link: Web Security
VPN (Virtual Private Network)

Overview
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a safe and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the internet. VPN technology was originally developed to allow remote workers to securely connect to corporate networks in order to access resources as if they were physically on-premise. Today, VPNs are widely used for securing internet connections and ensuring privacy.
Key Features of VPN
- Encryption: VPNs encrypt data traffic, which prevents eavesdropping and makes communication secure over public networks.
- Remote Access: Allows users to connect to a private network from anywhere that has internet access.
- Anonymity: By masking the user’s IP address, VPNs can enhance online anonymity and protect users from being tracked.
VPN Flow
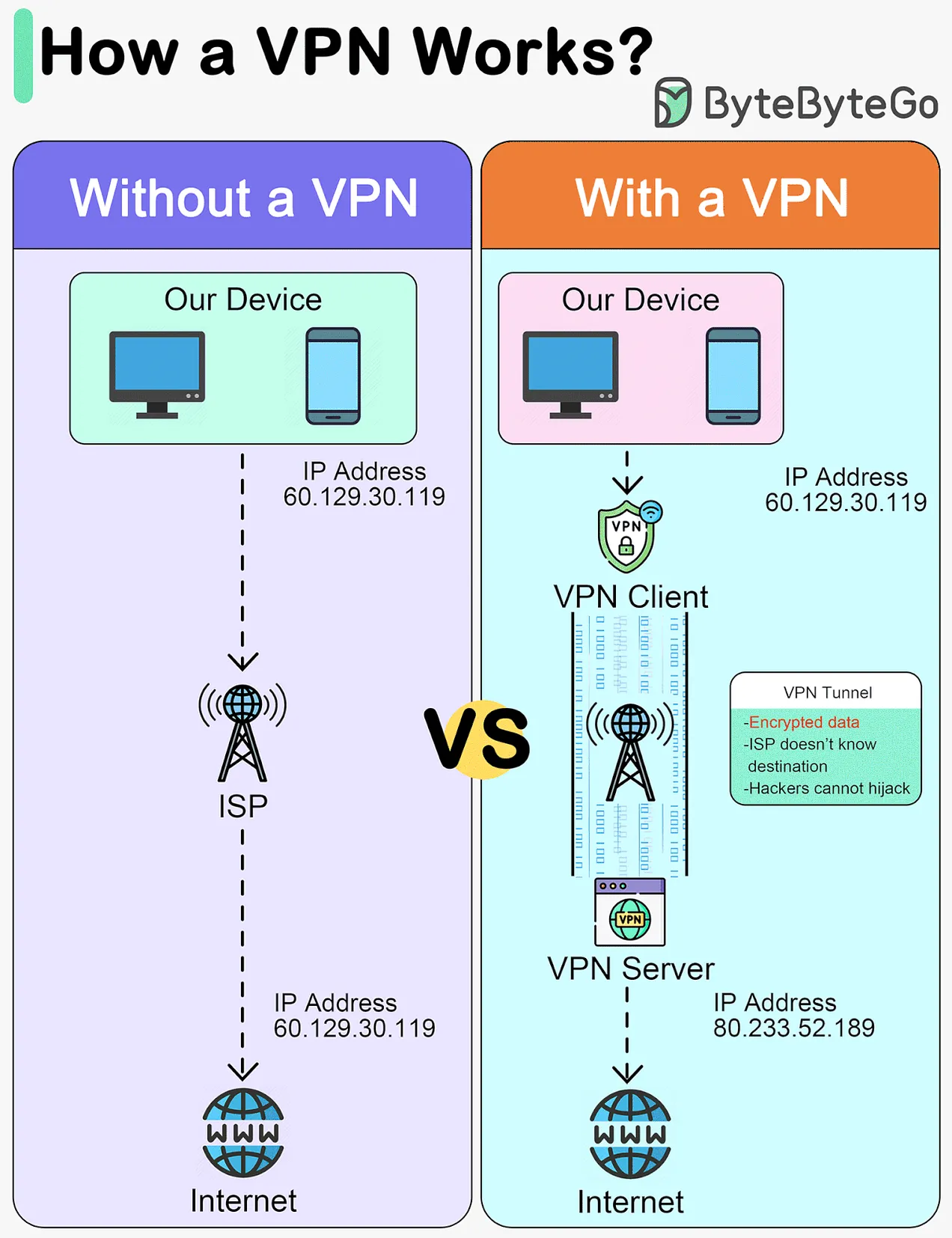
How VPN Works?
A VPN works by routing your device’s internet connection through the VPN’s private server rather than your Internet Service Provider(ISP) . Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Initiation: The user initiates a VPN connection to a VPN server, which can be controlled by the employer or a VPN service provider.
- Authentication: The VPN client and server authenticate each other using chosen authentication methods.
- Tunneling: After authentication, a secure tunnel is established through which all the network traffic is sent.
- Encryption: Data sent through the tunnel is encrypted to keep it confidential and secure.
VPN Protocols
VPNs use different protocols to establish a secure connection, including:
- IPSec: Internet Protocol Security is used to secure Internet communication across an IP network.
- OpenVPN: A robust and highly configurable VPN solution that uses the OpenSSL library and SSLv3/TLSv1 protocols.
- WireGuard: A newer protocol that aims for simpler setup and higher speeds with a lean codebase.
Use Cases
Common Uses of VPN
- Secure Access to Business Networks: Employees can access corporate applications securely from anywhere in the world.
- Personal Privacy and Security: Individuals use VPNs to protect their privacy when accessing the internet, especially when connected to a public Wi-Fi network.
- Content Accessibility: VPNs can bypass geographical restrictions and censorship by routing the connection through servers in different countries.
Advantages of VPN
Pros
- Enhanced Security: VPNs provide a high level of security by encrypting internet connections to safeguard data from hackers or government surveillance.
- Improved Privacy: Users can surf the web anonymously without their activities being tracked.
- Network Scalability: Organizations can enable remote network access without the need for extensive physical infrastructure.
Conclusion
VPNs are essential for enhancing online security, protecting personal privacy, and enabling remote access to resources over the internet. Whether for individual privacy or corporate security, VPN technology plays a crucial role in creating a secure and private online experience.