link: Relational Databases, Non-Relational Databases
Relation vs Non-Relational Databases
Diagrams
Content
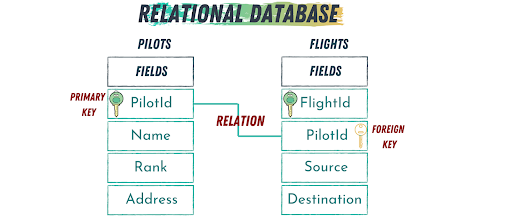
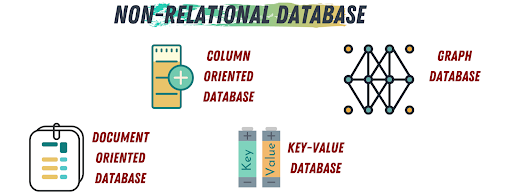
Relational and non-relational databases are the two primary types of data management systems used in application development, each serving different needs and use cases. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right database type for specific applications.
| Feature | Relational Databases | Non-Relational Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Query Language | SQL: Enables complex queries and transactions. | Flexible query techniques suited to the data model (e.g., MongoDB’s query language). |
| Schema | Fixed schema: Data must conform to pre-defined tables and columns. | Schema-less: Data structure can be altered on the fly. |
| Data Integrity | High integrity: Uses constraints and normalization to ensure data accuracy. | Variable integrity: Prioritizes flexibility and speed over strict consistency. |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling: Often requires more powerful hardware to scale. | Horizontal scaling: Easily distributes data across multiple servers. |
| Flexibility | Rigidity in schema can hinder changes and rapid development. | Highly flexible, allowing for rapid changes to data formats without downtime. |
| Performance | Optimized for complex queries involving multiple tables and relationships. | Optimized for fast retrieval of large volumes of simple queries. |
| Consistency Models | Strong consistency with ACID compliance. | Often uses eventual consistency, which may not guarantee immediate consistency. |
| Technology Maturity | Mature with extensive tools, community, and support. | Generally newer with growing tools and community support. |
| Use Cases | Banking systems, enterprise applications with complex business logic. | Real-time big data applications, content management systems with varying data types. |
| Pros | Complex querying capabilities, data integrity, mature technologies. | Scalability, flexibility, performance. |
| Cons | Limited scalability, rigid schema structure. | Consistency challenges, management complexity in distributed environments. |