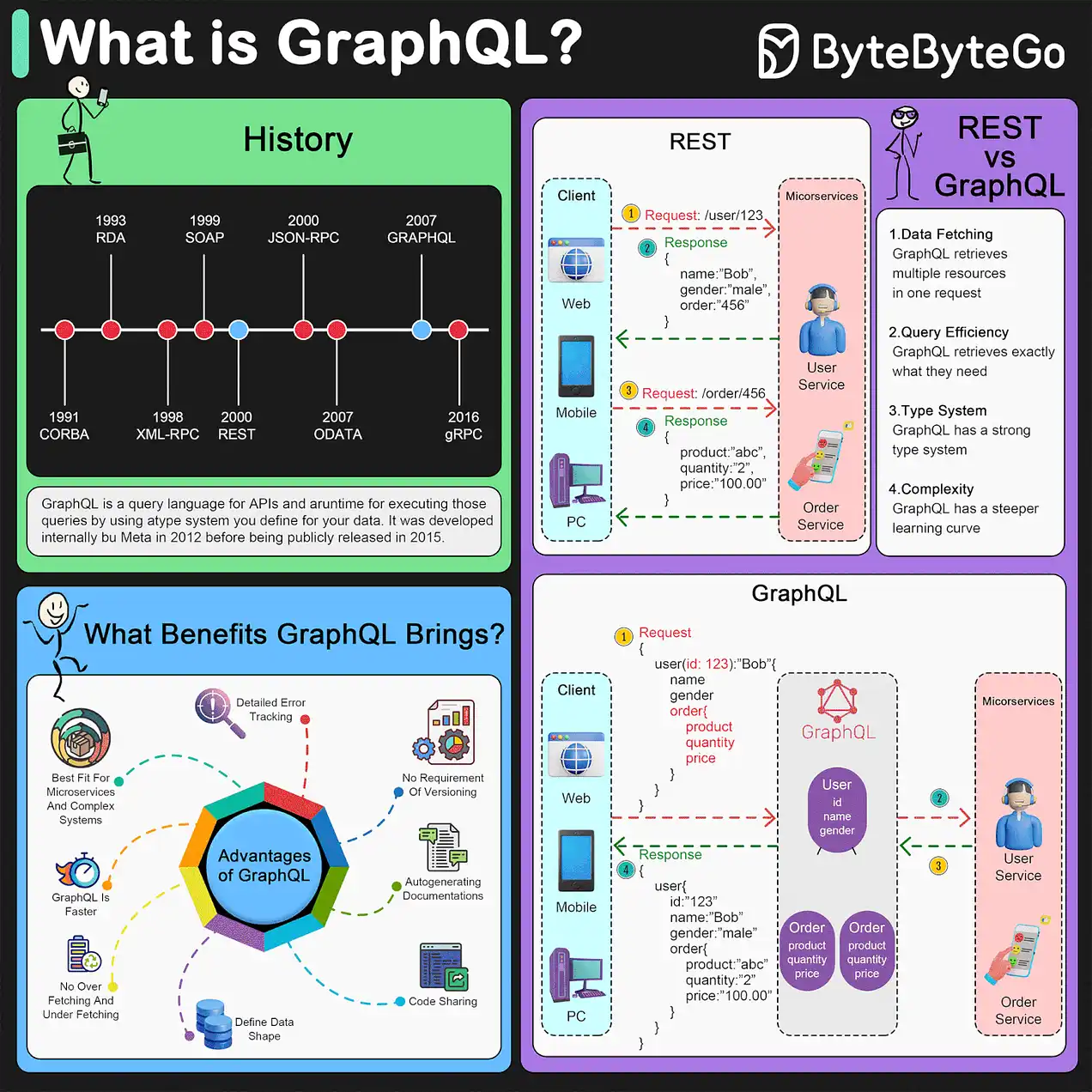
link: API Architectures
GraphQL

Diagram
GraphQL Diagram
Overview
Important
GraphQL is a query language and a server-side runtime (typically served over HTTP).
