link: Database
Relational Databases (SQL)
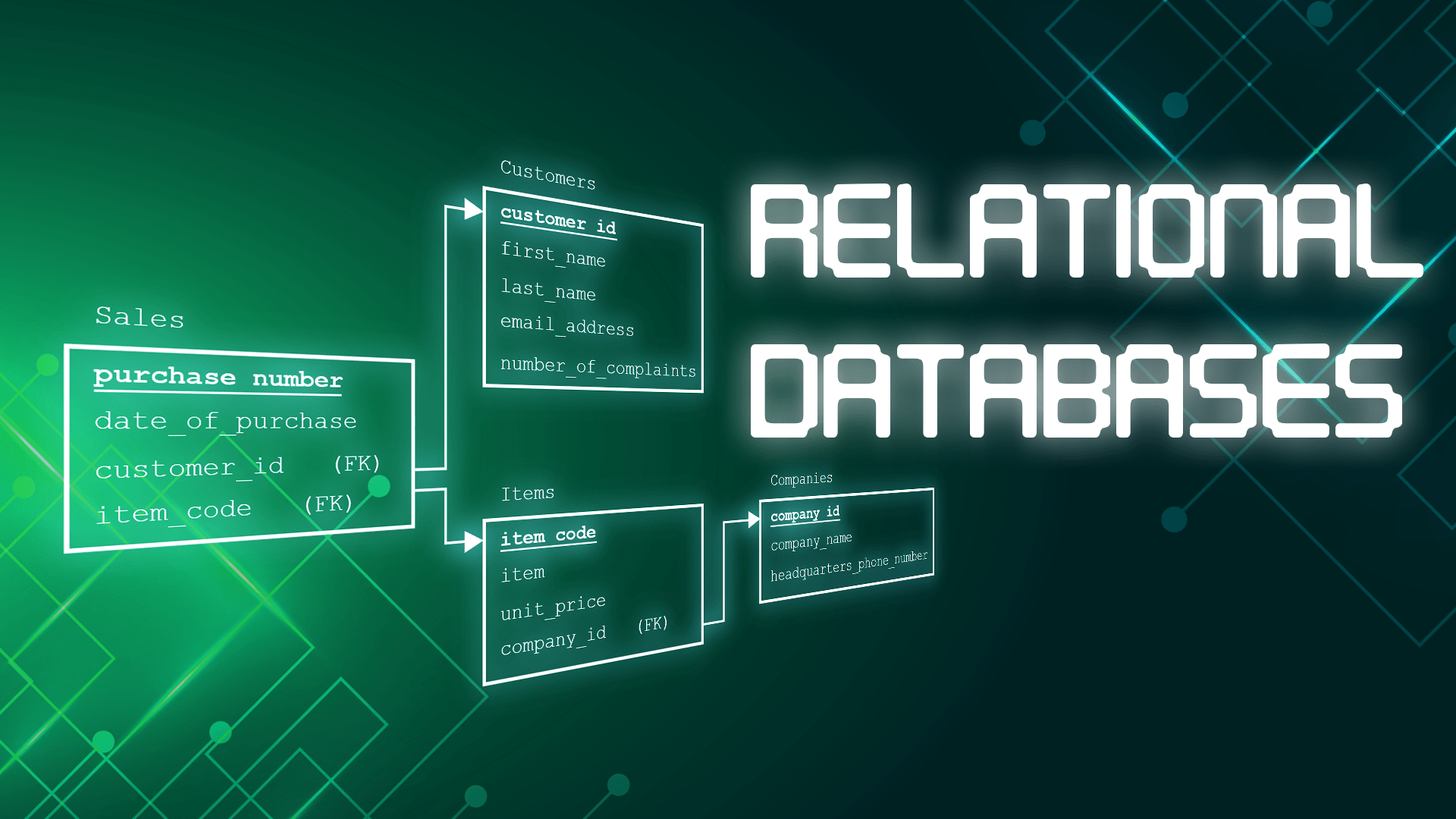
Overview
Relational databases organize data into tables, which can be linked by defining relationships between them. This structure allows for the efficient retrieval, insertion, updating, and management of data. SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language used to interact with relational databases, providing powerful tools for data manipulation and querying.
Content
Key Concepts
Relational databases are based on the relational model, an intuitive and straightforward method of representing data in tables that correspond to real-world entities and relationships:
Important
- Tables: The core components of relational databases, tables hold data in rows and columns. Each table represents a data entity (e.g., customers, orders), and each row in the table represents a single record.
- Primary and Foreign Keys: Primary keys uniquely identify each row in a table, while foreign keys link rows between tables, establishing relationships.
- Normalization: A process to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity by organizing fields and table relationships.
- SQL: The language used to create, manage, and manipulate relational databases. SQL commands allow you to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data, as well as create and modify the database structure itself.
Types of Relational Databases
Several relational database management systems (RDBMS) cater to different needs, from enterprise solutions to open-source alternatives:
- Oracle Database: Highly scalable for enterprise needs with robust features including advanced security and analytics.
- MySQL: Popular open-source RDBMS, widely used for web applications.
- Microsoft SQL Server: Known for deep integration with other Microsoft services, suitable for complex enterprise environments.
- PostgreSQL: Open-source RDBMS that supports advanced data types and performance optimization.
- SQLite: Lightweight, file-based database, ideal for small to medium-sized applications
Implementation Overview
Implementing a relational database involves several critical steps:
- Database Design: Define the tables, fields, and relationships. The design should follow normalization rules to ensure the database is efficient and reduces redundancy.
- SQL Operations: Use SQL for various operations:
- DDL (Data Definition Language): Commands such as
CREATE,DROP,ALTERused to define and modify database schema. - DML (Data Manipulation Language): Commands like
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETEused to handle data within tables. - DCL (Data Control Language): Commands like
GRANTandREVOKEused to define access controls.
- DDL (Data Definition Language): Commands such as
- ACID Properties: Ensure the accuracy and integrity of data through constraints, and manage multiple database actions with transactions that are atomic, consistent, isolated, and durable (ACID).
Usefull Topics
- SQL Session: Refers to a connection established between a database and a client that lasts for the duration of the user’s interaction with the database.
- Data Integrity and Transactions: Ensure the accuracy and integrity of data through constraints, and manage multiple database actions with transactions that are atomic, consistent, isolated, and durable (ACID).
- SQL Query Performance:
- Data Normalization - Data normalization is a design approach used to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity by organizing fields and table relationships in databases.
- Database Indexing: Strategies for optimizing data retrieval and database performance.
Summary
Summary
Relational databases provide a structured format to store and manipulate data efficiently. By using tables, keys, and normalization, along with the SQL language, these databases support complex data interactions and ensure high levels of data integrity. They are fundamental in applications requiring robust data manipulation capabilities, from small businesses to large enterprises.