Database Scaling
Diagram
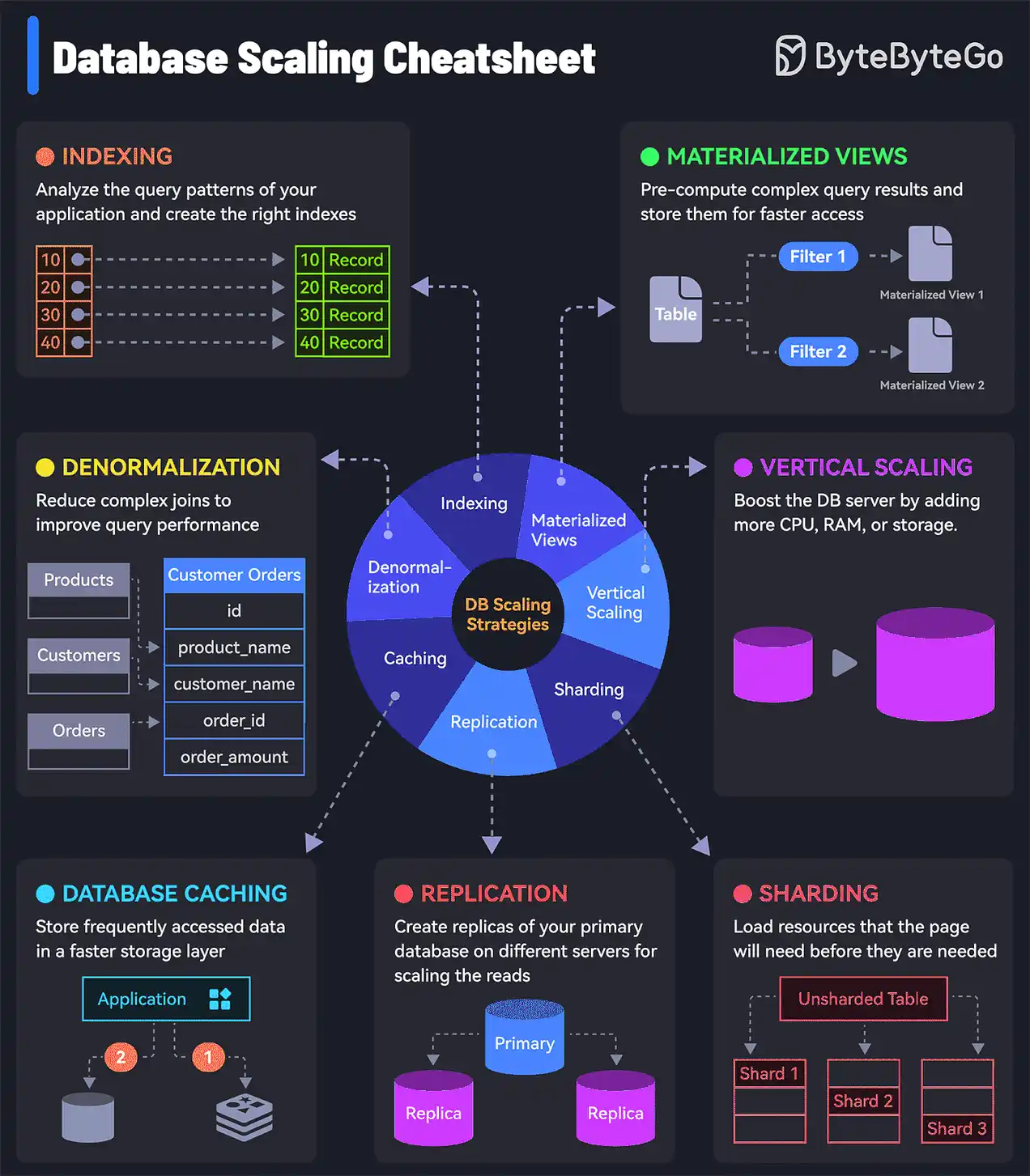
Overview
Database Scaling is the process of improving the performance and capacity of a database to handle increased loads and ensure fast response times. Scaling is crucial for applications that need to manage large volumes of data and high transaction rates. There are various techniques and strategies to achieve effective database scaling, each suited for different scenarios and requirements.
Types of Database Scaling
Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up)
Vertical scaling involves adding more resources (CPU, RAM, SSD) to a single server to improve its capacity and performance. This approach is straightforward but has limits and can be expensive.
Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out)
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers or nodes to a database system to distribute the load. This approach offers better scalability and fault tolerance.
Techniques for Database Scaling
Common Database Scaling Techniques
Database Indexing: Improves query performance by creating indexes on frequently queried columns. Indexes allow the database to find rows faster than scanning the entire table.
Normalization: Organizes data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity by dividing large tables into smaller, related ones. This process can help in reducing the amount of data that needs to be managed and queried.
Caching: Stores frequently accessed data in a cache (in-memory storage) to reduce the load on the database and improve response times. Caching can be implemented at various levels, including application, database, and network.
Data Replication: Copies data from one database server to another to distribute the load and provide redundancy. Replication can be synchronous or asynchronous and helps in improving read performance and fault tolerance.
Database Sharding: Divides a database into smaller, more manageable pieces called shards, each hosted on a separate server. Sharding distributes data and load, making it easier to scale horizontally.
Materialized Views: Pre-computed views that store the results of a query. These views can improve query performance by providing quick access to frequently requested data.
Vertical Scaling: Involves upgrading the hardware (CPU, RAM, storage) of a single server to improve its capacity and performance. Vertical scaling is easier to implement but has physical and cost limitations.