link: Patterns In General
Architectural Patterns
Overview

Architectural patterns are high-level strategies that guide the overall layout and design of software systems. These patterns help tackle common architectural issues like how to efficiently manage data flow, integrate various parts of a system, and balance between performance and maintenance. By standardizing the architecture, these patterns ensure that the system is scalable, robust, and aligned with business objectives.
Abstract
Architectural patterns are key to developing well-organized software architectures. They provide a tested roadmap for building systems that are adaptable to changing requirements and capable of handling various scalability challenges.
Diagrams
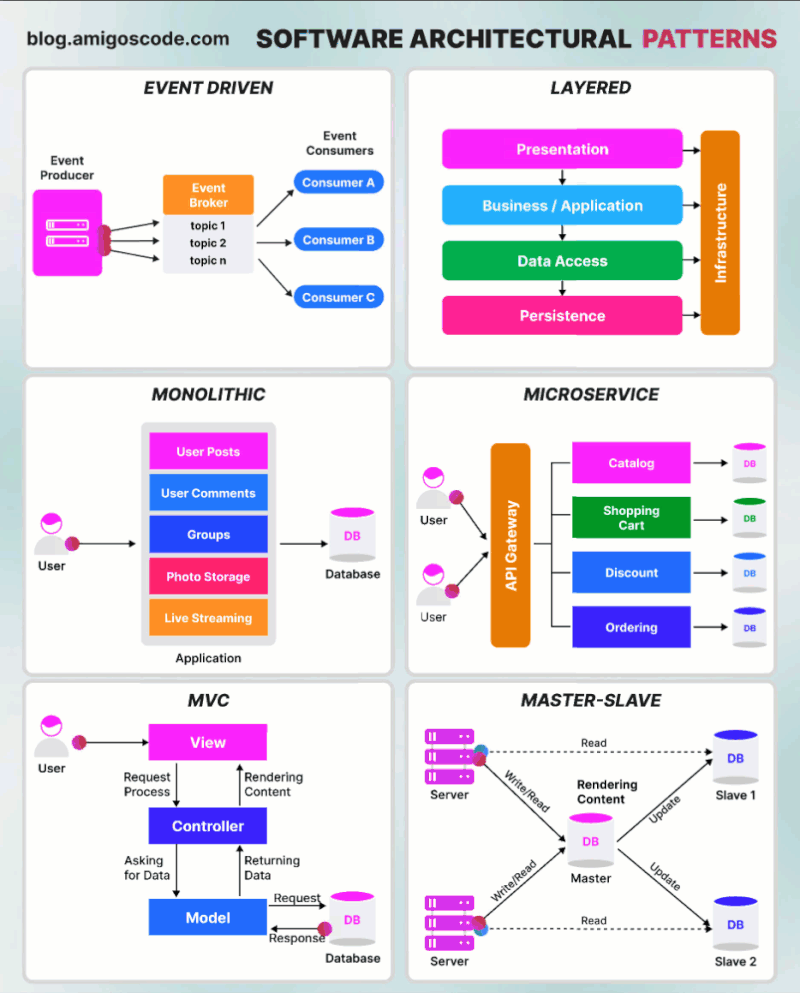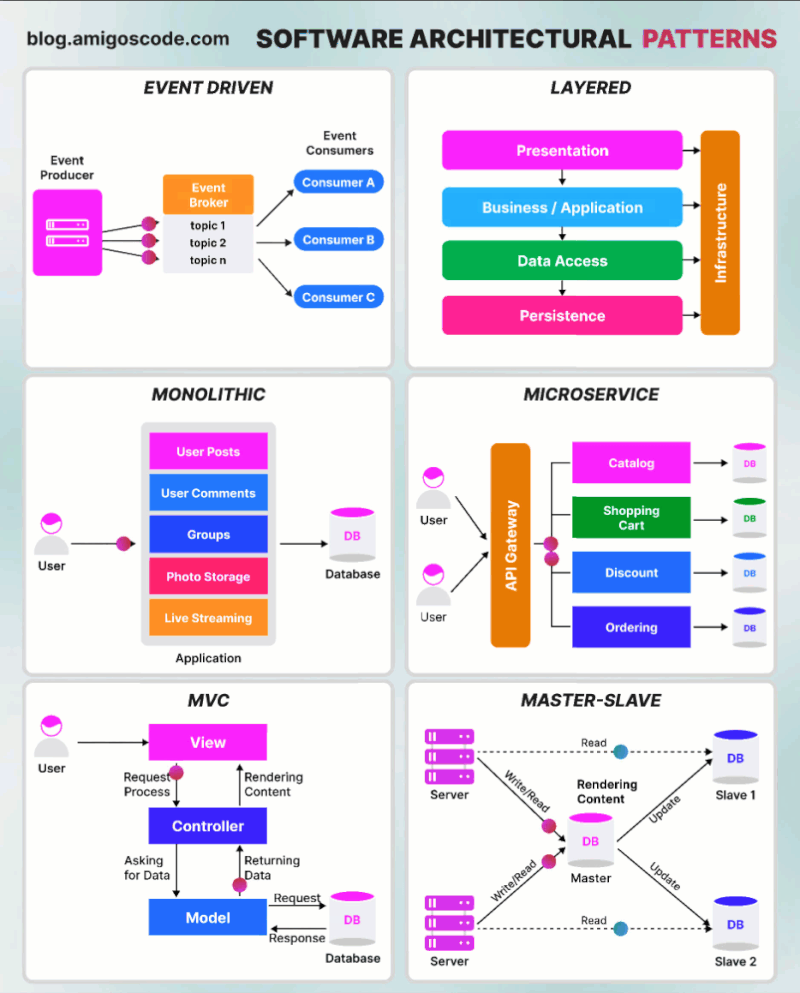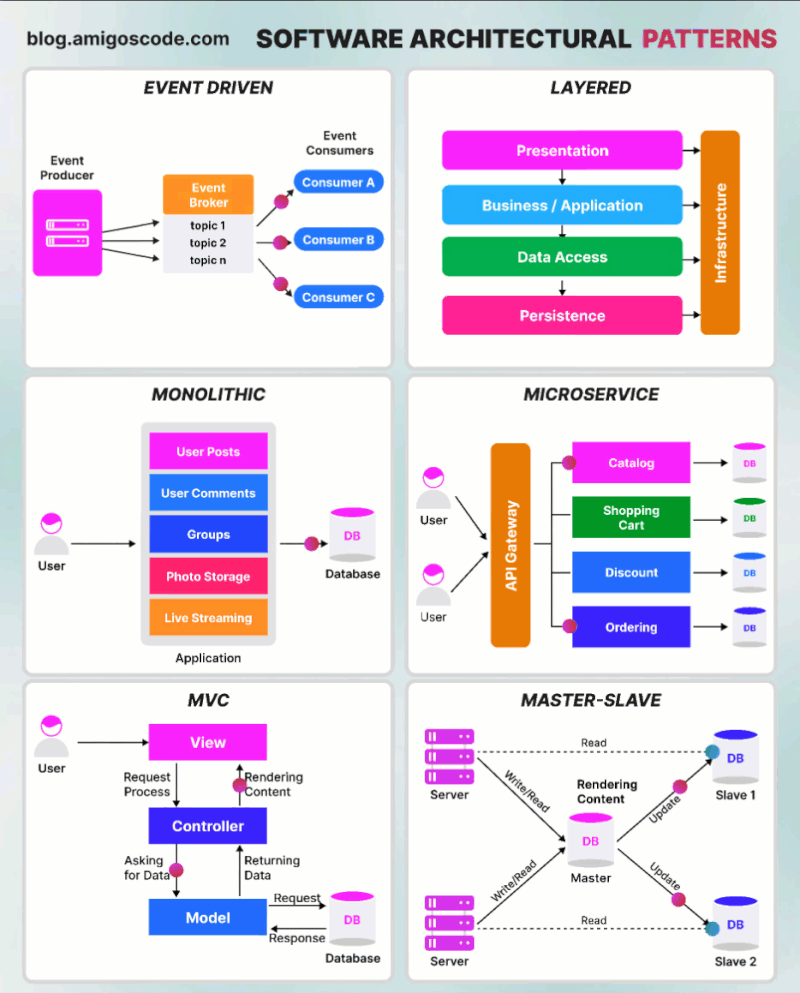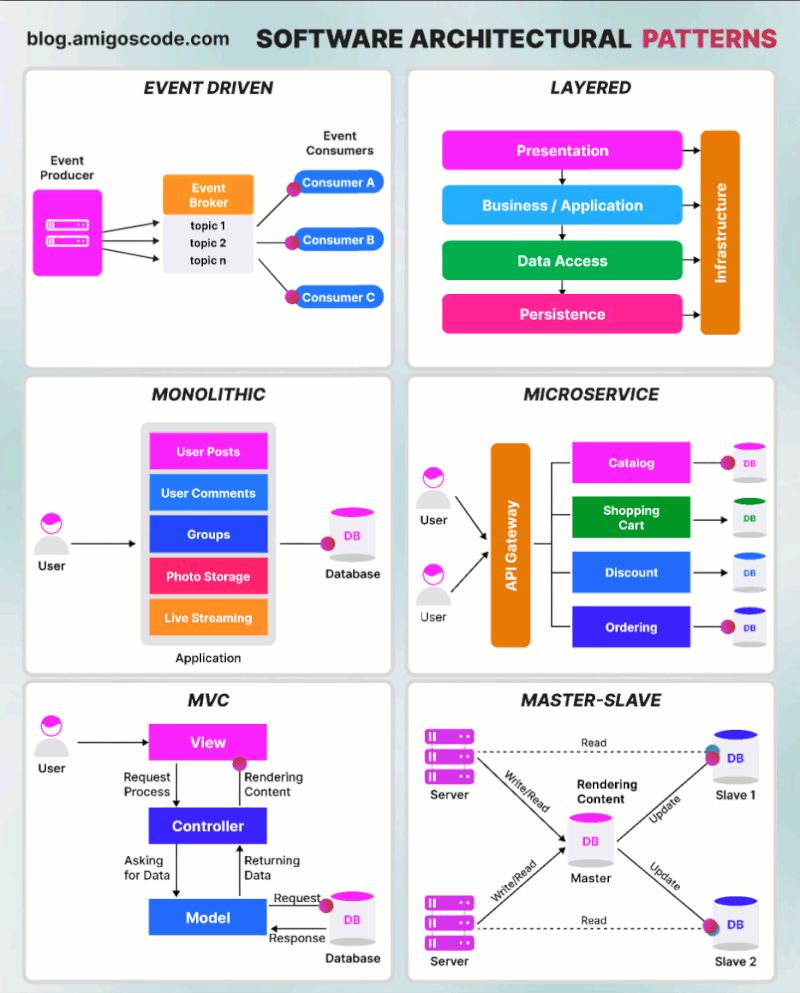
Content
Key Concepts
The following are some of the primary architectural patterns used in system design, each addressing specific Structural and operational needs:
