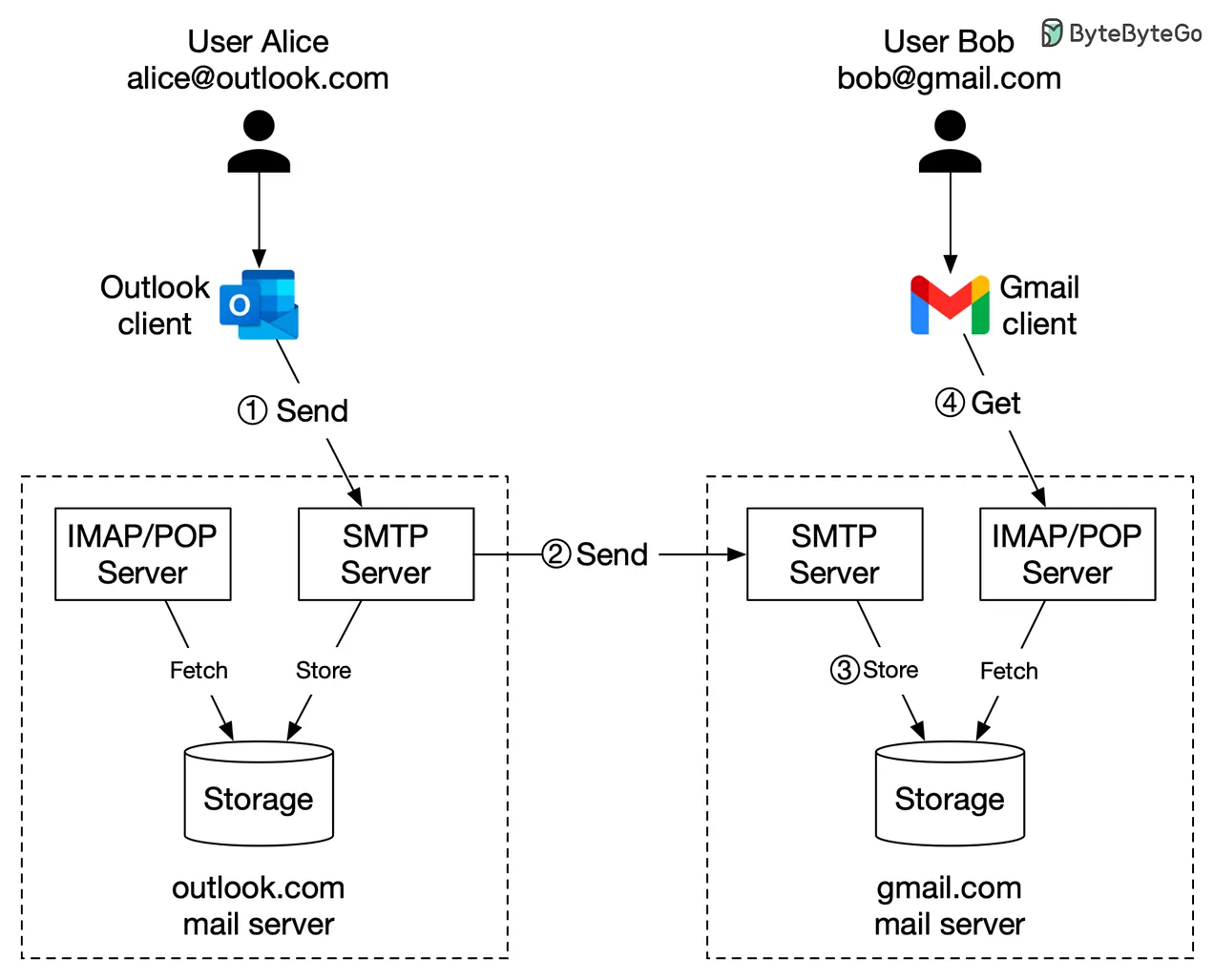
Example of SMTP Usage
Example
When a user sends an email, their email client interacts with the SMTP server using SMTP commands. The server then processes these commands to send the email to the recipient’s SMTP server. If the recipient is within the same domain, the email is directed to the appropriate account. Otherwise, it is sent to an external SMTP server closer to the recipient’s location.
Conclusion
SMTP is a foundational internet protocol essential for email transmission. Understanding SMTP’s operation, including its flow and commands, is crucial for IT professionals managing email services and infrastructure. This protocol’s efficiency and simplicity have made it the backbone of email communication worldwide.