link: Multi-Factor Authentication
One-Time Password
Diagram
OTP Diagram
Overview
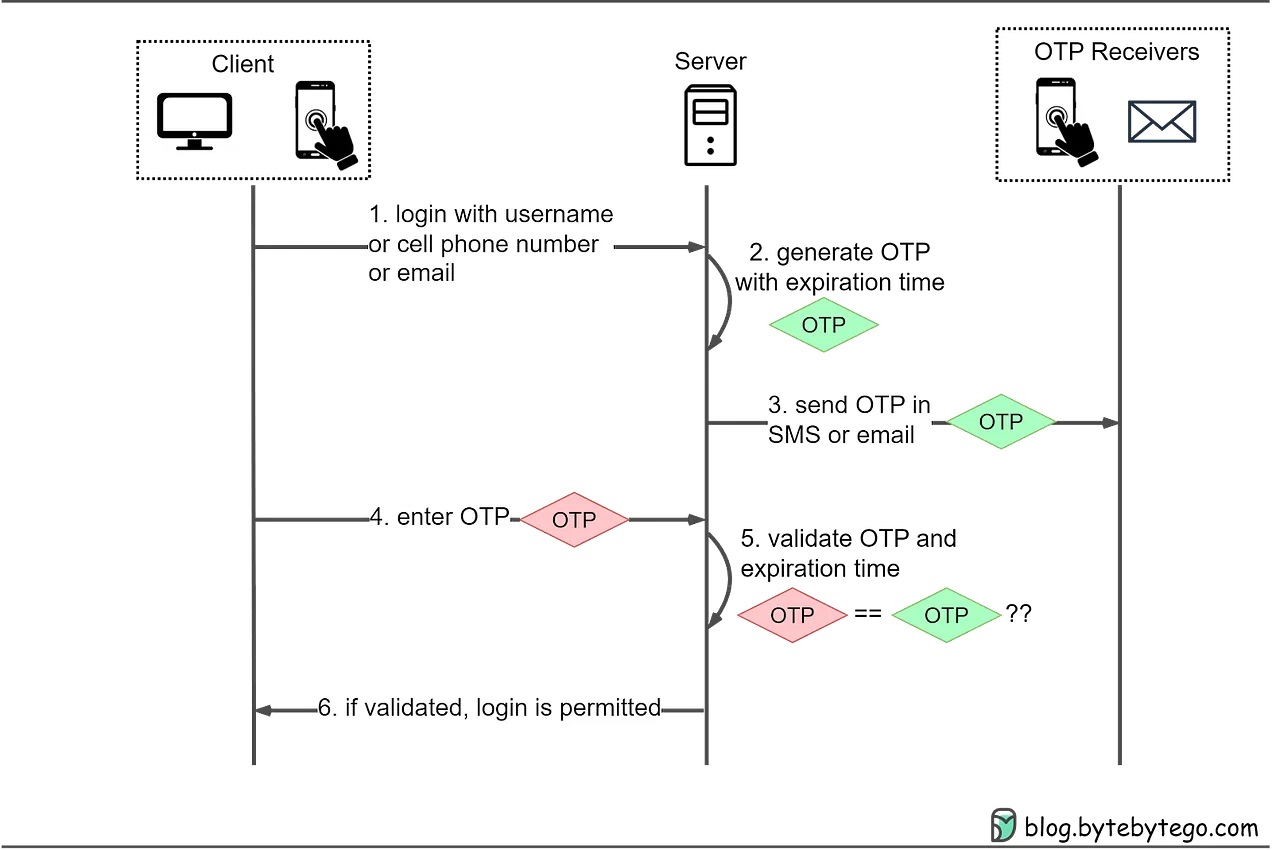
A One-Time Password (OTP) is a unique, temporary code that is used for a single Authentication session or transaction. OTPS are an effective way to enhance security by mitigating the risks associated with static passwords. They are widely used in two-factor authentication (2FA) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) systems.
How OTP Works
- Generation: An OTP is generated using an algorithm that ensures the code is unique and valid for only a short period or a single use.
- Delivery: The OTP is delivered to the user via a predefined method, such as SMS, email, or a dedicated authentication app.
- Usage: The user enters the OTP as part of the authentication process. The server verifies the OTP against the expected value.
- Validation: If the OTP matches the expected value, the user is authenticated. The OTP is then invalidated and cannot be used again.
Types of OTP
Types of OTP
- Time-Based OTP (TOTP): Generates a new password at fixed intervals, typically every 30 or 60 seconds. The password is valid only for the duration of the interval.
- Event-Based OTP (HOTP): Generates a new password based on a counter that increments with each new password request. The password is valid until it is used or a new one is generated.
- SMS OTP: Delivered to the user via SMS. It is typically valid for a short period or until it is used.
- Email OTP: Delivered to the user via email. It is similar to SMS OTP in terms of validity and usage.
Use Cases
- Online Banking: Used for secure login and transaction verification.
- E-commerce: Ensures secure payments and account access.
- Enterprise Security: Protects access to corporate systems and sensitive data.
- Password Reset: Provides a secure method for resetting forgotten passwords.
Pros/Cons
Pros
- Enhanced Security: Provides an additional layer of security beyond static passwords.
- Ease of Use: Simple for users to understand and implement.
- Dynamic Nature: OTPS are unique and expire quickly, reducing the risk of interception and reuse.
Cons
- Delivery Dependency: Relies on the availability of the delivery method (e.g., SMS, email).
- Potential Delays: OTP delivery can be delayed due to network issues, impacting user experience.
- Implementation Complexity: Requires secure generation, delivery, and validation mechanisms.