link:
Caching
Overview
Caching is a technique used to store copies of data in temporary storage (cache) so that future requests for that data can be served faster. By reducing the need to repeatedly access slower storage layers or perform compute-intensive operations, caching improves performance and reduces latency.
Key Concepts
Important
- Cache: A temporary storage area where frequently accessed data can be stored for rapid access.
- Cache Hit: When the requested data is found in the cache.
- Cache Miss: When the requested data is not found in the cache, necessitating access to the primary storage.
- Eviction Policy: A strategy used to decide which items to remove from the cache when it becomes full.
- Consistency: Ensuring that the cache and the primary data store remain in sync.
- Latency: The time delay between a user’s action and the response from the system.
Caching Tools
Info
- Redis: An in-memory data structure store used as a database, cache, and message broker. Known for its high performance and support for various data structures.
- Memcached: A distributed memory caching system, commonly used to speed up dynamic web applications by alleviating database load.
- Varnish: A web application accelerator also known as a caching HTTP reverse proxy, designed to handle high traffic websites.
- Ehcache: An open-source, standards-based cache that boosts performance, offloads the database, and simplifies scalability.
- Hazelcast: An in-memory data grid that provides distributed data structures, caching, and computing.
Implementation Considerations
Note
- Cache Invalidation: Ensuring stale data is removed or updated.
- Cache Size Management: Deciding on the appropriate cache size based on the use case.
- Data Consistency: Strategies to maintain consistency between the cache and the primary storage.
- Security: Ensuring that sensitive data is not cached insecurely.
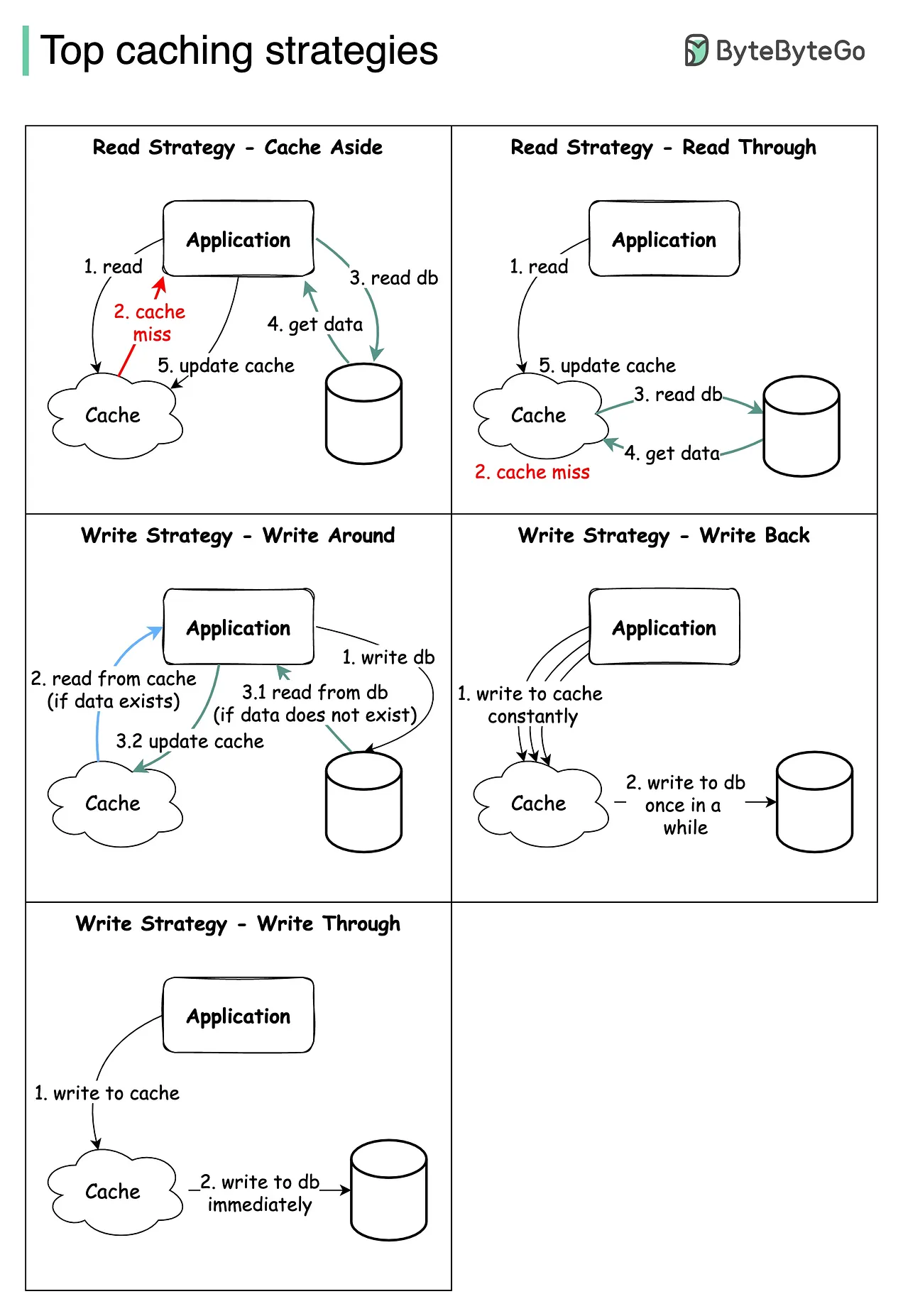
Caching Strategies
Diagram
Link to original
Use Cases
- Web Applications: To store frequently accessed web pages, API responses, and static resources.
