link: Message brokers, Key-Value Databases
Redis
Overview
Redis (Remote Dictionary Server) is an open-source, in-memory data structure store that can be used as a database, cache, and message broker. Known for its high performance and low latency. It is widely used for building real-time applications due to its ability to handle millions of requests per second with sub-millisecond latency.
Key Features
Overview
Link to originalData Structures
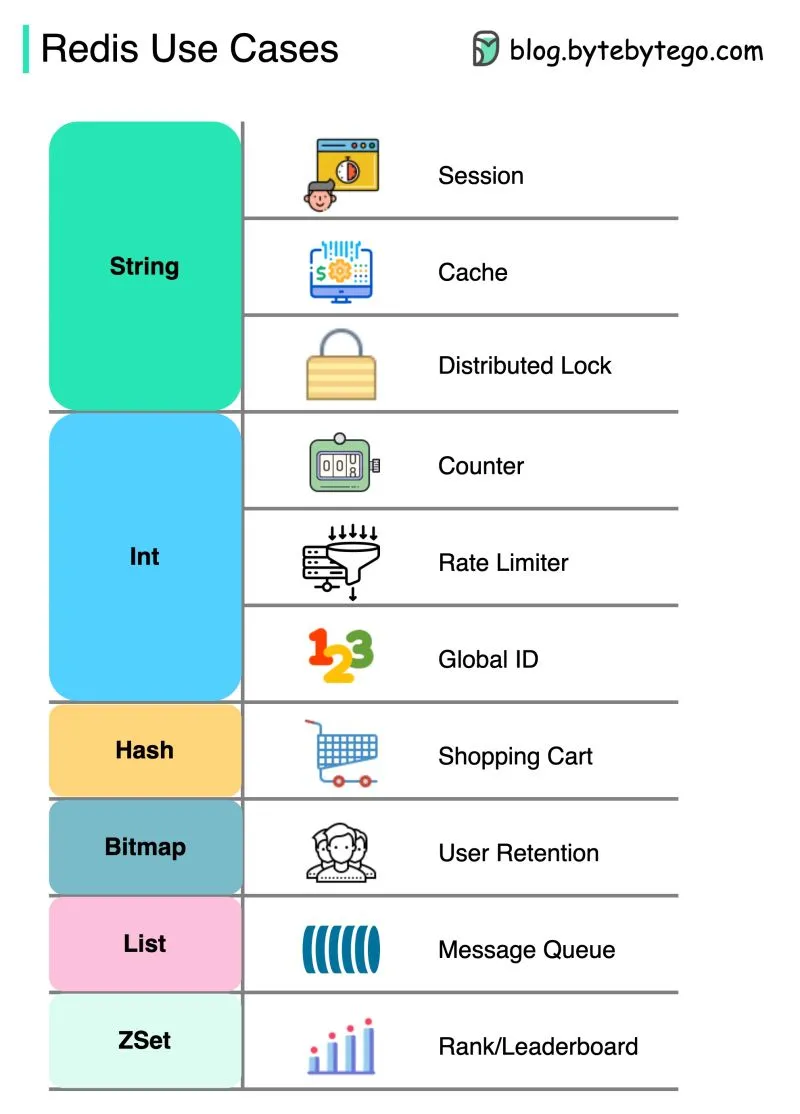
- Strings: The simplest type of value, can hold any type of data including binary.
- Hashes: Ideal for storing objects and user profiles.
- Lists: Ordered collections of strings, useful for queues.
- Sets: Unordered collections of unique strings, ideal for relationships and tags.
- Sorted Sets: Like sets but with an associated score, useful for leaderboards.
- Bitmaps: For bit-level operations.
- HyperLogLogs: For approximate counting of unique items.
Persistence
Redis offers two persistence options to balance durability and performance:
- RDB (Redis Database): Snapshots the dataset at specified intervals.
- AOF (Append Only File): Logs every write operation for more durable persistence.
High Availability and Scalability
Redis ensures high availability and scalability through:
- Replication: Master-Slave replication with automated failover.
