source: https://refactoring.guru/course
Extract Variable

Replace Method with Method Object

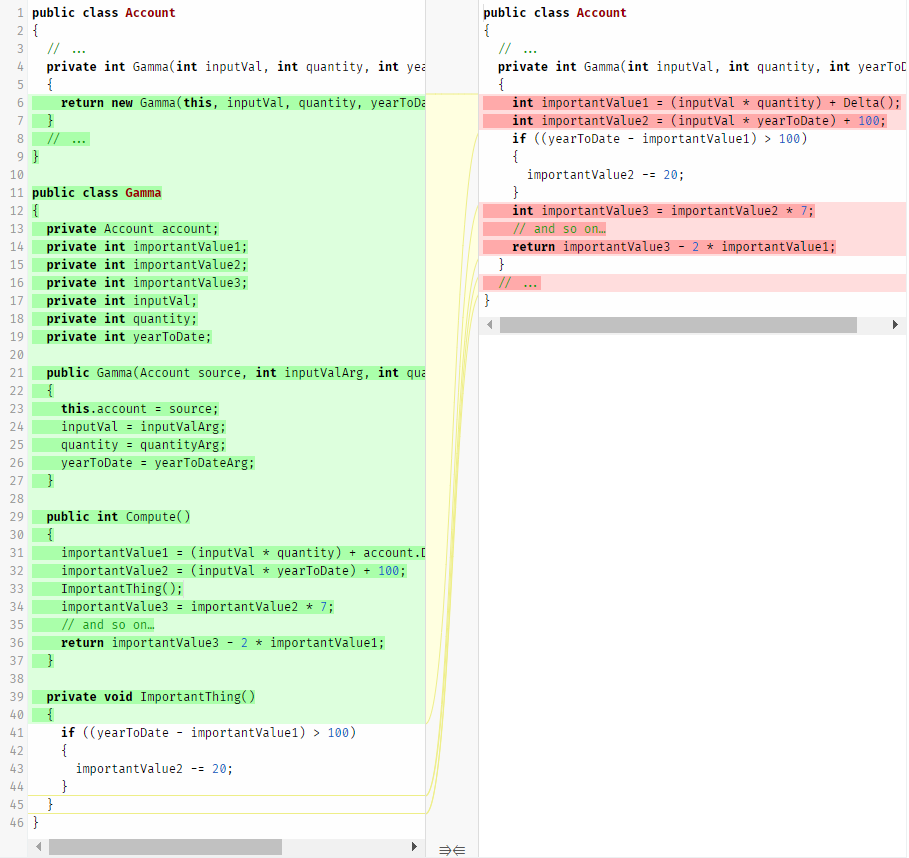
Encapsulate Collection
Encapsulate Collection , Encapsulation
Example:
Before(Wrong):
public class Course
{
public bool IsAdvanced
{
get;
set;
}
public Course(string name, bool isAdvanced = false)
{
// ...
}
}
public class Person
{
private List<Course> courses;
public List<Course> Courses
{
get{
return courses;
}
set{
courses = value;
}
}
}
// Client code
Person kent = new Person();
List<Course> s = new List<Course>();
s.Add(new Course("Smalltalk Programming"));
s.Add(new Course("Appreciating Single Malts", true));
kent.Courses = s;
Assert.AreEqual(2, kent.Courses.Count);
Course refact = new Course("Refactoring", true);
kent.Courses.Add(refact);
kent.Courses.Add(new Course("Brutal Sarcasm"));
Assert.AreEqual(4, kent.Courses.Count);
kent.Courses.Remove(refact);
Assert.AreEqual(3, kent.Courses.Count);
int count = 0;
foreach (Course c in kent.Courses)
{
if (c.IsAdvanced)
count++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Advanced courses: " + count);After(Correct):
public class Course
{
public bool IsAdvanced
{
get;
set;
}
public Course(string name, bool isAdvanced = false)
{
// ...