GraphQL is a powerful query language and runtime for APIs that allows querying data from any number of different sources, unlike traditional query languages that are tied to specific data stores. It enables clients to request exactly what they need, making it highly efficient for both developers and applications. GraphQL is not limited to any specific type of data store and can fetch data from databases, micro-services, or even underlying RESTful APIs.
Key Features of GraphQL
GraphQL stands out due to its flexibility in data fetching and structured approach to queries and mutations:
Info
- Fetch Only What You Need: Clients can specify exactly the data they need, nothing more, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching.
- Single Endpoint: Uses a single endpoint to handle all actions, simplifying API management compared to REST which may use multiple endpoints.
- Strongly Typed Schema: Every GraphQL service defines a set of types which completely describe the set of possible data you can query, enhancing predictability and reliability of the API.
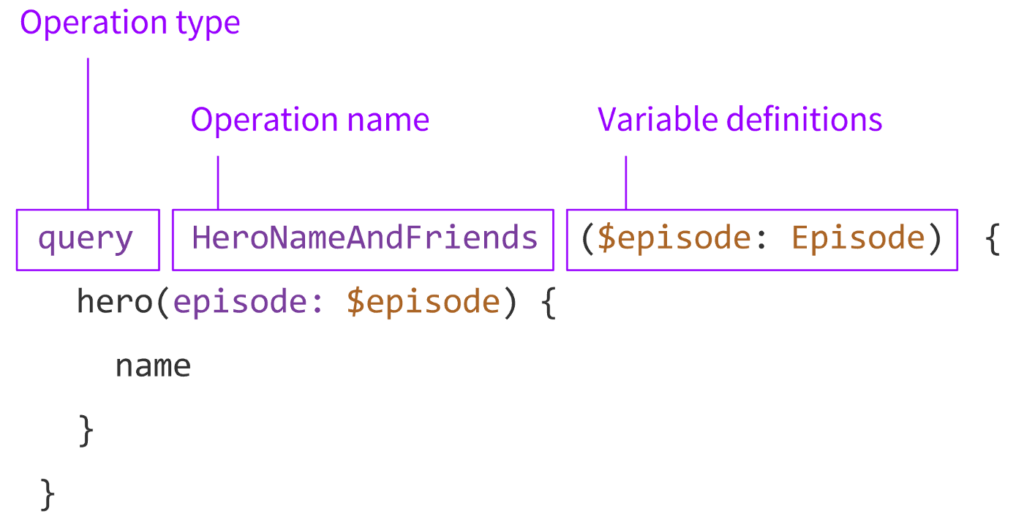
Queries and Mutations
GraphQL queries are designed to fetch data, similar to GET calls in REST, while mutations are used to modify data, akin to POST or DELETE methods in REST:
Example
How GraphQL Works
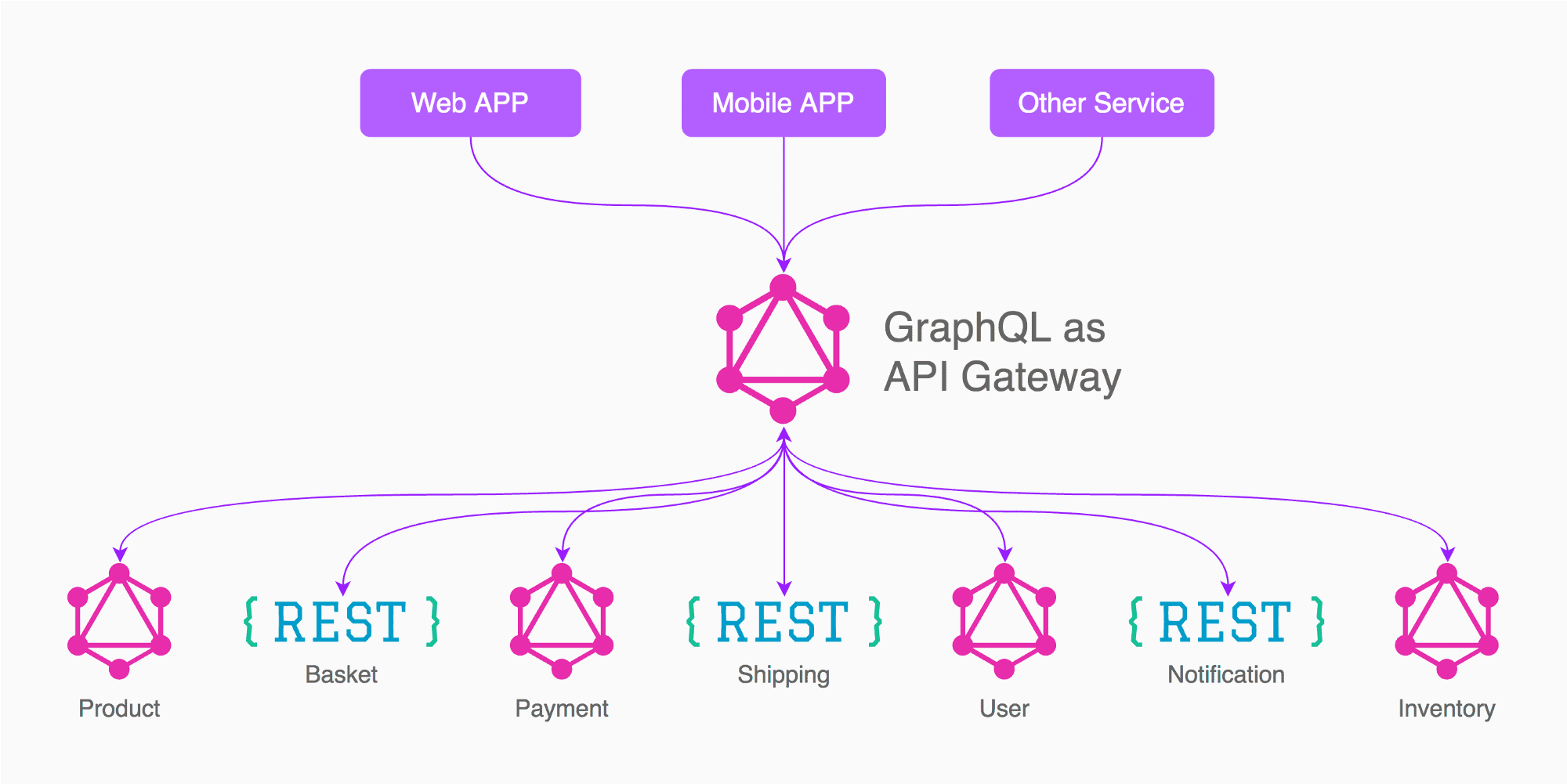 GraphQL can be API Gateway
GraphQL can be API Gateway
The operation of GraphQL involves several key steps to ensure precise and efficient data retrieval:
- Design Your GraphQL Schema: Define types like
