link: API
API Architectures
Diagram
Visual Diagrams
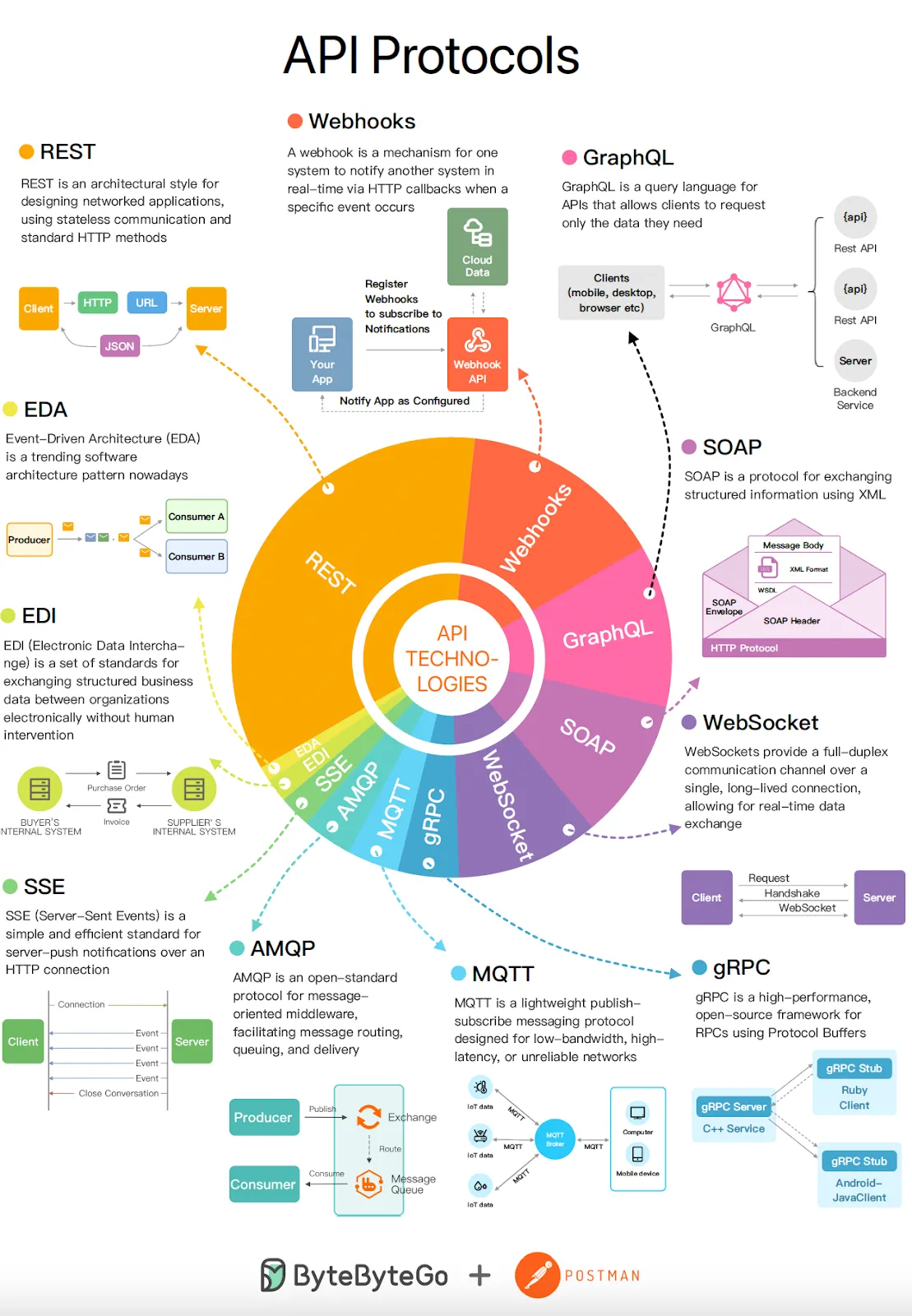
General API Protocols Overview
Overview
Choosing the right API architecture is crucial for the success of any application, influencing how effectively it communicates internally and with external systems. Various architectural styles cater to different needs, from simple data transfer to complex real-time interactions.
