link: Microservices Architecture
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation)
Overview
CQRS, or Command Query Responsibility Segregation, is a design pattern in software architecture that separates the responsibilities of reading data (queries) and writing data (commands). This segregation helps optimize, scale, and enhance the maintainability of the system by allowing independent evolution of read and write models.
Abstract
CQRS stands for Command Query Responsibility Segregation. It is an Architectural Patterns pattern that separates read and write operations, allowing for more efficient data handling and system scalability.
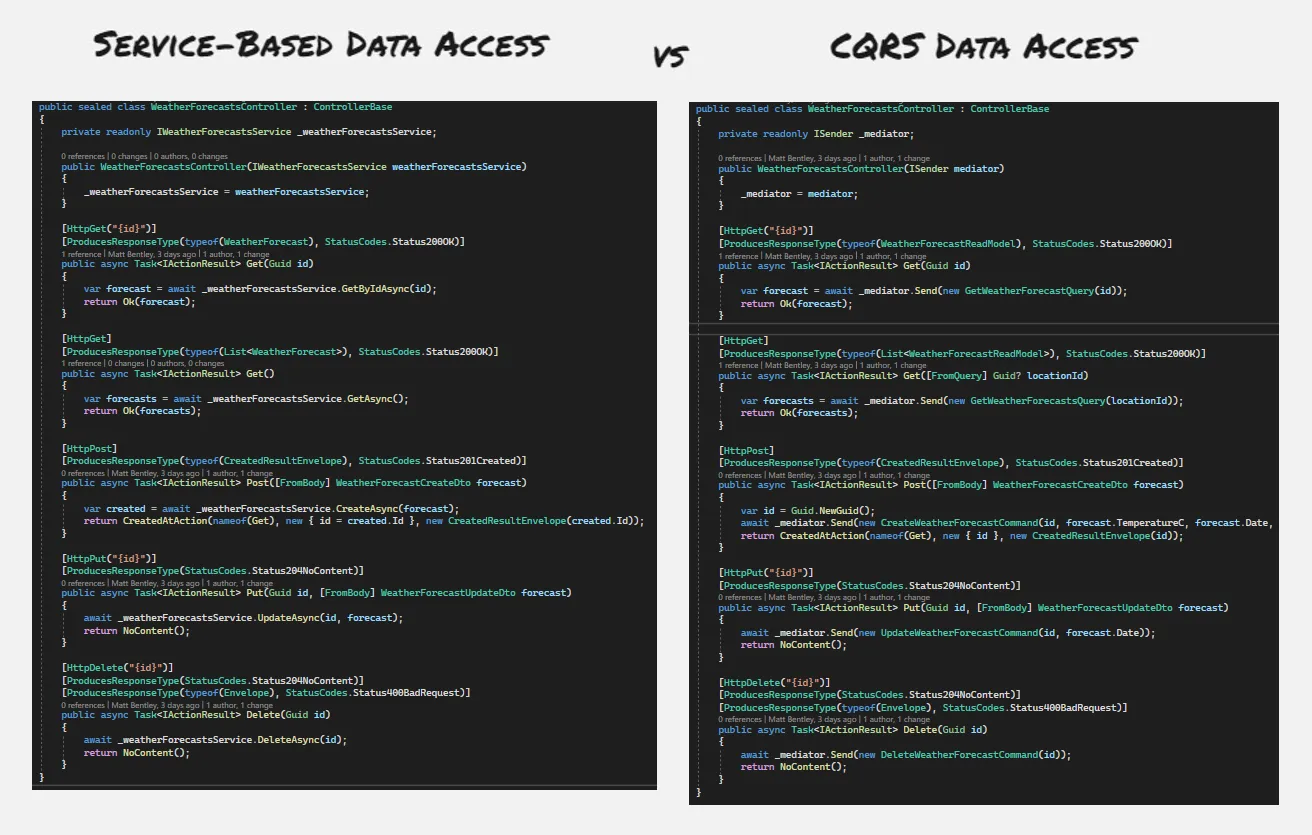
The following shows how a Weather Forecast can be created and read using CQRS compared to service-based implementations.