Important
- Monolithic Architecture Pattern
- Layered Architecture Pattern
- Model-View-Controller Pattern
- Onion Architecture Pattern
- Client-Server Architecture Pattern
- Microservices Architecture Pattern
- Serverless Architecture Pattern
- Event-driven Architecture Pattern
- Message-driven Architecture Pattern
- Event Sourcing Architecture Pattern
- Domain Driven Design
- Actor Architecture Pattern
- Reactive Architecture
- Microkernel Architecture Pattern
- Space-Based Architecture Pattern
- Master-Slave Architecture Pattern
- Pipe-Filter Architecture Pattern
- Broker Architecture Pattern
- Peer-to-Peer Architecture Pattern
- Cloud Architecture
- Distributed Systems
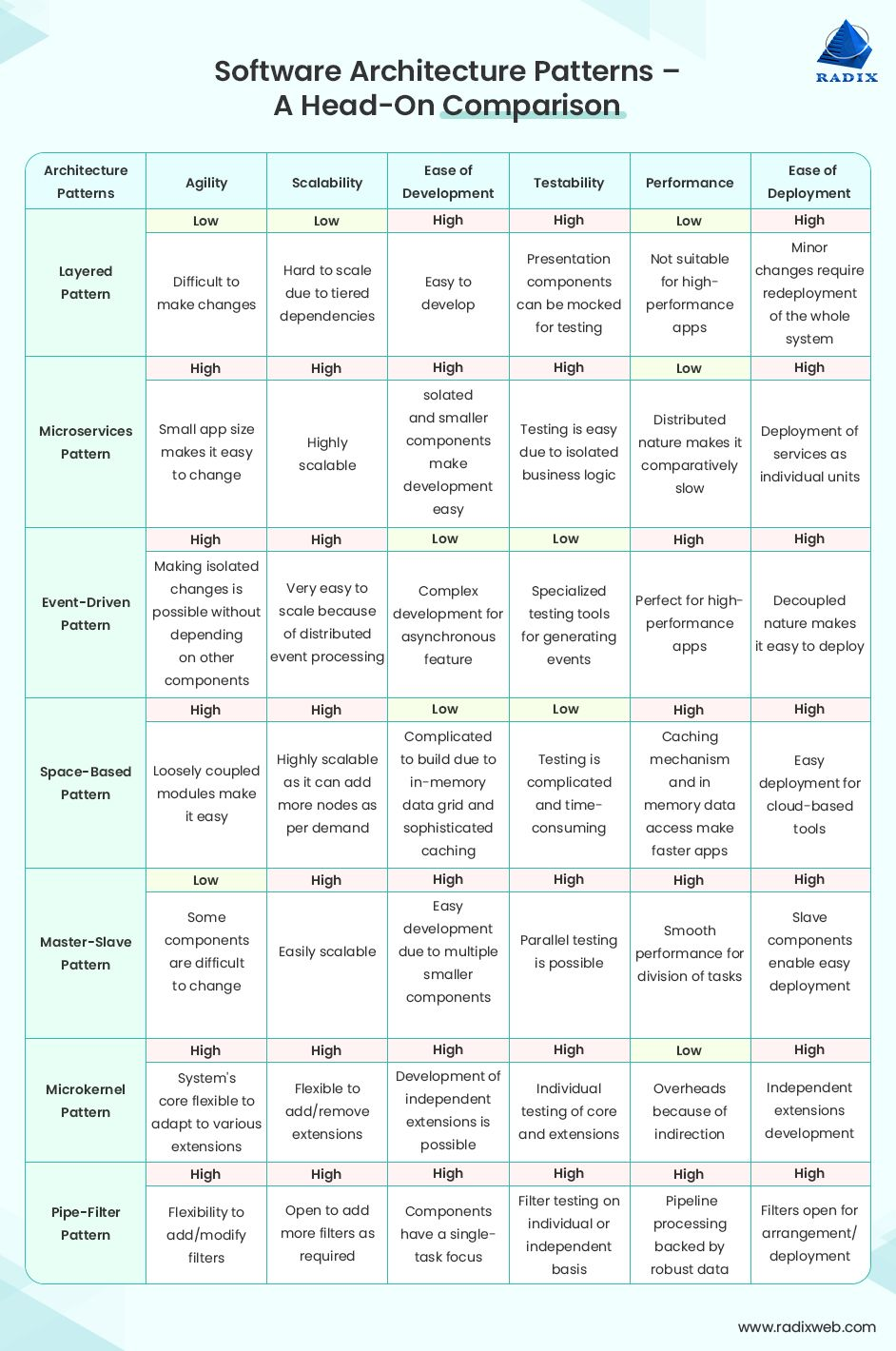
Implementation Overview
Implementing architectural patterns involves several critical considerations to ensure that the system’s design aligns with its intended functions and requirements:
-