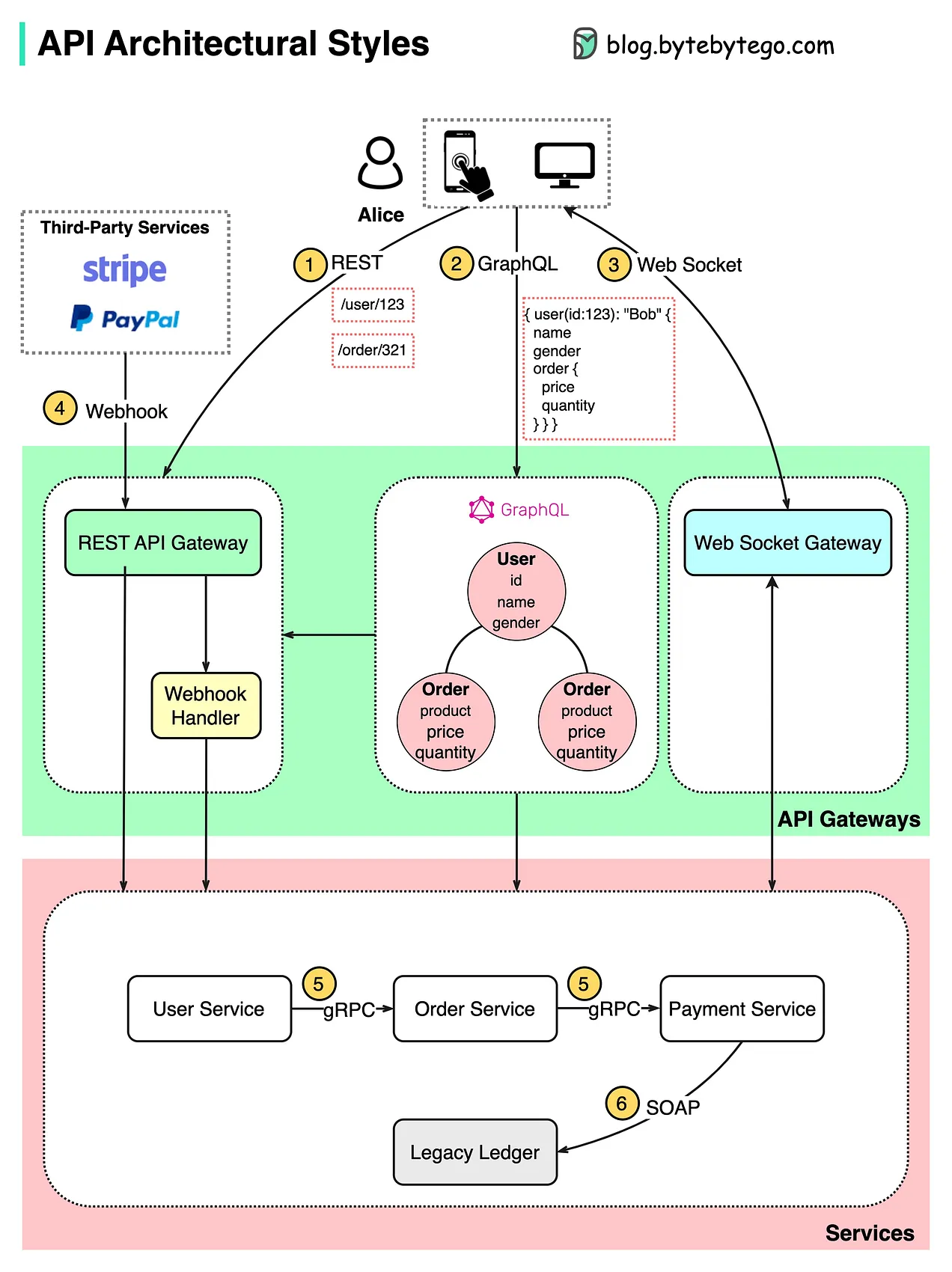
API Architectural Styles
API architectural styles are designed to suit specific scenarios and requirements, each offering unique advantages:
API Architectural Styles
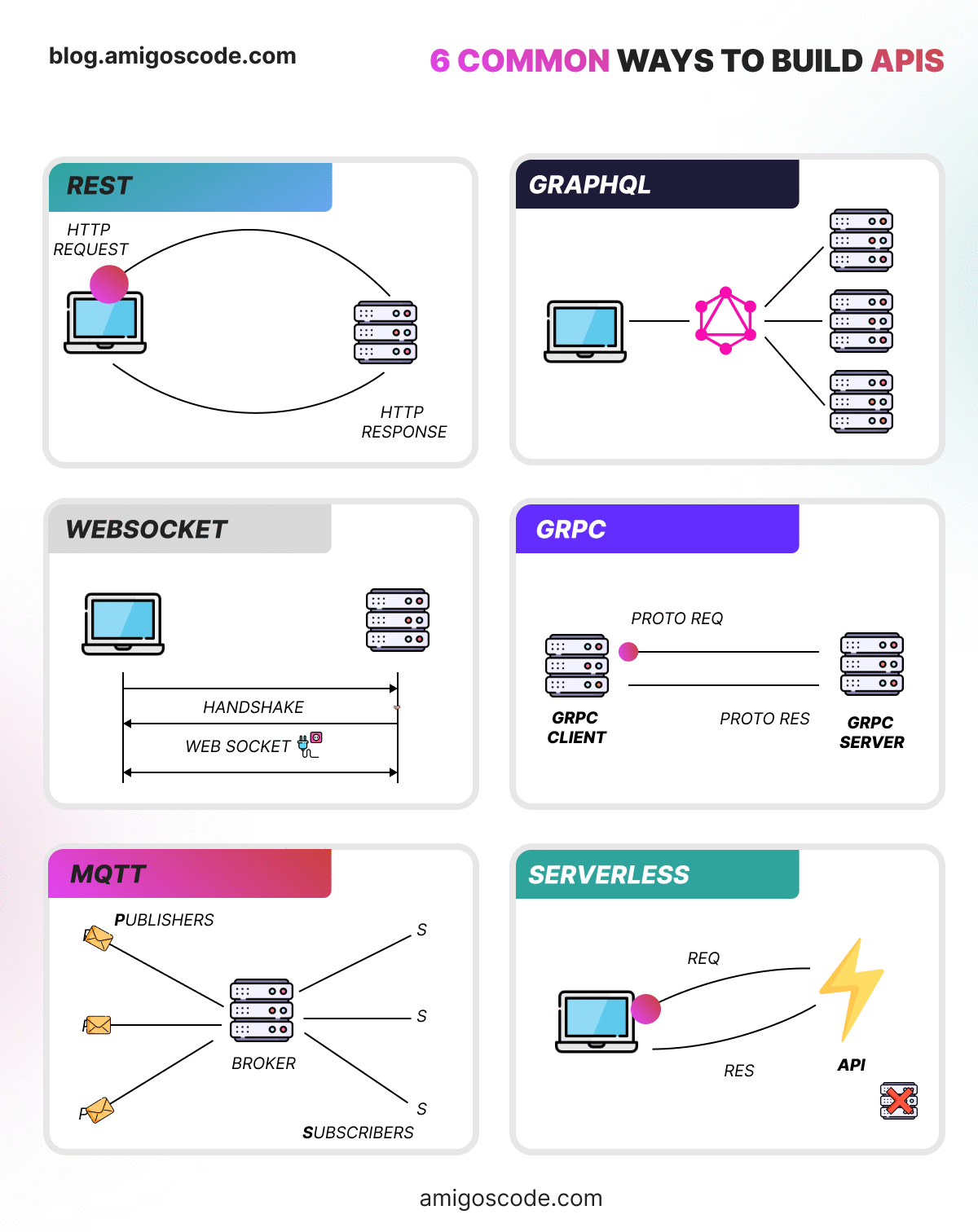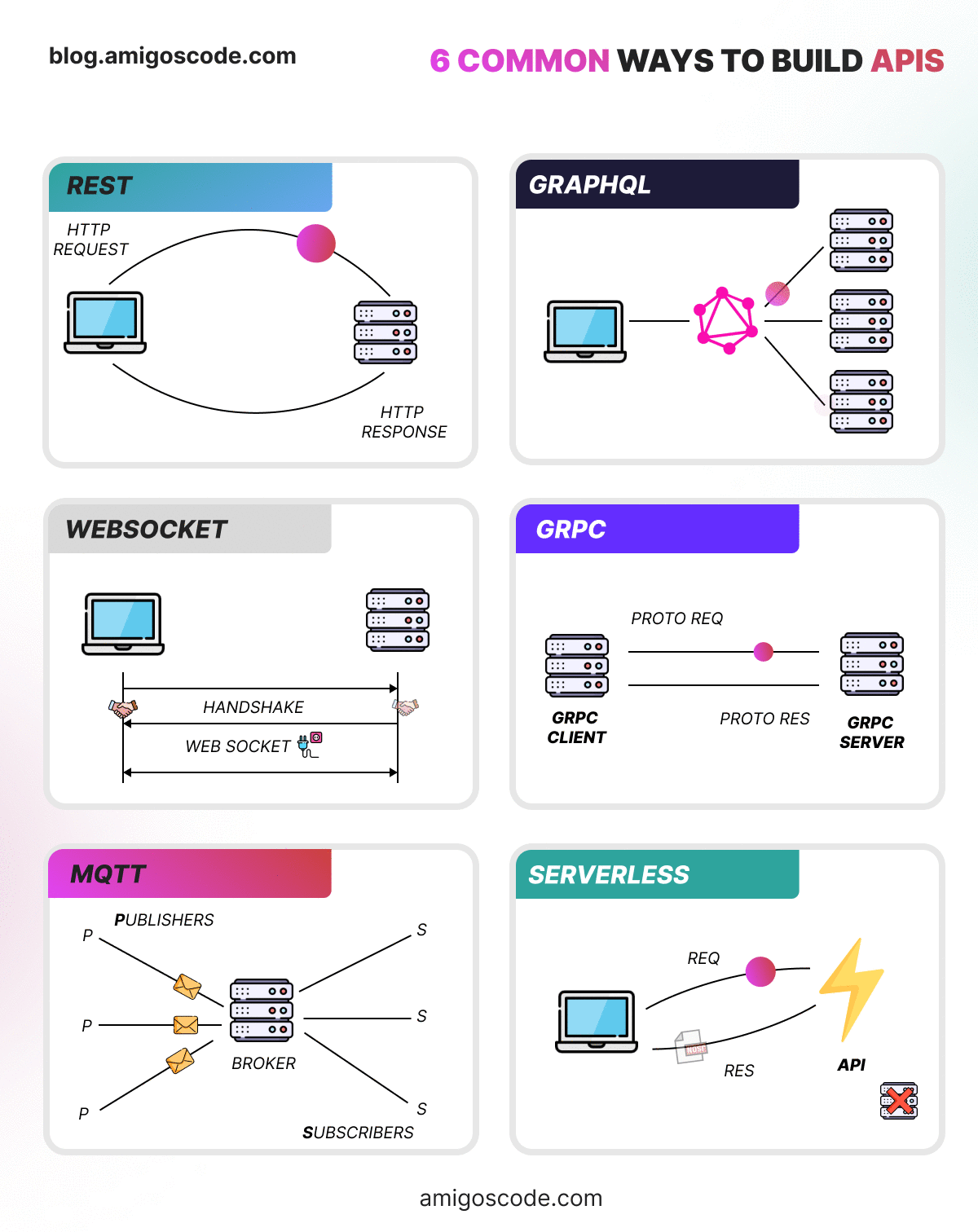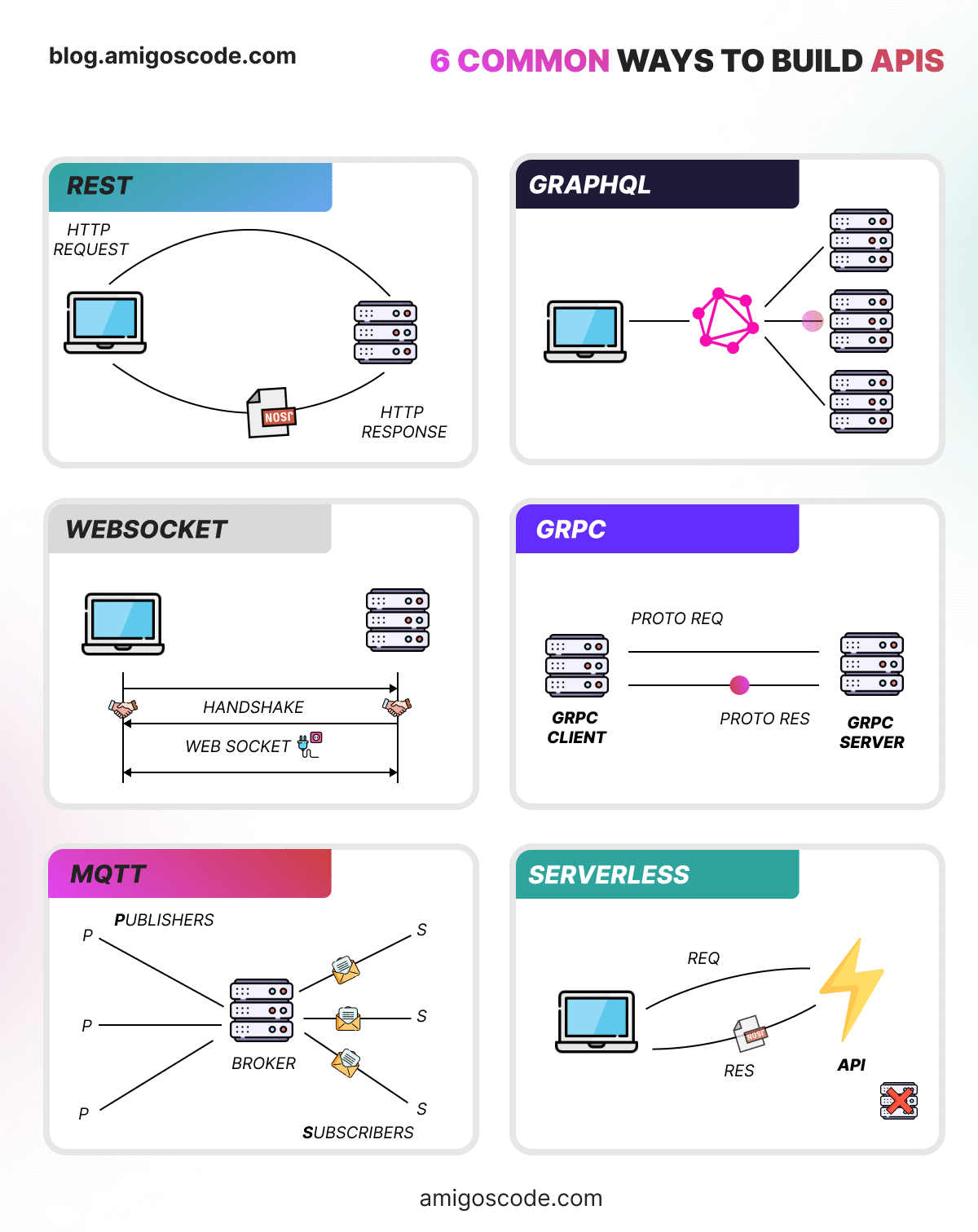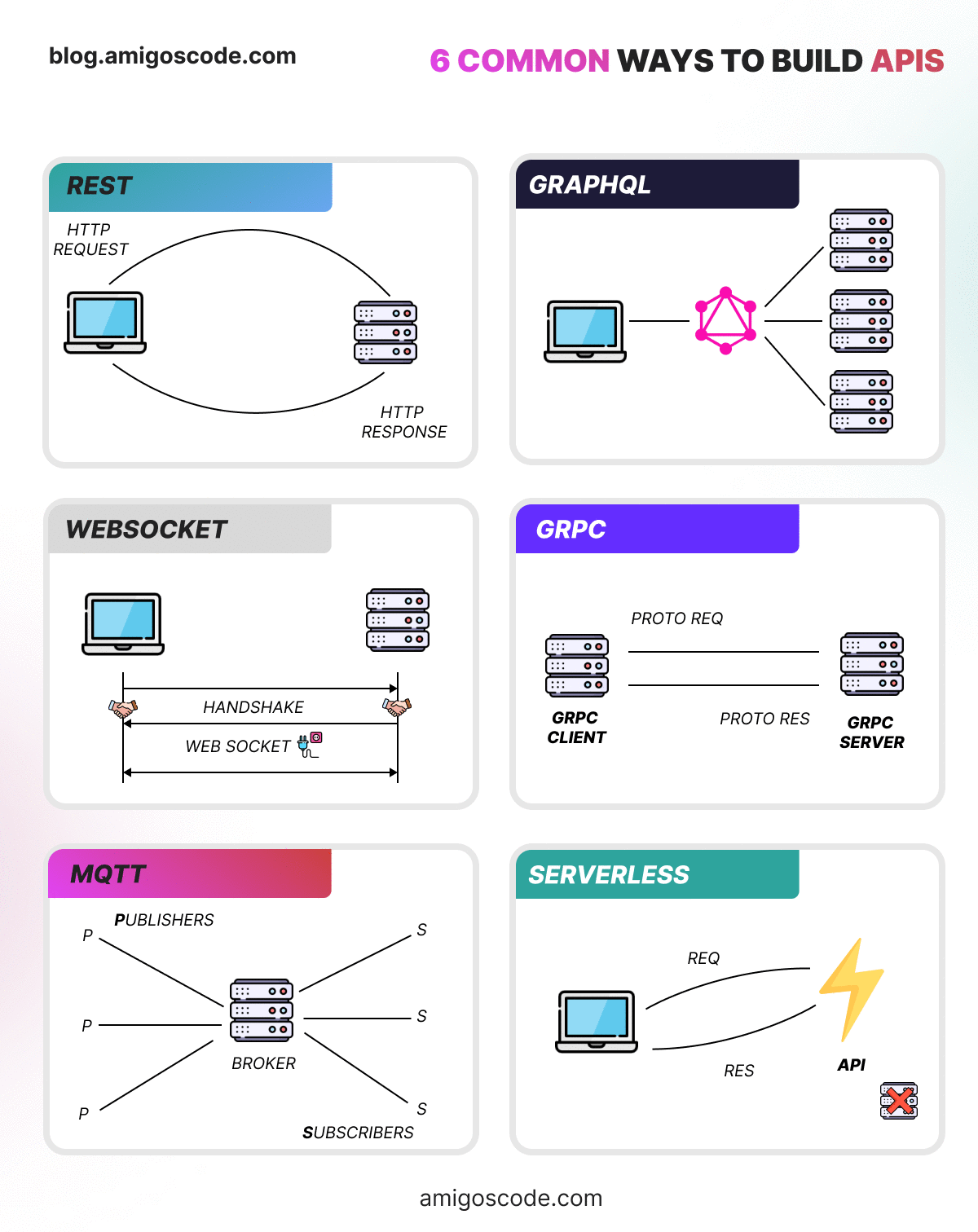
- REST API: Emphasizes simplicity and statelessness, leveraging standard HTTP methods. REST is highly scalable and flexible, making it ideal for general web services.
- SOAP API: Utilizes XML for structured data exchange, with strict standards that enhance security, suitable for enterprise-level applications.