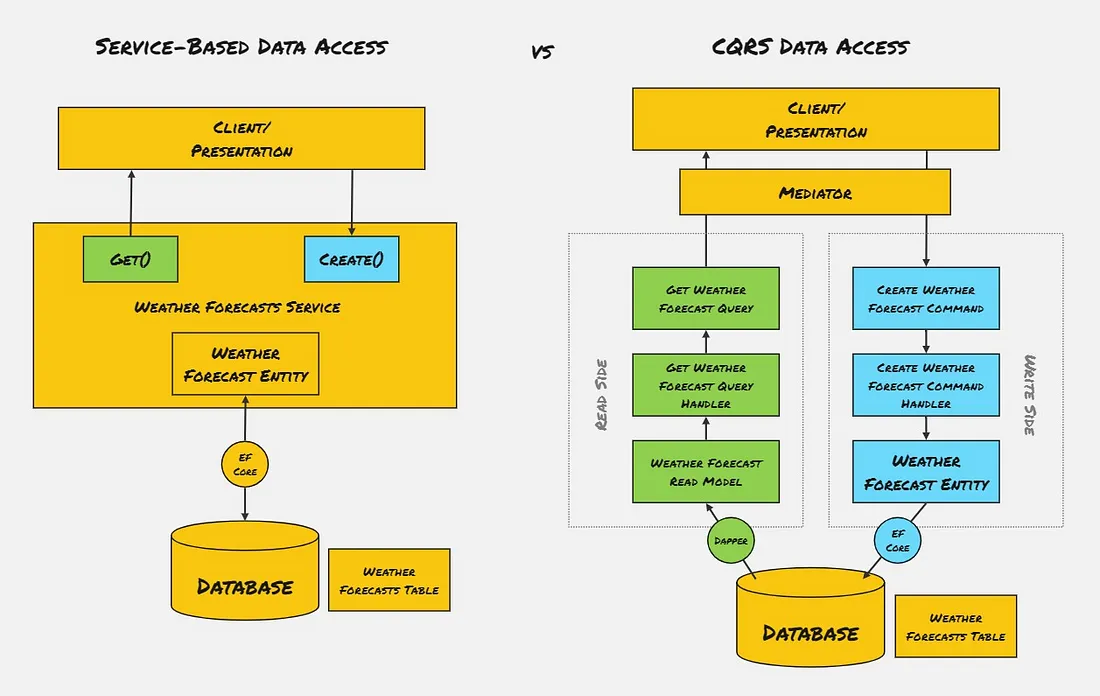
Architecture
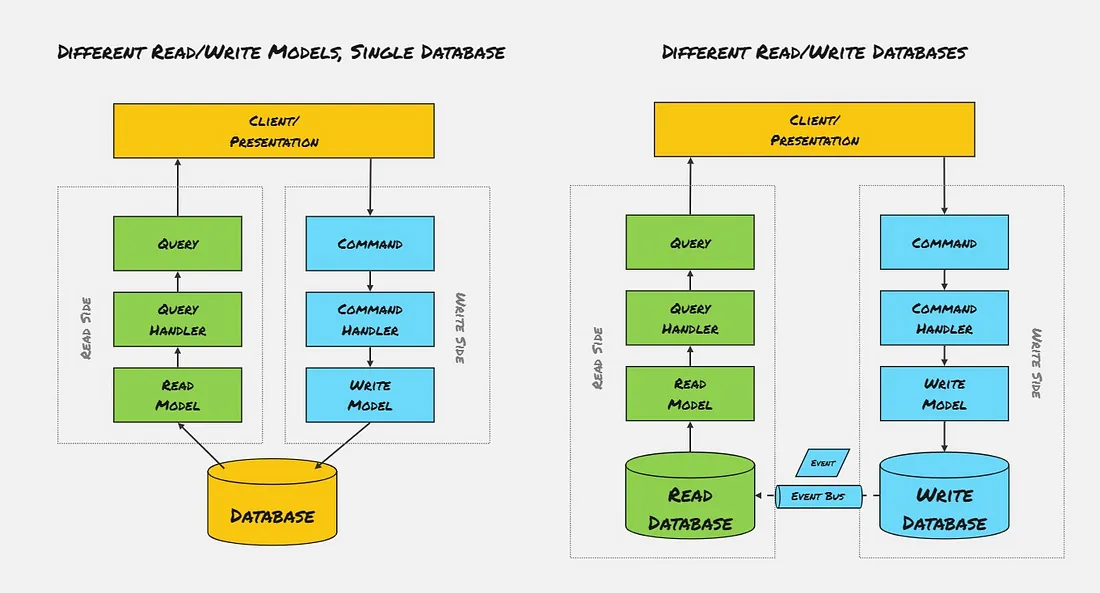
CQRS can use the same database or different databases for READ/WRITE operations
Key Concepts
Command and Query Separation
- Commands: Represent actions that change the state of the system. They encapsulate all the information needed to perform the change.