Understand System Requirements: Before selecting a pattern, thoroughly understand the system’s functional and non-functional requirements. This understanding helps in choosing the most appropriate pattern that aligns with the system’s scalability, performance, and maintenance needs.
-
Evaluate Pattern Compatibility: Assess how well the chosen pattern fits with the existing system architecture or the planned architecture for new projects. Compatibility includes technology stacks, team expertise, and the operational environment.
-
Plan for Adaptability: Ensure that the architecture can adapt to future changes in requirements. This may involve making design choices that allow easy modification of the system structure or behavior without significant overhauls.
-
Document and Communicate: Clearly document the architecture and the rationale for the chosen pattern. Effective communication with all stakeholders, including development teams, management, and clients, is crucial for successful implementation.
-
Iterative Refinement: Implement the architecture in stages, where possible, and refine the design iteratively based on testing and feedback. This approach helps in mitigating risks associated with architectural decisions.
-
Integration Testing: Rigorously test the system to ensure that all components interact as expected according to the architectural design. Pay special attention to interfaces and data flow between components.
Summary
Cheat Sheet
Architectural patterns are indispensable tools in the software development process, guiding the design and integration of system components. They help developers build complex, scalable, and efficient systems that are well-equipped to adapt to future needs and growth. Utilizing these patterns effectively ensures that software architectures are not only robust but also aligned with strategic business outcomes.
References
10 Software Architecture Patterns You Must Know About
Software Architecture Patterns: Types, Benefits and Comparison