link: Architectural Patterns
Client-Server Architecture Pattern
Diagram
Overview
Client-Server Architecture is a fundamental computing model that structures applications as clients and servers, each with specific roles and responsibilities. This architecture pattern is widely used for network applications and services, where the server hosts resources and services that clients request and consume.
Abstract
The Client-Server Architecture simplifies network design by clearly separating the client and server roles, enabling efficient communication and resource sharing across a network.
Content
Key Concepts
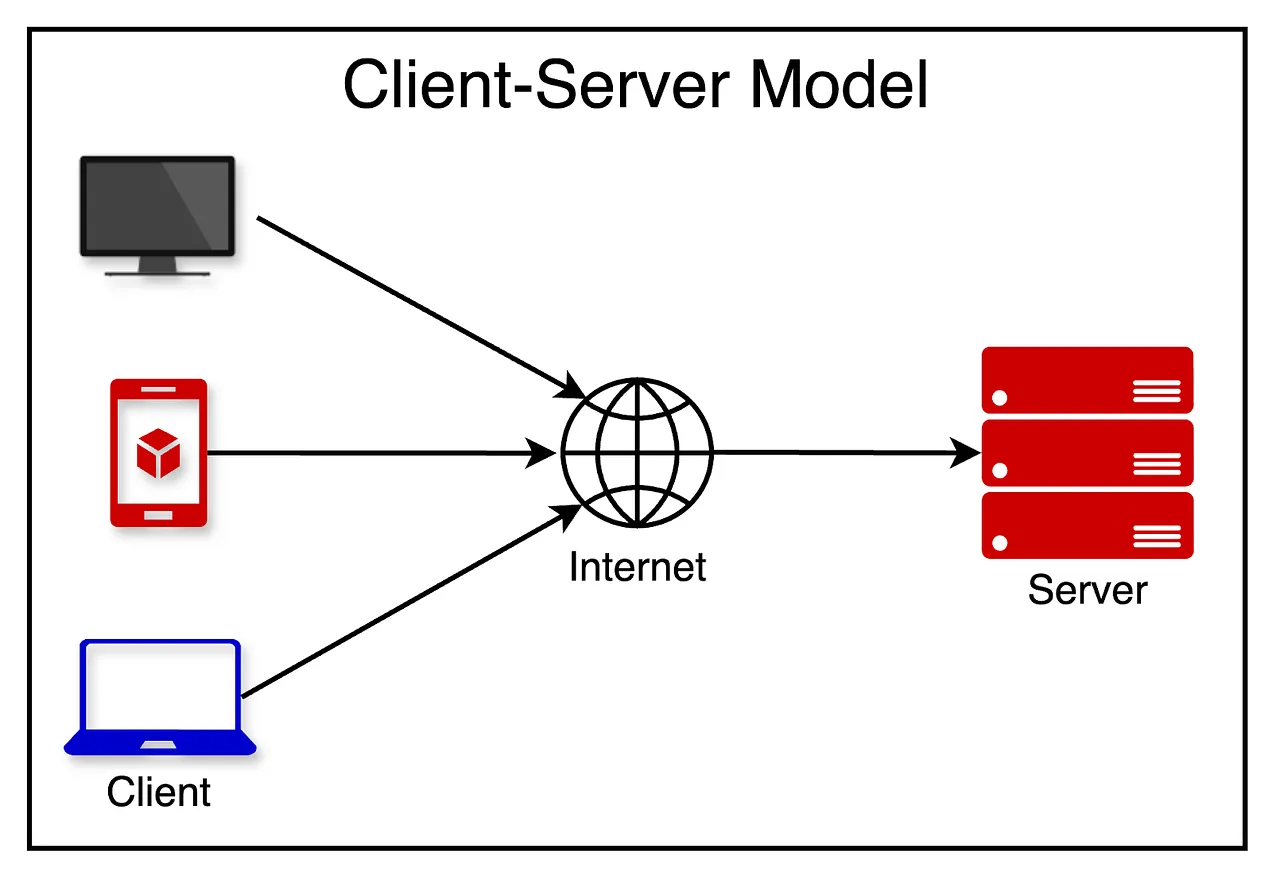
The Client-Server Architecture organizes networked systems into two types of components: clients that request services and servers that provide services. This separation enhances scalability, maintainability, and security of applications:
Important
- Clients: Typically user interfaces that request data or service functionality from servers. They interact with the user and display the data provided by the servers.
- Servers: Powerful systems or software that manage network resources and services. They respond to requests from clients by providing data, functionality, or both.
- Communication: Clients and servers communicate over a network, often using a standardized protocol such as HTTP. This communication is managed through request and response messages.
Implementation Overview
To implement the Client-Server Architecture effectively, consider the following guidelines:
- Client Independence: Clients should be as independent as possible from the servers, interacting only through well-defined interfaces.
- Scalability of Servers: Servers must be capable of handling multiple client requests simultaneously and scalable to accommodate growing numbers of clients.
- Security Measures: Security is crucial, as the client-server model is often exposed to various security threats. Implement robust authentication, encryption, and access controls.
Summary
Summary
Client-Server Architecture is a robust model for building applications that separate data and service management (server side) from the user interface and request management (client side). This separation helps manage complexity and enhances the efficiency of networked systems. It is suitable for applications ranging from simple networks to complex enterprise environments.
Warning
Proper implementation requires careful consideration of scalability, security, and client independence to avoid common pitfalls such as server overload and security vulnerabilities.