Date and Time: 2023-10-22 18:24 Status:LearningIT Tags: OAuth 2.0 ,OAuth 2.0 Flows , Authentication and Authorization, API authentication
OAuth 2.0 Authorization code flow
Authorization code flow is redirect-based flow
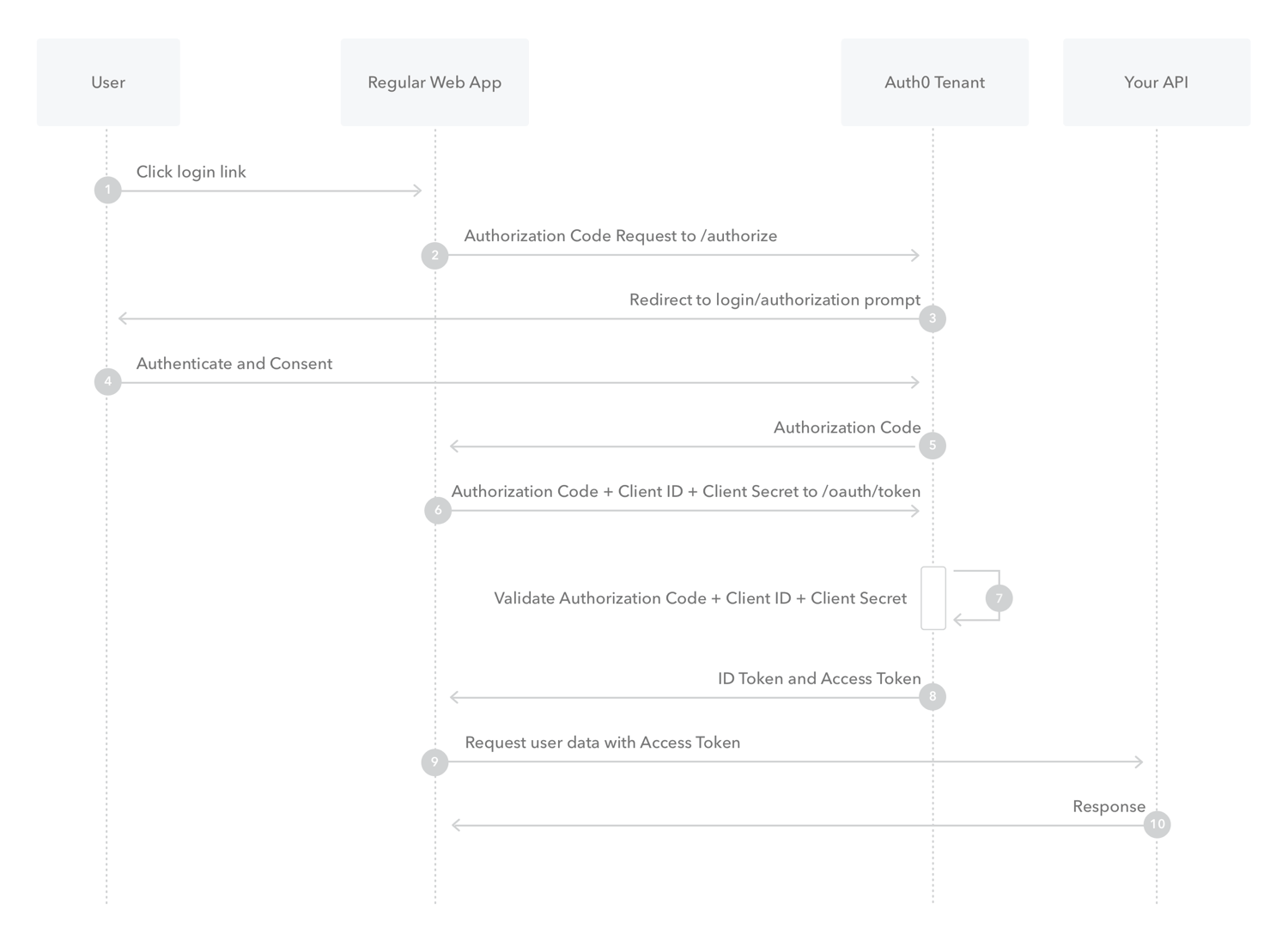
In the example above, we mentioned that the authorization server generates a code and shares it with the client after the user successfully logs in. This code, known as an “authorization code,” is the most secure and common type of authorization grant. It involves a two-step process. First, the client redirects the user to the authorization server, where the user logs in and grants permission. The authorization server then provides an authorization code to the client. In the second step, the client exchanges the authorization code for an access token and, optionally, a refresh token.
Example
First look at the request flow below.