- GraphQL API: Enables clients to precisely define the data they need, reducing the number of requests and improving efficiencies in dynamic web applications.
- Webhooks API: Facilitates real-time data push through HTTP callbacks, ideal for applications that require instant updates.
- WebSockets: Establishes a full-duplex communication channel that remains open, allowing real-time, bi-directional interactions over a single TCP between client and server. Ideal for features like live chat and online gaming.
- gRPC API: Uses HTTP 2.0 and Protobuf for efficient, high-performance communication in microservices architectures, supporting advanced features like streaming.
Comparison
Feature REST API SOAP API GraphQL API Webhooks API WebSockets gRPC API Communication Type Stateless Stateful Stateless Event-driven Full-duplex Full-duplex Protocol HTTP HTTP HTTP HTTP TCP HTTP 2.0 Characteristics Simple, flexible, uses standard HTTP methods Strict standards, uses XML, high security Allows clients to request exactly what they need Uses callbacks to deliver data in real time Maintains a persistent connection for real-time, bidirectional communication Efficient, low-latency, supports streaming Scalability High Moderate High Depends on implementation High High Security Level Moderate High Moderate Moderate Moderate High Typical Use Cases General web services, mobile apps, social networks Enterprise applications, financial services, complex transactions Dynamic web apps, real-time data fetching Automating workflows, real-time updates Live chat, online gaming, collaborative environments Microservices, high-performance internal services
Key Insights
- Communication Type: Reflects how data is managed between client and server, with stateless systems like REST and GraphQL not maintaining any server state, unlike stateful systems like SOAP.
- Scalability: Highlights the architecture’s ability to handle increases in users or data volume. REST, GraphQL, and gRPC excel due to their efficient handling of requests and connections.
- Security Level: Some architectures, such as SOAP and gRPC, offer more robust security features crucial for managing sensitive or critical data.
- Typical Use Cases: Each API style is optimal for specific scenarios, from general web services (REST) to complex financial transactions (SOAP) and real-time interactive applications (Websockets, gRPC).