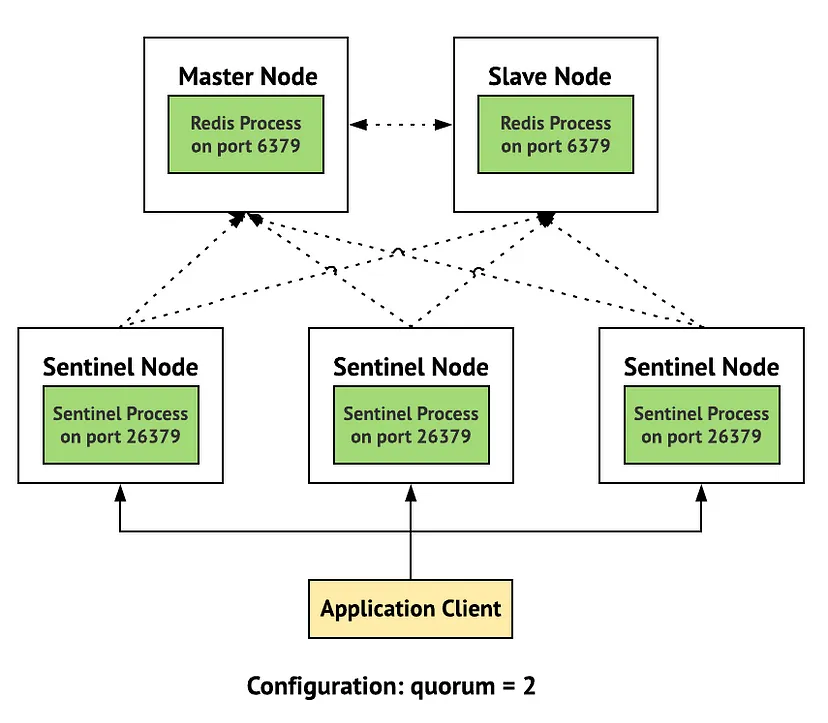
- Sentinel: Monitors master and slave instances, providing automatic failover.
- Cluster: Distributes data across multiple nodes, ensuring horizontal scalability and fault tolerance.
Performance
Redis provides extremely fast data access through:
- In-Memory Storage: Fast access and manipulation.
- Lua Scripting: Atomic execution of complex operations.
- Pipelining: Reduces latency by batching commands.
Security
Redis offers robust security features:
- Authentication: Requires clients to authenticate with a password.
- Encryption: Supports TLS for encrypted connections.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Fine-grained access control to commands and data.
Use Cases
Use Cases
- Caching: Caching frequently accessed data to reduce load on primary databases and improve application performance.
- Session Management: Storing user session data for web applications, providing fast and efficient session retrieval and updates.
- Real-Time Analytics: Processing and analyzing real-time data streams, such as user activity tracking and financial transactions.
- Message brokers: Implementing message brokers using Redis lists or streams for reliable and scalable message passing.
- Leaderboards: Managing real-time leaderboards using sorted sets to rank users or items by score.
How It Works
Basic Operations
- Connecting to Redis: Clients connect to the Redis server using TCP/IP.
- Executing Commands: Clients send commands to perform operations like
SET,GET,HSET,LPUSH,ZADD, etc. - Data Storage: Data is stored in memory and can be persisted to disk using RDB or AOF.
- Replication and Clustering: Redis can replicate data to slave nodes and distribute data across a cluster for high availability and scalability.
Example Workflow
Consider a web application that uses Redis for session management:
- User Logs In: The application stores the user’s session data in Redis.
- Session Retrieval: For each user request, the application retrieves the session data from Redis.
- Session Update: Any updates to the session are written back to Redis.
- Session Expiry: Sessions have a TTL (Time To Live) and are automatically removed when expired.
