link: Non-Relational Databases
Key-Value Databases
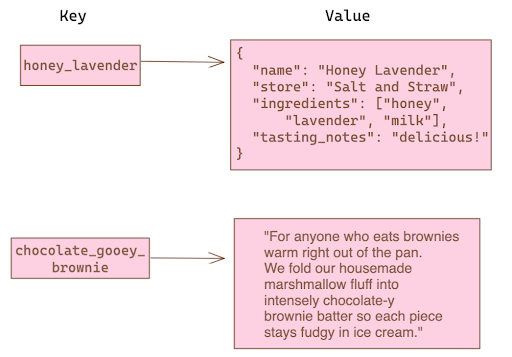
Content
Key-value databases are a type of non-relational database that store data as a collection of key-value pairs, where a key serves as a unique identifier to access its associated value. These databases excel in scenarios requiring high-speed lookups, making them ideal for session stores, caching, and situations where data is frequently read but less frequently updated.
The simplicity of the key-value model allows for high performance and scalability, especially in distributed configurations. Data can be stored in a variety of formats including strings, JSON, or even serialized objects, depending on the specific database capabilities.
Example
- Redis: An in-memory key-value store known for its speed and the richness of its data types. It is often used as a cache or message broker.
- Amazon DynamoDB: A managed NoSQL service that supports both key-value and document data models, providing seamless scalability and integration with AWS applications.
- Etcd: A key-value store that is often used for configuring distributed systems. It provides a reliable way to store data across a cluster of machines.
- Riak: Designed for distributed systems, it offers high availability, fault tolerance, and operational simplicity.