link: Web Security
Software Testing
Diagram
Overview
Software Testing is a critical process in the software development lifecycle that ensures the quality, functionality, performance, and security of applications. It involves evaluating and verifying that a software product meets the specified requirements and works as expected. Various types of testing are employed to cover different aspects of software quality.
Key Concepts
Software Testing involves several key principles and practices to ensure comprehensive coverage and reliability:
Important
- Test Cases: Specific scenarios or conditions under which the software is tested to verify its behavior.
- Test Suites: Collections of test cases grouped together for execution.
- Assertions: Conditions or rules applied to verify the correctness of test outcomes.
- Defects/Bugs: Issues identified during testing that need to be resolved to improve software quality.
- Test Automation: The use of tools and scripts to automate the execution of test cases, improving efficiency and consistency.
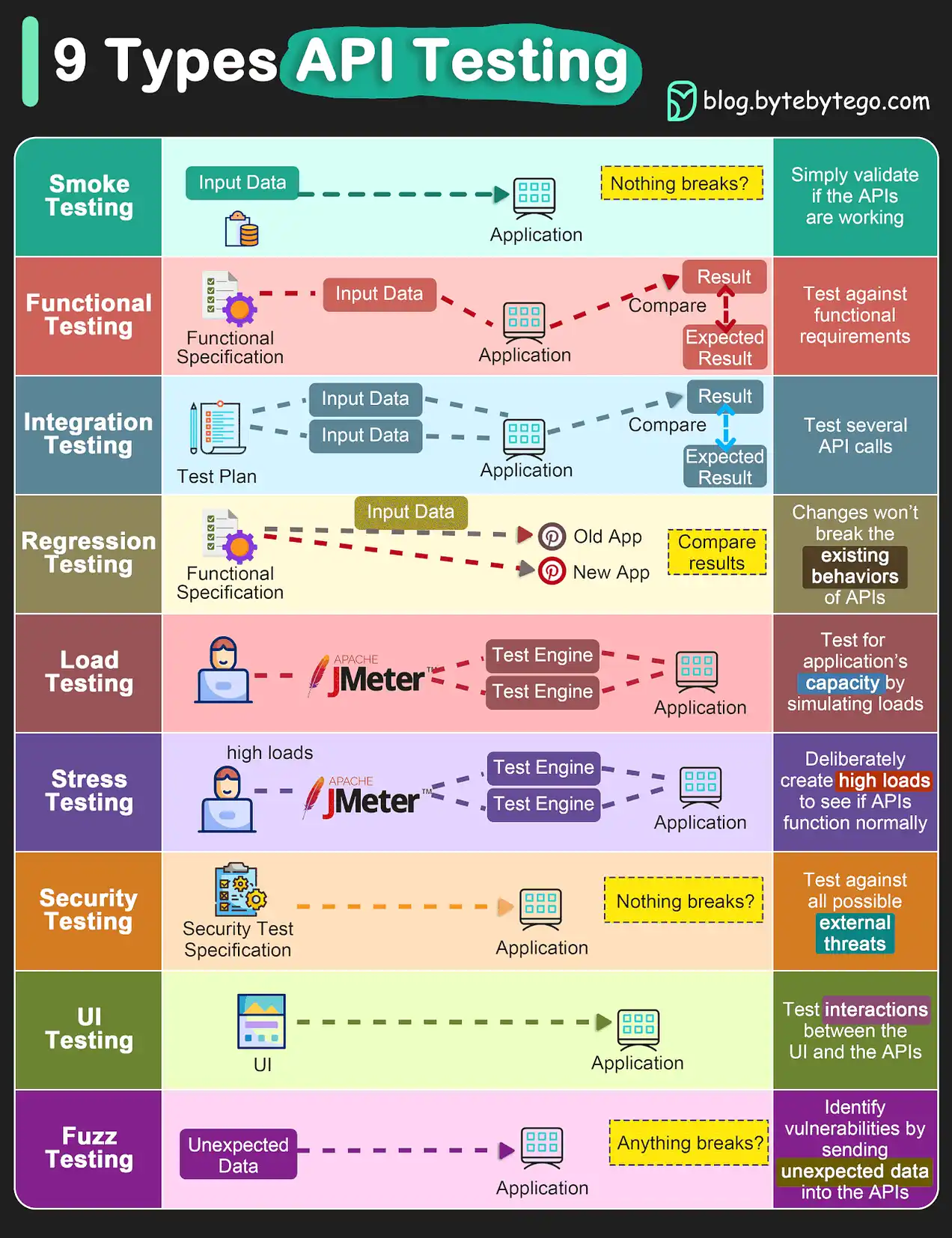
Types of Software Testing
Software Testing can be categorized into various types, each serving a specific purpose and targeting different aspects of the application:
Types of Software Testing
- Smoke Testing: Preliminary testing to check if the basic functionality of the application works correctly.
- Functional Testing: Verifies that the application functions as expected, covering all possible scenarios and inputs(Unit Testing, [ntegration Testing).
- Regression Testing: Revalidates the application after changes or updates to ensure that existing functionality remains unaffected.
- Stress Testing: Tests the application’s behavior under extreme load conditions to identify breaking points and ensure stability.
- Security Testing: Assesses the application for vulnerabilities, ensuring that data is protected and unauthorized access is prevented.
- Usability Testing: Evaluates the application’s user interface and overall user experience to ensure it is intuitive and user-friendly.
- Compatibility Testing: Ensures the application works correctly across different devices, browsers, and operating systems.
- Fuzz Testing: Involves sending random or invalid data to the application to identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure robustness.
Best Practices
Best Practices
- Comprehensive Test Coverage: Ensure all aspects of the application are tested, including edge cases and error conditions.
- Automated Testing: Use automation tools to run tests frequently and consistently.
- Continuous Integration: Integrate testing into the CI/CD pipeline to catch issues early.
- Mocking and Virtualization: Use mock servers to simulate API behavior during development and testing.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of test cases, scenarios, and results for future reference and debugging.
Conclusion
Software Testing is a critical component of ensuring the reliability, performance, and security of software systems. By employing various types of testing, such as unit, smoke, functional, integration, regression, load, stress, security, API, usability, acceptance, compatibility, and fuzz testing, developers and testers can ensure that applications meet the required standards and provide a robust and seamless user experience.