link: Web Communication Protocols
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Overview
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers designed to provide high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end-users.
Content
Key Features of CDNs
CDNs optimize web content delivery to improve user experience across the globe. Here are the major features:
Key Features:
- Redundancy: Distributes load across multiple, redundant servers to reduce the risk of server overloads.
- Speed: Delivers content from servers closest to the user, significantly reducing latency.
- Scalability: Efficiently handles sudden spikes in web traffic.
- Security: Offers enhanced security features such as DDoS protection and secure transmission protocols.
How CDNs Work
CDNs manage the delivery of web content through a process designed to ensure efficiency and speed:
CDN Workflow:
- Caching Content: Static content is stored (‘cached’) on various servers once a user first requests it.
- Server Selection: The CDN selects the nearest server to the user for subsequent requests, minimizing latency.
- Content Delivery: The server delivers the cached content to the user. If the content isn’t cached yet, it is fetched from the origin server, cached, and then delivered.
Benefits of Using CDNs
Using a CDN can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of a website or web service:
Advantages of CDNs:
- Improved Load Times: Faster page loads from using the nearest server to the user.
- Reduced Bandwidth Costs: Lower costs due to reduced data load on the origin server.
- Increased Content Availability and Redundancy: Better handling of traffic and hardware failures.
- Enhanced Security: Features like DDoS mitigation and secure certificate management improve overall security.
CDN Example
Real-World Example
Scenario: Improving Website Access Speed with CDN
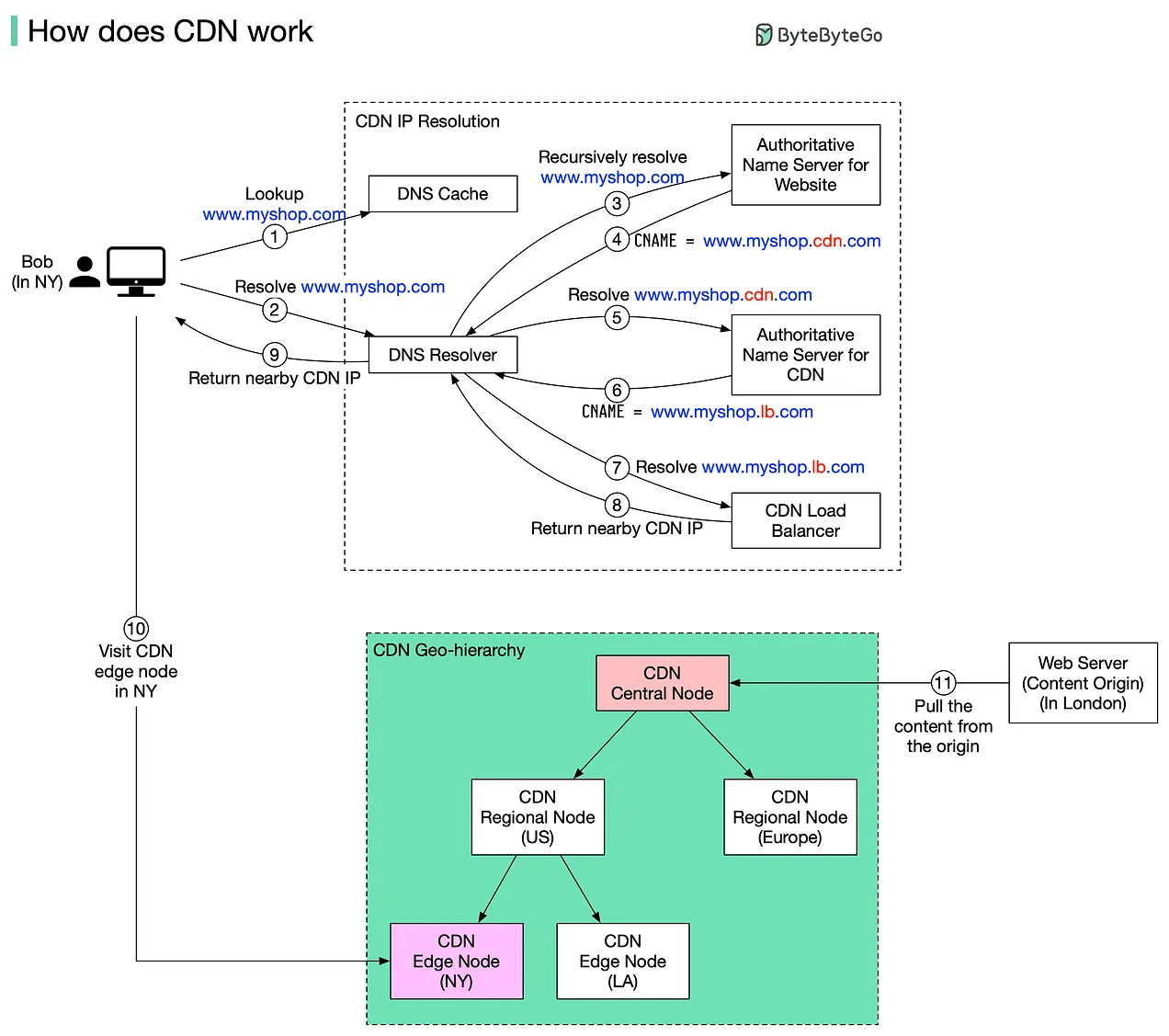
Imagine Bob, who resides in New York, wants to visit an e-commerce website based in London. Without a CDN, his requests would have to travel across the Atlantic, resulting in slow response times. However, with a CDN, the website content is cached closer to where Bob lives, dramatically speeding up the loading process.
Domain Name Lookup: Bob types www.myshop.com into his browser. The browser first checks its local DNS cache.
DNS Resolver Inquiry: If the domain name is not in the local cache, the browser contacts the ISP’s DNS resolver.
Recursive Resolution: The DNS resolver performs a recursive lookup to find the authoritative name server for the domain, asking it to resolve the domain name.
CDN Integration: Instead of returning the IP address of the London server, the authoritative name server returns an alias pointing to www.myshop.cdn.com, the CDN domain.
Contacting the CDN Domain: The DNS resolver queries the authoritative name server for www.myshop.cdn.com.
Load Balancer Query: The authoritative name server directs the resolver to www.myshop.lb.com, the domain for the CDN’s load balancer.
Optimal Edge Server Selection: The CDN load balancer evaluates the user’s IP address, ISP, content requested, and current server load to select the best CDN edge server.
Retrieving IP Address: The load balancer provides the IP address of the optimal CDN edge server.
Final IP Address Resolution: The DNS resolver returns this IP address to Bob’s browser.
Accessing the Content: Bob’s browser contacts the CDN edge server to load the website. The server first checks its cache for both static content (like HTML pages and images) and dynamic content.
Content Fetching from CDN: If the needed content is not on the edge server, the request escalates to regional, and possibly central CDN servers. If still unavailable, it fetches directly from the origin server in London.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks are vital for maintaining fast, reliable, and secure delivery of digital content. They are especially crucial for websites with a global audience, ensuring that all users, no matter their location, have a consistent and secure experience. Integrating a CDN can drastically improve site performance, manage bandwidth more efficiently, and bolster security measures.