link: Relational Databases
SQL Operations
Overview
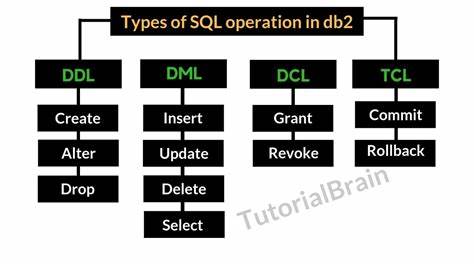
Structured Query Language (SQL) is the primary language used for interacting with relational databases. It encompasses a range of commands categorized into Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), and Transaction Control Language (TCL), each serving distinct purposes in database management and manipulation.
SQL Command Categories
Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to define and modify database schema without affecting the data itself. Key DDL commands include:
- CREATE: Builds a new table, a view of a table, or other object in the database.
- ALTER: Modifies an existing database object, such as a table.
- DROP: Deletes an entire table, a view of a table or other objects in the database.
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are crucial for handling the data within the tables. Common DML commands are:
- SELECT: Retrieves data from a database.
- INSERT: Inserts data into a table.
- UPDATE: Modifies existing data within a table.
- DELETE: Removes data from a table.
Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL commands manage the rights, permissions, and other controls of the database system. These include:
- GRANT: Gives user’s access privileges to the database.
- REVOKE: Withdraws access privileges given with the GRANT command.
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands help manage transactions to ensure data integrity by grouping several DML actions into a single operation that either saves all changes or none:
- COMMIT: Saves all changes made during the current transaction.
- ROLLBACK: Restores the database to the last committed state.
SQL also includes advanced features and clauses that enhance querying and data manipulation capabilities:
Enhanced Query Capabilities
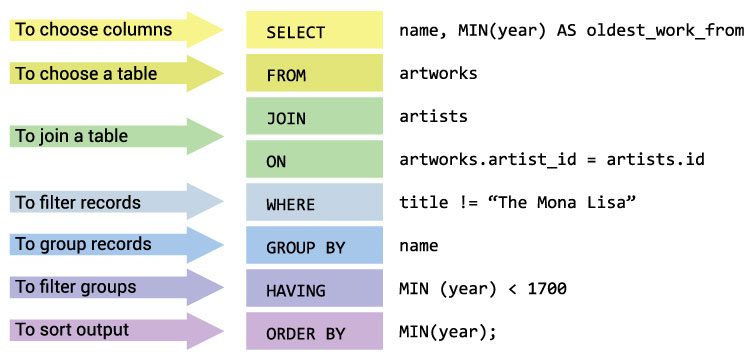
- JOIN: Combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column.
- WHERE: Filters records to include only those that meet a specified condition.
- DISTINCT: Eliminates duplicate records from the results.
- GROUP BY: Groups rows sharing a property into summary rows.
- HAVING: Filters records that work on aggregated results.
- ORDER BY: Specifies the order in which to return the rows.
- LIMIT: Restricts the number of rows returned.
- UNION, UNION ALL, INTERSECT, EXCEPT: Combine results from multiple
SELECTstatements.
Advanced SQL Features
This section delves into sophisticated SQL capabilities that enable more complex operations and greater control over database transactions and data manipulation:
- SQL Advanced Features: Reusable SQL scripts that can perform operations such as data validation or complex calculations within the database server, reducing client-server communication. (Functions)
- SQL Triggers and Events: Automatically executed actions in response to specific changes or events within the database, ensuring data integrity and automating routine tasks.
- Advanced Querying Techniques: Includes using window functions for data over sets of rows, and recursive queries which are essential for dealing with hierarchical or nested data structures.