Related Topics
Related Topics
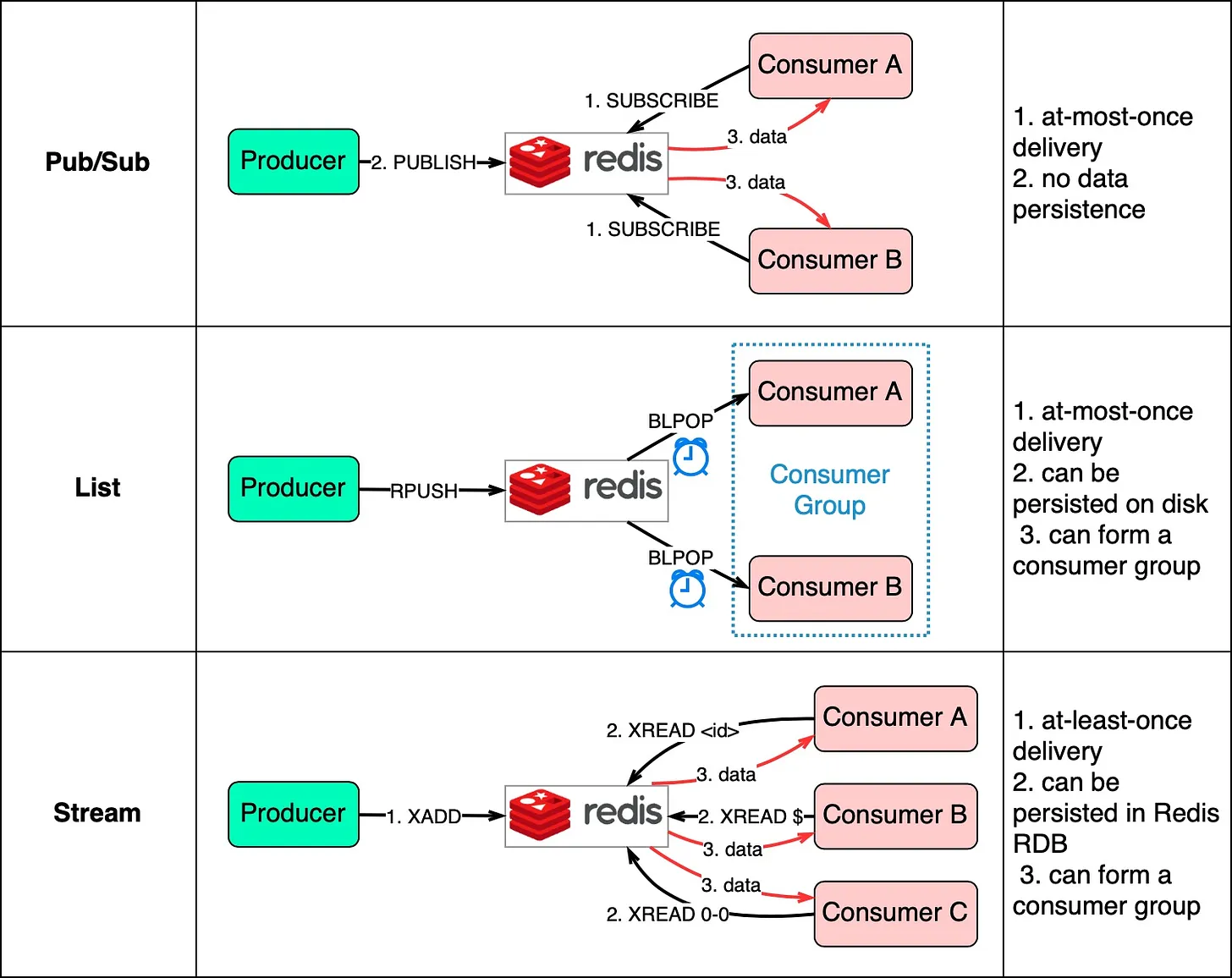
- Message Queues: Redis can be used to implement message queues using its list data structure.
- Message Topics: Redis Pub/Sub feature for real-time messaging.
- Caching: Redis is widely used as a caching solution to improve application performance.
- Session Management: Using Redis to store and manage user sessions for web applications.
- Distributed Systems: Redis provides features like replication and clustering for building distributed systems.
- Redis Data Structures: Detailed usage and examples of Redis data structures like strings, hashes, lists, sets, and sorted sets.
Redis is a powerful tool for building fast, scalable, and resilient applications. Its rich set of features and support for various data structures make it a versatile choice for a wide range of use cases. By leveraging Redis, developers can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of their applications.
Redis-Backed Queue
Diagram
Link to original
Refences
Redis Sentinel — High Availability | Medium
The 6 Most Impactful Ways Redis is Used in Production Systems