- Characteristics:
- Modify data.
- Often return void or minimal acknowledgment (e.g., success/failure status).
- Handled synchronously or asynchronously.
- Characteristics:
- Queries: Retrieve data without modifying it. They focus on fetching the data that the client needs.
- Characteristics:
- Do not modify data.
- Return data in a suitable format.
- Should be side-effect free.
- Characteristics:
Example
- Command Examples: “CreateOrder”, “UpdateCustomerInfo”, “DeleteProduct”
- Query Examples: “GetOrderDetails”, “ListCustomers”, “FetchProductById”
C# Recommendations
Using Record Type for commands is a good approach.
Pros and Cons
Pros
- Scalability: Separate read and write workloads can be scaled independently, optimizing resource usage.
- Performance: Queries can be optimized for read performance without affecting write operations, and vice versa.
- Flexibility: Allows different data models for reading and writing, which can simplify complex domains.
- Maintainability: Codebases are easier to manage and extend due to the clear separation of concerns.
Cons
- Complexity: Implementing CQRS adds complexity to the system, requiring more code and understanding.
- Consistency Issues: Achieving eventual consistency can be challenging and may not be suitable for all applications.
- Learning Curve: Requires a good understanding of domain-driven design and Event Sourcing, which can be a steep learning curve for developers.
Implementation Overview
Implementing CQRS involves several key steps and considerations:
Define Commands and Queries
- Identify Commands: Determine the operations that will modify the system’s state.
- Identify Queries: Determine the data retrieval operations needed by the system.
Design the Data Models
- Write Model: Create a model optimized for processing commands, often normalized to ensure consistency.
- Read Model: Create one or more models optimized for queries, often denormalized for quick access.
Separate Data Stores (Optional)
- Use different databases or storage mechanisms for read and write operations to optimize performance further.
Command Handlers and Query Handlers
- Command Handlers: Implement logic to process commands and update the state.
- Query Handlers: Implement logic to retrieve data efficiently based on the read model.
Event Handling (if using Event Sourcing)
- Capture events resulting from command execution.
- Update the read model based on these events to keep it in sync with the write model.
Event Sourcing Integration
CQRS is often used in conjunction with Event Sourcing, where state changes are stored as a sequence of events. This integration can further enhance the benefits of CQRS by providing a complete history of state changes and supporting more complex business logic.
Example Scenario
Weather API (C#)
E-commerce Order Management
Commands:
- PlaceOrder: Command to create a new order.
- CancelOrder: Command to cancel an existing order.
- UpdateOrderStatus: Command to update the status of an order.
Queries:
- GetOrderDetails: Query to retrieve detailed information about a specific order.
- ListOrdersByCustomer: Query to retrieve all orders placed by a specific customer.
- GetOrderStatus: Query to check the current status of an order.
Implementation Steps:
- Define Commands: Create command classes for each write operation (e.g.,
PlaceOrderCommand,CancelOrderCommand).- Define Queries: Create query classes for each read operation (e.g.,
GetOrderDetailsQuery,ListOrdersByCustomerQuery).- Design Write Model: Create entities and repositories optimized for command handling.
- Design Read Model: Create views or projections optimized for queries.
- Implement Command Handlers: Write logic to handle each command and update the state.
- Implement Query Handlers: Write logic to handle each query and return the required data.
- Integrate Event Sourcing: Capture events on state changes and update the read model accordingly (if using Event Sourcing).
Summary
Summary
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) is a powerful architectural pattern that separates read and write operations, enhancing system scalability, performance, and maintainability. By dividing the responsibilities, CQRS allows for independent optimization of data retrieval and modification, making it ideal for complex and high-performance systems. When combined with Event Sourcing, CQRS provides even greater flexibility and insight into system behavior over time.
Related Topics
Summary
- Microservices Architecture: CQRS is often used in microservices to separate read and write operations, allowing each microservice to optimize its own data access patterns and improve scalability.
- Event Sourcing: Often used together with CQRS to maintain a complete history of changes and support complex business logic by storing state changes as a sequence of events.
- Domain Driven Design: CQRS aligns well with Domain-Driven Design principles by separating the concerns of command and query, allowing each part of the domain to be modeled and optimized independently.
- Distributed Systems: CQRS helps manage complexity in distributed systems by decoupling read and write operations, improving scalability and performance.
- Scalability: CQRS enhances scalability by allowing independent scaling of read and write operations, optimizing resource usage.