link: Microservice Architecture, Cloud Architecture
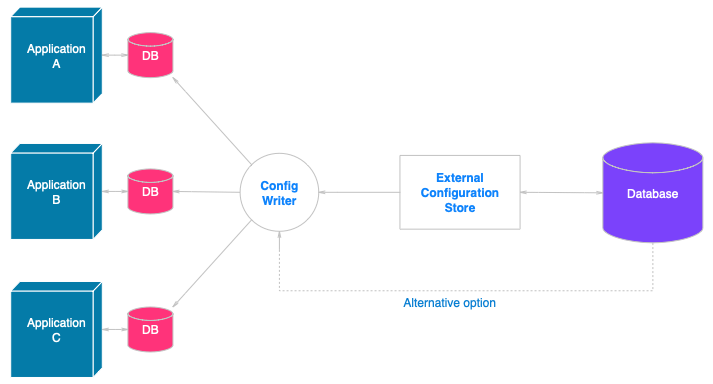
Externalized Configuration
Diagram
Overview
Externalized Configuration refers to the practice of managing application settings outside of the application’s deployable artifacts. This pattern is pivotal in dynamic environments where applications must adapt without redeployment, particularly in microservices architectures where services require configuration independence to scale and evolve seamlessly.
Abstract
Externalized Configuration facilitates dynamic adjustments and environment-specific setups for applications, enhancing flexibility and reducing downtime for configuration changes.
Key Concepts
Externalized Configuration is structured around several key principles:
Important
- Dynamic Configuration: Enables real-time configuration changes without the need for restarting or redeploying applications.
- Environment Specificity: Supports distinct configurations for different environments (development, testing, production), allowing for seamless environment transitions.
- Centralized Management: Often utilizes centralized configuration servers like Spring Cloud Config, Consul, or etcd, which manage and disseminate configurations across services.
Implementation Overview
Steps to Implement Externalized Configuration
- Use Configuration Servers: Deploy a configuration management system that centralizes and automates the delivery of configuration settings.
- Decouple Configuration: Store configuration separately from the codebase and application binaries to ensure that configurations can be changed independently of application deployments.
- Secure Sensitive Data: Encrypt sensitive configuration data, such as API keys and passwords, to protect it in transit and at rest.
- Version Control: Maintain configuration changes in a version-controlled repository to track changes and revert configurations if necessary.
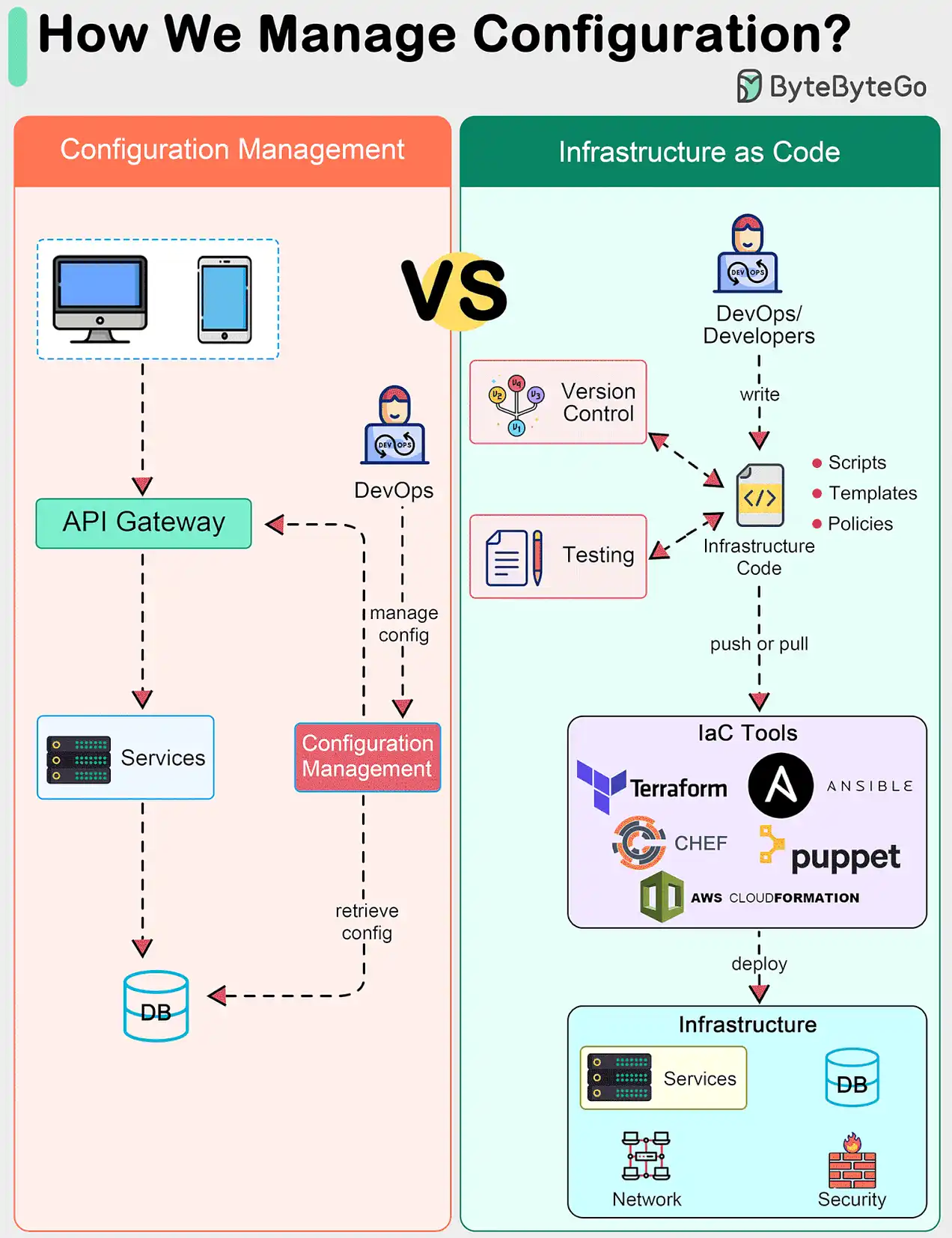
Managing Configuration
Traditional configuration management vs IaC.
Summary
Summary
Externalized Configuration is a critical pattern for modern software development, particularly in microservices architectures. It allows applications to adapt quickly to new requirements and different environments without code changes, supporting continuous delivery and improving system resilience.