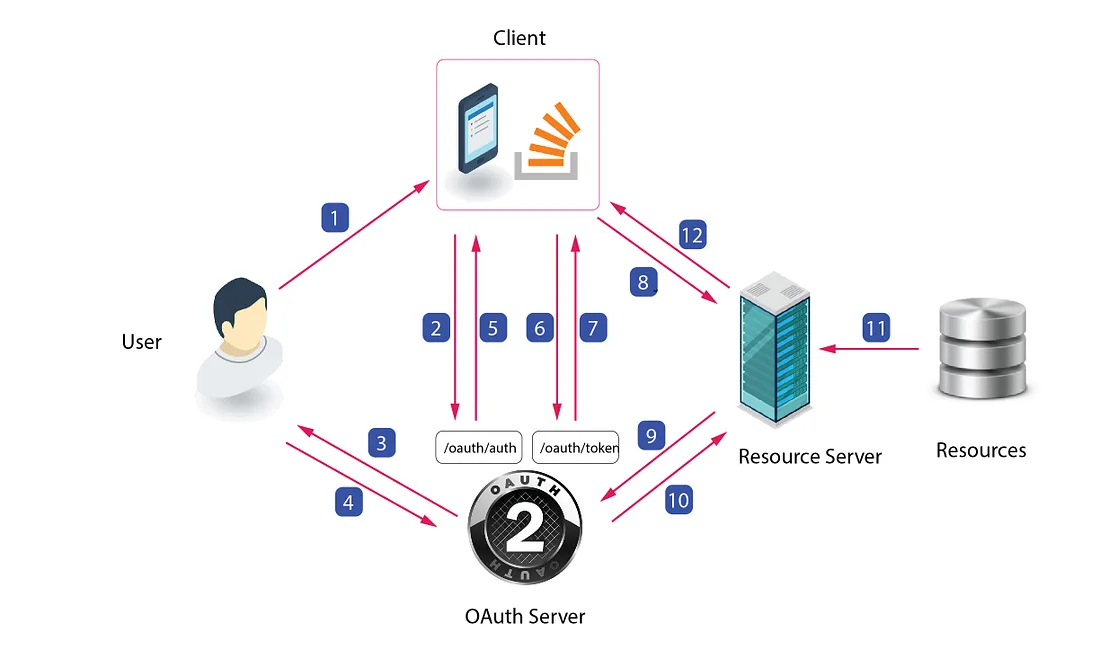
- User press the
Sign up with GoogleButton on the (Client)third-party application. (Stackoverflow) - Application call API endpoint
/oauth/authon the OAuth server with the following parameters.
- Client_id = Client id is predefined id for each clients. In our scenario, Google has given a unique client-id to Stackoverflow when registering.
- Response_type = Response type is
codeas the response of this request is authorization code. - Scope = Scope is data that the application wants to access.
- State = The state code is used for if there are many requests, it is required to match each response to their request.
- Redirect_url = OAuth server doesn’t send a response upon request is received. Therefore, when OAuth wants to send back the response to the client with authorization code, a URL is required. Redirect URL is used as that URL. URL should be URL-encoded as it will be used by OAuth server Sample request
> GET /oauth/auth/?response_type=code&scope=name%20phone%20birthdate&client_id=s4564fdf&state=djbd875s&redirect_url=https%3A%2F%2Fstackoverflow.com%2Fusers%2Foauth%2Fgoogle
>
> HTTP/1.1 Host:account.google.com
- Google OAuth server asks the user to enter user credentials and permissions to give access scope that requested by StackOverflow.
- User give credentials and permissions
- OAuth server generates an authorization code that expires in a few minutes and sends it back to the client using redirect-URL. The server also stores the authorization code for future usage. Sample response
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Location:https://stackoverflow.com/users/oauth/google?code=d34ut6f83h744fn374tf38f939&state=djbd875s
-
Now client requests again from the OAuth server for an access token using authorization code. In this request client_id, client_secret, grant_type, and authorization code should be included. As client_id and client_secret are sensitive data they should be encoded into base64 and put in the header.
If client_id = stack and client_secret = stack_pass,
stack:stack_passshould encoded to base64.base64("stack:stack_pass")="c3RhY2s6c3RhY2tfcGFzcw=="Sample request
POST /oauth/token/ HTTP/1.1
Host: account.google.com
Content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Basic c3RhY2s6c3RhY2tfcGFzcw==
grant_type=authorization_code&code=d34ut6f83h744fn374tf38f939
- Now OAuth server checks the validity of the authorization code and validity of clientid and clientsecret. If they are valid OAuth server generates and stores an access key and a refresh key (can be used together with JSON Web Tokens but it is not necessary) . Then both of them are sent back to the client with the expiration time. This access token and refresh token is stored in client application for future usage. Sample response
> HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: application/jason
>
> { “access_token”: “yfg46tr730as74r1”,
>
> “token_type”: “Bearer”,
>
> “refresh_token”: “92r38y49024ut04r”,
>
> “expires_in”: 3600,}
- When the application wants access to user data, it sends a request to Resource server with the access token. Sample Request
GET /api Authorization: Bearer yfg46tr730as74r1
Host: www.google.com
-
& 10. The resource server checks the validity of the access token using the OAuth server.