}
}
public class Person
{
private List<Course> courses = new List<Course>();
public ReadOnlyCollection<Course> Courses
{
get{
return new ReadOnlyCollection<Course>(courses);
}
}
public int NumberOfAdvancedCourses
{
get{
int count = 0;
foreach (Course c in courses)
{
if (c.IsAdvanced)
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
public int NumberOfCourses
{
get{
return courses.Count;
}
}
public void InitializeCourses(List<Course> newCourses)
{
Assert.IsTrue(courses.Count == 0);
courses.AddRange(newCourses);
}
public void AddCourse(Course course)
{
courses.Add(course);
}
public void RemoveCourse(Course course)
{
courses.Remove(course);
}
}
// Client code
Person kent = new Person();
kent.AddCourse(new Course("Smalltalk Programming"));
kent.AddCourse(new Course("Appreciating Single Malts", true));
Assert.AreEqual(2, kent.NumberOfCourses);
Course refact = new Course("Refactoring", true);
kent.AddCourse(refact);
kent.AddCourse(new Course("Brutal Sarcasm"));
Assert.AreEqual(4, kent.NumberOfCourses);
kent.RemoveCourse(refact);
Assert.AreEqual(3, kent.NumberOfCourses);
Console.WriteLine("Advanced courses: " + kent.NumberOfAdvancedCourses);
### Refactoring Checklist
## Duplicate Observed Data
## Duplicate Observed Data
![[Pasted image 20230904132911.png]]
### Example:
#### Before(Wrong):
```C#
public partial class IntervalWindow : Form
{
public IntervalWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void CalculateLength()
{
int start = int.Parse(tbStart.Text);
int end = int.Parse(tbEnd.Text);
int length = end - start;
tbLength.Text = length.ToString();
}
private void CalculateEnd()
{
int start = int.Parse(tbStart.Text);
int length = int.Parse(tbLength.Text);
int end = start + length;
tbEnd.Text = end.ToString();
}
private void OnTextBoxLeave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TextBox tb = sender as TextBox;
if (tb != null)
{
int tmp;
if (!int.TryParse(tb.Text, out tmp))
tb.Text = "0";
if (tb == tbStart)
{
CalculateLength();
}
else if (tb == tbEnd)
{
CalculateLength();
}
else if (tb == tbLength)
{
CalculateEnd();
}
}
}
}After(Correct):
public partial class IntervalWindow : Form, IObserver<Interval>
{
private Interval subject;
private string Start
{
get{ return subject.Start; }
set{ subject.Start = value; }
}
private string End
{
get{ return subject.End; }
set{ subject.End = value; }
}
private string Length
{
get{ return subject.Length; }
set{ subject.Length = value; }
}
public IntervalWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
subject = new Interval();
subject.Subscribe(this);
OnNext(subject);
}
public void OnNext(Interval interval)
{
tbStart.Text = interval.Start;
tbEnd.Text = interval.End;
tbLength.Text = interval.Length;
}
// No implementation needed: Method is not called by the Interval class.
public void OnError(Exception e)
{
// No implementation.
}
// No implementation needed: Method is not called by the Interval class.
public void OnCompleted()
{
// No implementation.
}
private void OnTextBoxLeave(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TextBox tb = sender as TextBox;
if (tb != null)
{
int tmp;
if (!int.TryParse(tb.Text, out tmp))
tb.Text = "0";
if (tb == tbStart)
{
this.Start = tb.Text;
subject.CalculateLength();
}
else if (tb == tbEnd)
{
this.End = tb.Text;
subject.CalculateLength();
}
else if (tb == tbLength)
{
this.Length = tb.Text;
subject.CalculateEnd();
}
}
}
}
public class Interval: IObservable<Interval>
{
private List<IObserver<Interval>> observers;
private string start = "0",
end = "0",
length = "0";
public string Start
{
get{ return start; }
set{ OnValueChanged(ref start, value); }
}
public string End
{
get{ return end; }
set{ OnValueChanged(ref end, value); }
}
public string Length
{
get{ return length; }
set{ OnValueChanged(ref length, value); }
}
public Interval()
{
observers = new List<IObserver<Interval>>();
}
private void OnValueChanged(ref string oldValue, string newValue)
{
if (!string.Equals(oldValue, newValue, StringComparison.Ordinal))
{
oldValue = newValue;
foreach (var observer in observers)
observer.OnNext(this);
}
}
public IDisposable Subscribe(IObserver<Interval> observer)
{
if (!observers.Contains(observer))
{
observers.Add(observer);
observer.OnNext(this);
}
return null;
}
public void CalculateLength()
{
int start = int.Parse(this.Start);
int end = int.Parse(this.End);
int length = end - start;
this.Length = length.ToString();
}
public void CalculateEnd()
{
int start = int.Parse(this.Start);
int length = int.Parse(this.Length);
int end = start + length;
this.End = end.ToString();
}
}Refactoring Checklist
Replace Type Code with Subclasses
Example:
Example:
Before(Wrong):
public class Employee
{
// ...