Real-Time Notification Architectures
Real-Time Notification Architectures
Diagrams
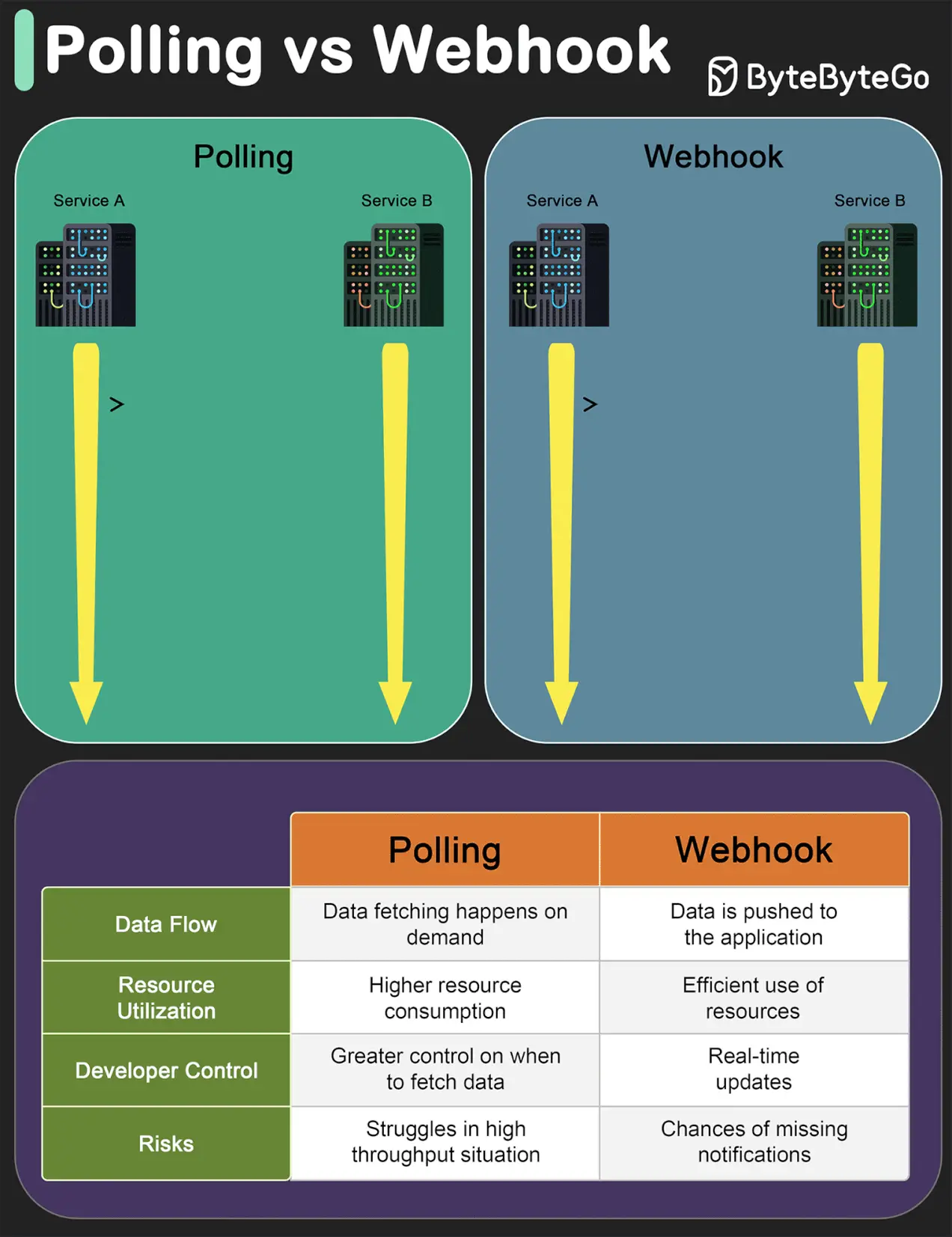
Polling vs Webhook
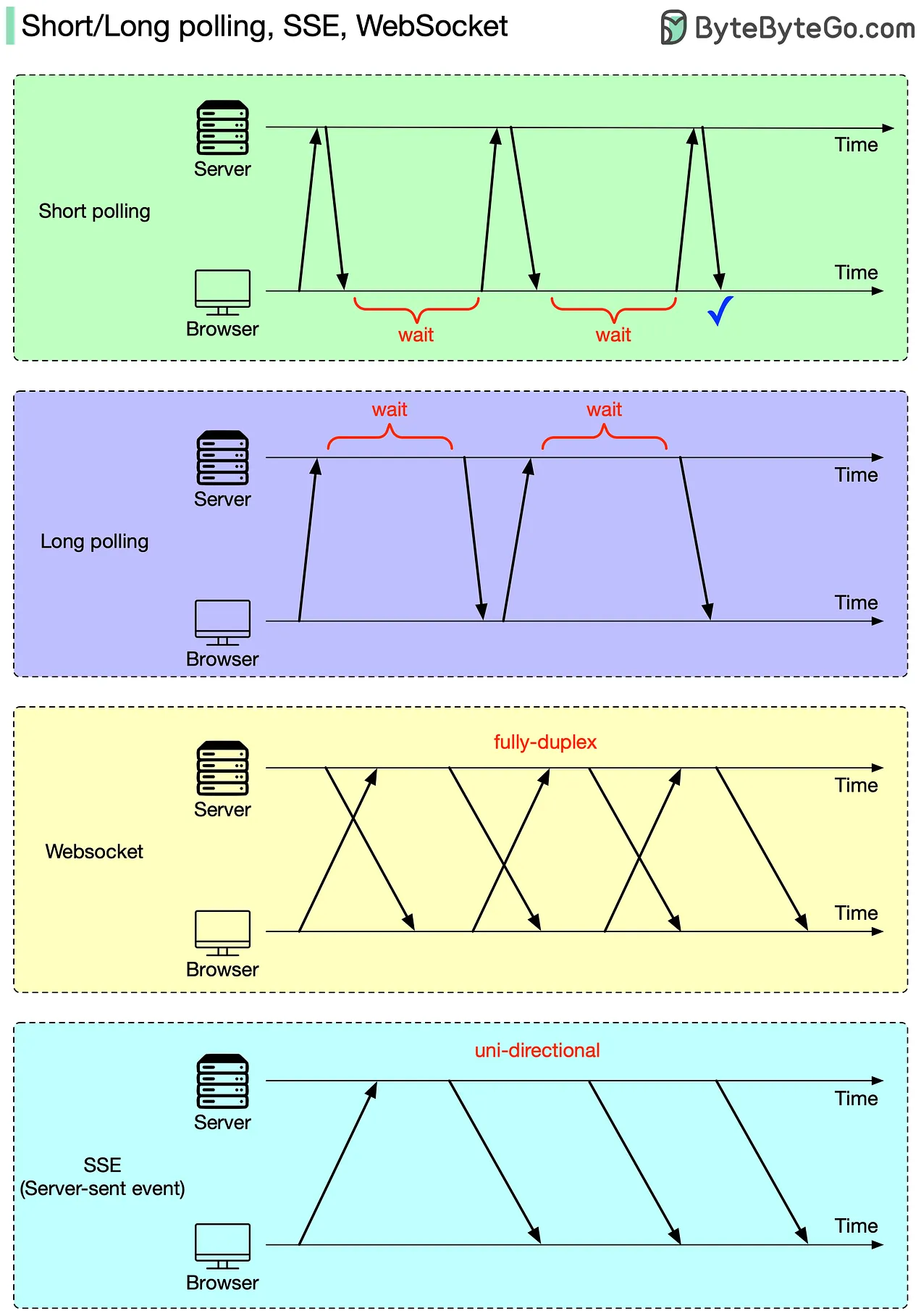
Short/long polling, SSE, WebSocket
Overview
Real-time notification architectures are crucial in software development for applications that require immediate data exchange. These systems ensure that data is transmitted without delay, supporting features like live updates and interactive functionalities.
Key Principles
Important
Comparison
Comparison
Parameter Webhooks API WebSockets HTTP Polling Server-Sent Events (SSE) MQTT Type Event-driven Full-duplex Request-response Half-duplex Publish-Subscribe Description Real-time updates triggered by events Continuous, bi-directional communication Client periodically requests updates from the server Server pushes updates to clients for one-way data flow Lightweight messaging for low-bandwidth, high-latency environments Latency Moderate Very Low Moderate Low Moderate Bandwidth Use Depends on payload Moderate High Low Very Low Data Format JSON/XML Binary/Text JSON/XML Text Binary Auth Level Depends on implementation High Moderate Moderate High Unique Features Service integration with flexible payload formats Supports text and binary data for interactive services Simple to implement Simple, uses standard HTTP for unidirectional updates Ideal for IoT with intermittent connectivity Scalability Moderate High Low Moderate High Development Complexity Moderate Moderate Low Low High Conclusion
Real-time notification architectures are a cornerstone of modern applications that rely on instant data exchange. Choosing the right protocol or technology can dramatically impact the responsiveness and functionality of your application, making it vital to understand the characteristics and best uses of each option.
Link to original
Choosing the Right API Architecture
The selection of an API architecture depends on multiple factors:
- Performance Needs: Technologies like gRPC API are preferred for high performance and low latency.
- Data Complexity: GraphQL API offers a customized fetching approach beneficial in complex data scenarios.
- Security Requirements: SOAP API provides robust security features necessary for sensitive enterprise environments.
- Real-Time Data Flow: For applications needing instant updates, Websockets, SSE, Webhooks, and gRPC are excellent choices.
- General Usage: REST’s ease of implementation makes it widely applicable for most use cases.
Conclusion
Understanding the unique features and suitable applications of each API architecture helps in making informed decisions that align with specific project needs. Whether building a multi-platform service or a high-performance internal tool, selecting the appropriate architecture is key to effective and efficient API integration.