Job,Company, andLocationbased on the data requirements of your application. - Connect Resolvers to Data Sources: Implement resolver functions for each type that fetch data from specified sources, such as external APIs or other services.
- Execute Queries: Clients send queries to the GraphQL server, specifying the exact data needed, which the server processes using the defined schema and resolvers to return the requested data.
Info
Runtime Considerations: GraphQL runs on a server where it dynamically resolves data requests based on the defined schema, independent of the data’s source.
Pros/Cons of GraphQL
Pros
- Efficient Data Loading: Aggregates all needed data in a single request.
- Reduced Overfetching and Underfetching: Only the exact needed data is exchanged.
- Rapid Development: Frontend changes like adding fields don’t require backend modifications.
- Powerful Developer Tools: Tools like GraphiQL provide robust environments for testing and debugging GraphQL queries.
Cons
- Complexity for Developers: Managing queries and integrating with existing systems can be complex.
- Performance Issues: Complex queries can strain servers if not optimized.
- Caching Complications: Unlike REST, caching in GraphQL is more involved due to the variability of query patterns.
Conclusion
GraphQL revolutionizes data fetching in modern applications, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. It’s particularly beneficial in environments where rapid iteration and precise data fetching are crucial. However, developers must navigate its complexity and manage performance to fully leverage its capabilities.