link: Architectural Patterns
Model-View-Controller Pattern
Diagram
Overview
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern is a widely used architectural design pattern that separates an application into three interconnected components. This separation helps manage complexity in large applications, promotes organized code development, and supports an efficient team workflow.
Abstract
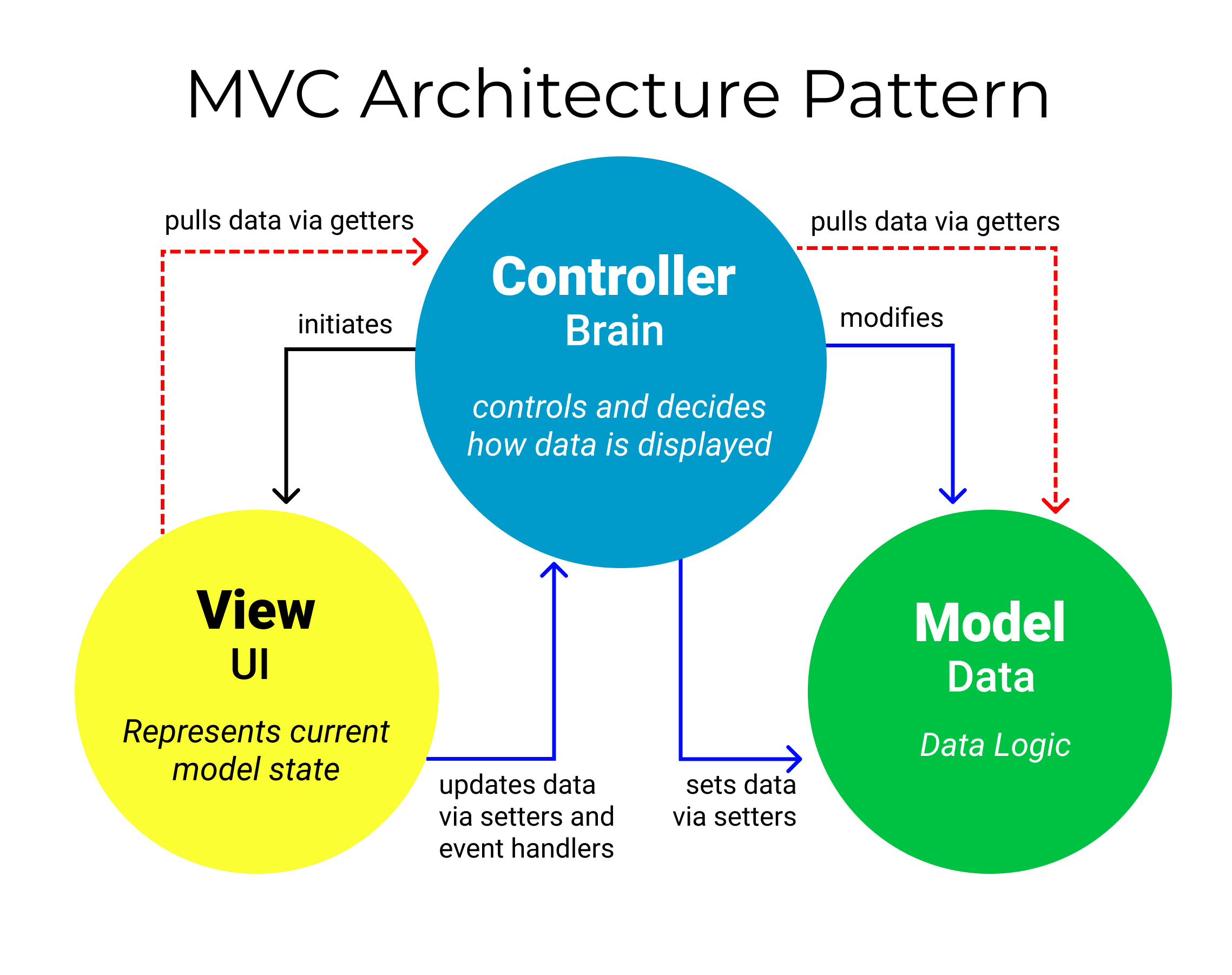
MVC is an instance of the Layered Architecture Pattern tailored for web applications. It divides the application into three layers: Model, View, and Controller, each responsible for specific aspects of the application’s functionality.
Content
Key Concepts
The MVC pattern structures web applications into three components that handle different aspects of the application development:
Important
- Model: The Model component stores data and its related logic. It represents data that is being transferred between the View and Controller components or any other business logic related to the data.
- View: The View component is used for all the UI logic of the application. It displays data from the Model to the user and sends user commands (e.g., button clicks) to the Controller.
- Controller: The Controller acts as an intermediary between the Model and the View. It listens to inputs from the View, processes them (with possible changes to the Model), and returns the updated data to the View.
Implementation Overview
- Separate Concerns: Clearly distinguish between the Model, View, and Controller components. This separation helps in managing code complexity and enhances maintainability.
- Define Interaction Rules: Ensure that each component interacts with the others only through well-defined interfaces. The Model should not have any knowledge of the View, and vice versa.
- Utilize Frameworks: Many web development frameworks (e.g., Django, Rails, Spring MVC) provide built-in support for the MVC pattern, which can simplify implementation.
Summary
Summary
The MVC pattern is a powerful, structured approach to web application development that helps separate data modeling, user interface, and control logic. This separation allows for more organized development and easier maintenance. MVC not only implements the principles of the Layered Architecture Pattern but also provides a clear framework for how different parts of an application should interact and be organized.
Components:
- Model: The backend that contains all the data logic
- View: The frontend or graphical user interface (GUI)
- Controller: The brains of the application that controls how data is displayed