link: Database
Non-Relational Databases
Overview
Non-relational databases, known as NoSQL databases, cater to diverse and large-scale data management needs that traditional relational databases (RDBMS) struggle with. These databases excel in scenarios requiring scalability, flexibility, and rapid iteration, making them ideal for big data applications and real-time web applications.
Abstract
NoSQL databases utilize dynamic schemas for unstructured data, enable horizontal scalability through data distribution across clusters, and are specialized to handle various data models like document, key-value, graph, and wide-column stores.
Content
Note
Non-relational databases are really helpful when there are a lot of unknowns about exactly what data you need to store, or when there is a large volume of data that might hold different attributes but that you still need to compare side-by-side.
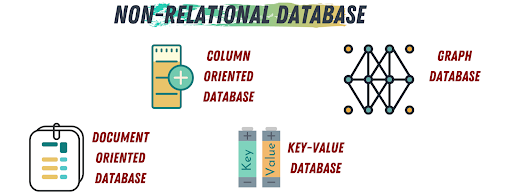
Types of Non-Relational Databases
Important
- Document-Oriented Databases: Store data in JSON, BSON, or XML documents, exemplified by MongoDB and CouchDB. They are schema-agnostic, enhancing flexibility for applications like content management and e-commerce.
- Key-Value Databases: Such as Redis and DynamoDB, manage data as key-value pairs, optimized for high-speed retrieval necessary for scenarios like caching and session management.
- Wide-Column Databases: Like Cassandra and HBase, these databases use a columnar data structure that allows for efficient data aggregation and scalability.
- Graph Databases: Employ nodes, edges, and properties to manage and analyze connected data, useful in applications like social networks and recommendation engines.
Core Features and Architecture
Scalability: Designed to scale out, NoSQL databases distribute data across multiple servers as opposed to scaling up on a single server like in traditional relational databases.
Performance: These databases handle large data volumes more efficiently, providing high performance for diverse data types and structures.
Data Model Flexibility: The lack of a fixed schema allows for easy modifications and adaptations to data structures on-the-fly, supporting agile development practice
Dive Deeper
CAP Theorem: Details the trade-offs involved between consistency, availability, and partition tolerance in distributed systems.
Transactions in NoSQL: Reviews different approaches to transaction management that diverge from traditional ACID models, suitable for distributed database environments
Content
Relational and non-relational databases are the two primary types of data management systems used in application development, each serving different needs and use cases. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right database type for specific applications.
Link to original
Feature Relational Databases Non-Relational Databases Query Language SQL: Enables complex queries and transactions. Flexible query techniques suited to the data model (e.g., MongoDB’s query language). Schema Fixed schema: Data must conform to pre-defined tables and columns. Schema-less: Data structure can be altered on the fly. Data Integrity High integrity: Uses constraints and normalization to ensure data accuracy. Variable integrity: Prioritizes flexibility and speed over strict consistency. Scalability Vertical scaling: Often requires more powerful hardware to scale. Horizontal scaling: Easily distributes data across multiple servers. Flexibility Rigidity in schema can hinder changes and rapid development. Highly flexible, allowing for rapid changes to data formats without downtime. Performance Optimized for complex queries involving multiple tables and relationships. Optimized for fast retrieval of large volumes of simple queries. Consistency Models Strong consistency with ACID compliance. Often uses eventual consistency, which may not guarantee immediate consistency. Technology Maturity Mature with extensive tools, community, and support. Generally newer with growing tools and community support. Use Cases Banking systems, enterprise applications with complex business logic. Real-time big data applications, content management systems with varying data types. Pros Complex querying capabilities, data integrity, mature technologies. Scalability, flexibility, performance. Cons Limited scalability, rigid schema structure. Consistency challenges, management complexity in distributed environments.