-
If the access token is valid, fetch the requested data from the database
-
Sends data back to the client.
Sample response
HTTP/1.1 200 Ok Content-Type: application/json
{“info”: “data”}
Authorization code flow Problems
When an authorization request is made, the authorization code grant type requires the authorization server to generate an authorization code, which is returned to the client application via a redirect URL. This code can then be exchanged for an access token, which can be used to access the user’s data.
An attacker can intercept the authorization code that is sent back to the client and exchange it for an access token, which can cause serious data leaks or breaches. One popular method malicious actors use to intercept authorization codes is by registering a malicious application on the user’s device. This malicious application will register and use the same custom URL scheme as the client application, allowing it to intercept redirect URLs on that URL scheme and extract the authorization code:
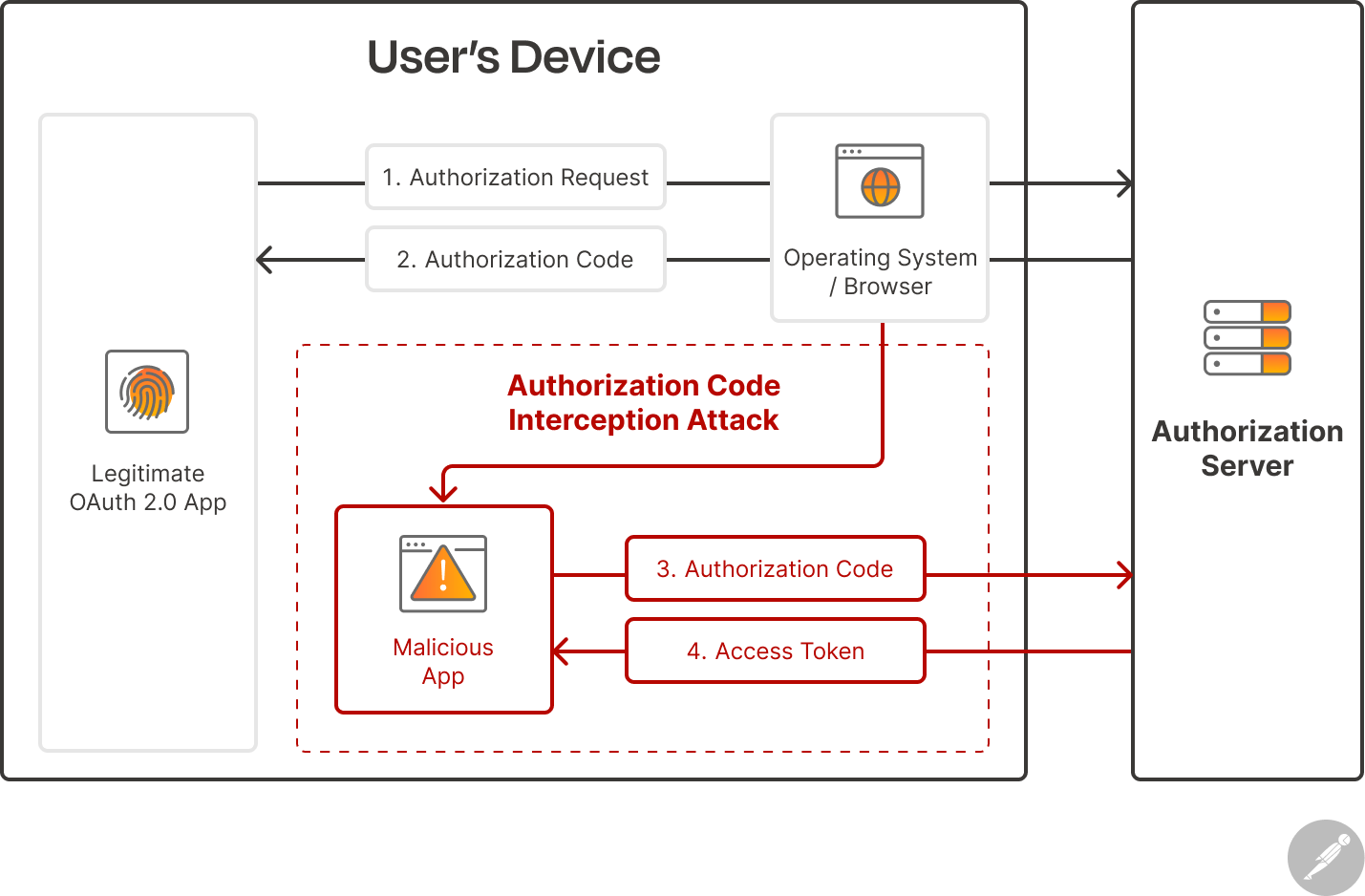
Reference:
https://medium.com/@vidura.prasangana16/what-is-oauth-2-0-476aabded278