link: Microservice Architecture, Cloud Architecture
Service Registry
Diagram
Overview
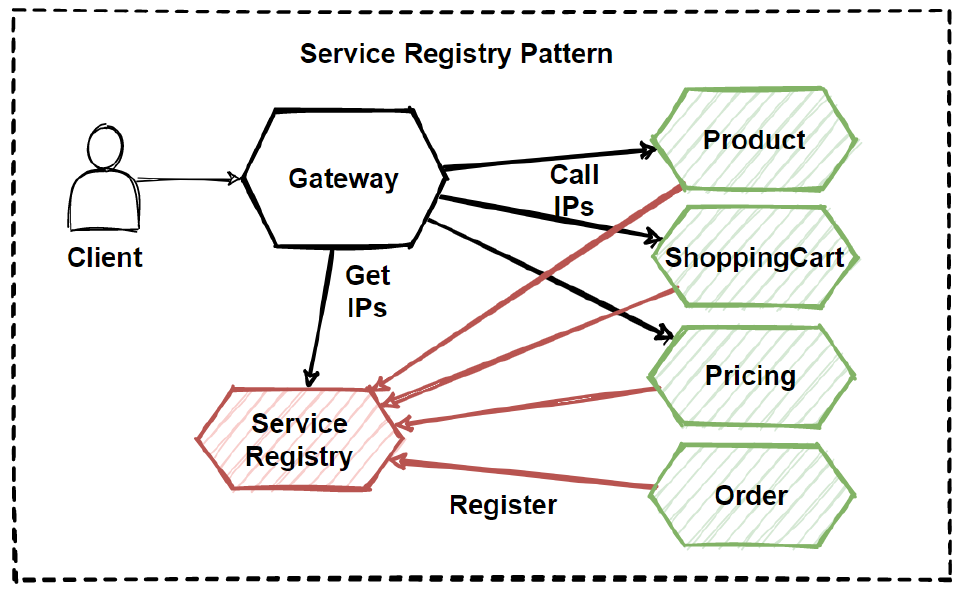
In a microservices architecture, a Service Registry serves as a central repository that keeps track of all the services within the system. It acts like a map, enabling services to locate and communicate with each other dynamically. This dynamic discovery is crucial in distributed systems where services may be constantly coming online or going offline. By registering with the Service Registry, each service makes its location and capabilities known, allowing other services to find and interact with it seamlessly.
Abstract
A Service Registry is like a directory for microservices, ensuring they can find and communicate with each other in a dynamic and distributed environment.
Key Concepts
Registration
Each service registers itself with the Service Registry upon startup, providing information about its location and available endpoints. This typically includes the service’s network address (IP and port), the name of the service, and any other metadata that may be useful for service discovery and communication.
Discovery
Other services and the API Gateway query the Service Registry to locate the services they need to communicate with. This allows for dynamic discovery of services, meaning that the client does not need to know the exact location of the service instances in advance. The API Gateway can route requests to appropriate services based on information from the Service Registry.
Health Checking
The Service Registry often includes health checks to ensure that registered services are available and healthy. This involves periodically pinging the services to verify their status. If a service fails a health check, it is removed from the registry, ensuring that clients do not attempt to communicate with an unhealthy service. The API Gateway can use this health information to make routing decisions, directing traffic only to healthy service instances.
Load Balancing
Some Service Registries may also provide load balancing capabilities, distributing incoming requests among multiple instances of a service. This helps in optimizing resource utilization and ensures that no single service instance becomes a bottleneck. The API Gateway can leverage load balancing information to distribute traffic efficiently.
Service Deregistration
When a service instance shuts down, it should deregister itself from the Service Registry. This ensures that the registry does not contain stale information, which could lead to failed requests. Proper deregistration helps maintain the accuracy and reliability of the service discovery process.
Important
Service discovery can be implemented on either the client-side or the server-side. Each approach has its own benefits and trade-offs.
Implementation Overview
Implementing a Service Registry involves integrating it into your Microservices Architecture and ensuring that services properly register and deregister themselves. Additionally, mechanisms for service discovery and health checking need to be implemented to facilitate seamless communication between services and the API Gateway.
Popular Tools
- AWS Service Discovery: A feature within AWS Cloud Map that allows for the automatic discovery of cloud resources like EC2 instances and ECS services.
- Azure Service Fabric: A platform that simplifies building and managing microservices, providing built-in service discovery, load balancing, and health monitoring.
- Netflix Eureka: A REST-based service for locating services for the purpose of load balancing and failover of middle-tier servers.
Each of these tools offers robust solutions for implementing Service Registries in microservices architectures. They handle registration, discovery, health checking, and sometimes even load balancing and security aspects, making them essential components for any distributed system.
Conclusion
A Service Registry is an essential component in a microservices architecture, enabling dynamic discovery and communication between services. By implementing a robust Service Registry, organizations can ensure their microservices can find and interact with each other efficiently, leading to a more resilient and scalable system.