- Database Queries: To cache results of expensive database queries, reducing load on the database.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): To cache and deliver content closer to users, reducing load times and bandwidth costs.
- Session Management: Caching session data to improve the performance of user session handling.
- Database Indexing: Both caching and indexing improve data retrieval times but use different approaches.
- Load Balancing: Often used in conjunction with caching to distribute loads efficiently across servers.
- Distributed Systems: Caching is crucial in distributed systems to reduce latency and improve performance.
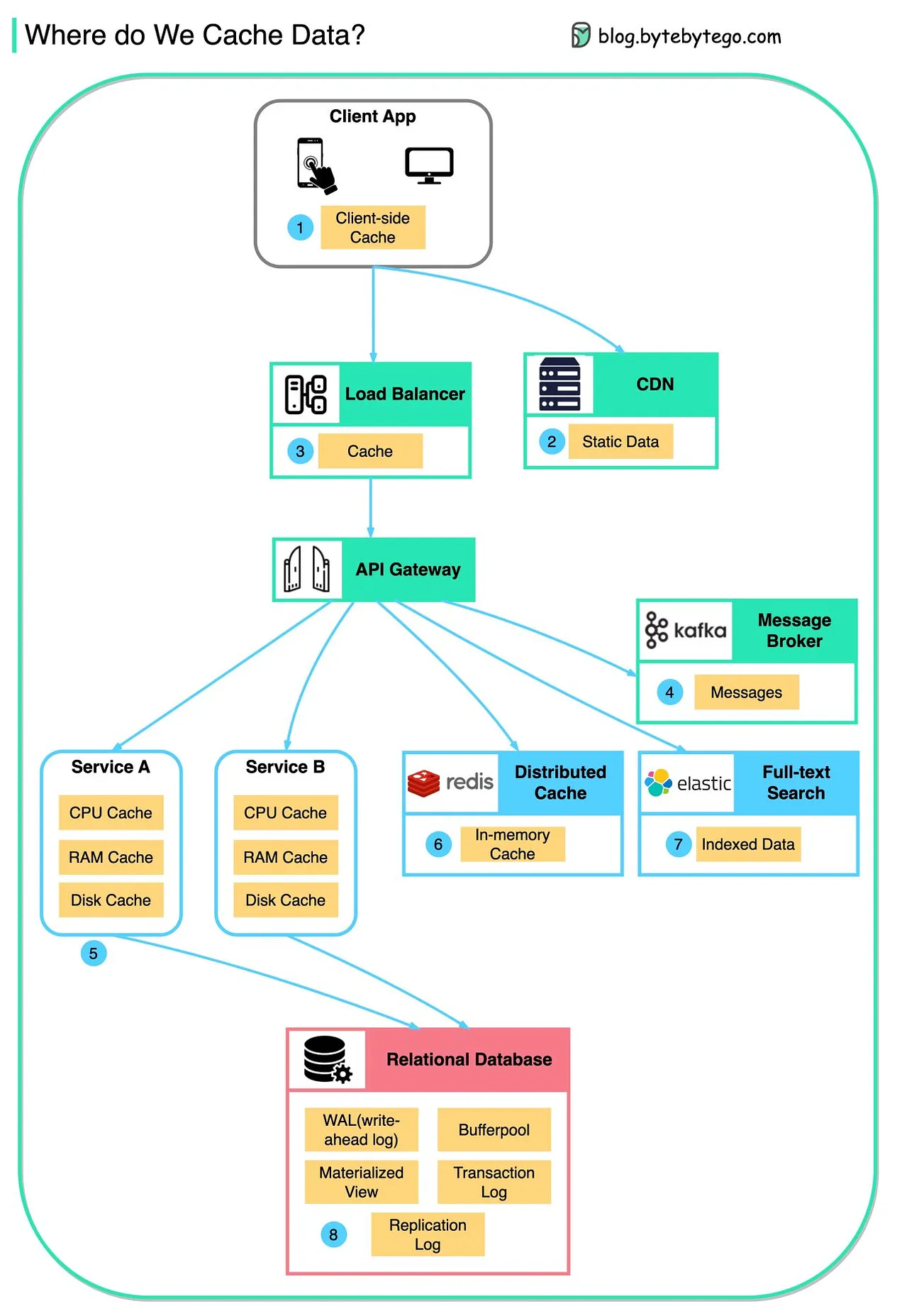
Where do we Cache Data?
Conclusion
Caching is a vital technique for enhancing the performance and responsiveness of applications by temporarily storing frequently accessed data. By understanding and implementing effective caching strategies, developers can significantly reduce latency, improve user experience, and optimize resource usage.
References
A Crash Course in Caching - Part 1 - by Alex Xu
A Crash Course in Caching - Part 2 - by Alex Xu