public const int ENGINEER = 0,
SALESMAN = 1,
MANAGER = 2;
public int type;
public int MonthlySalary
{ get; set; }
public int Commission
{ get; set; }
public int Bonus
{ get; set; }
public Employee(int type)
{
this.type = type;
}
public int PayAmount()
{
switch (type)
{
case ENGINEER:
return MonthlySalary;
case SALESMAN:
return MonthlySalary + Commission;
case MANAGER:
return MonthlySalary + Bonus;
default:
throw new Exception("Incorrect Employee Code");
}
}
}After(Correct):
public abstract class Employee
{
// ...
public const int ENGINEER = 0,
SALESMAN = 1,
MANAGER = 2;
public abstract int Type
{ get; }
public int MonthlySalary
{ get; set; }
public static Employee Create(int type)
{
switch (type)
{
case ENGINEER:
return new Engineer();
case SALESMAN:
return new Salesman();
case MANAGER:
return new Manager();
default:
throw new Exception("Incorrect Employee Code");
}
}
public virtual int PayAmount()
{
return MonthlySalary;
}
}
public class Engineer: Employee
{
public override int Type
{
get{ return Employee.ENGINEER; }
}
}
public class Salesman: Employee
{
public override int Type
{
get{ return Employee.SALESMAN; }
}
public int Commission
{ get; set; }
public override int PayAmount()
{
return MonthlySalary + Commission;
}
}
public class Manager: Employee
{
public override int Type
{
get{ return Employee.MANAGER; }
}
public int Bonus
{ get; set; }
public override int PayAmount()
{
return MonthlySalary + Bonus;
### Refactoring Checklist
### Refactoring Checklist
## Replace Type Code with State/Strategy
### Example:
![[Pasted image 20230904154438.png]]
### Example:
#### Before(Wrong):
```C#
public class Employee
{
// ...
public const int ENGINEER = 0,
SALESMAN = 1,
MANAGER = 2;
public int type;
public int MonthlySalary
{ get; set; }
public int Commission
{ get; set; }
public int Bonus
{ get; set; }
public Employee(int type)
{
this.type = type;
}
public int PayAmount()
{
switch (type)
{
case ENGINEER:
return MonthlySalary;
case SALESMAN:
return MonthlySalary + Commission;
case MANAGER:
return MonthlySalary + Bonus;
default:
throw new Exception("Incorrect Employee Code");
}
}
}After(Correct):
public class Employee
{
// ...
private EmployeeType type;
public int EmployeeCode
{
get{ return type.EmployeeCode; }
set{ type = EmployeeType.Create(value); }
}
public int MonthlySalary
{ get; set; }
public int Commission
{ get; set; }
public int Bonus
{ get; set; }
public Employee(int employeeCode)
{
this.type = EmployeeType.Create(employeeCode);
}
public int PayAmount()
{
return type.PayAmount(this);
}
}
public abstract class EmployeeType
{
public const int ENGINEER = 0,
SALESMAN = 1,
MANAGER = 2;
public abstract int EmployeeCode
{ get; }
public static EmployeeType Create(int code)
{
switch (code)
{
case ENGINEER:
return new Engineer();
case SALESMAN:
return new Salesman();
case MANAGER:
return new Manager();
default:
throw new Exception("Incorrect Employee Code");
}
}
public abstract int PayAmount(Employee employee);
}
public class Engineer: EmployeeType
{
public override int EmployeeCode
{
get{ return EmployeeType.ENGINEER; }
}
public override int PayAmount(Employee employee)
{
return employee.MonthlySalary;
}
}
public class Salesman: EmployeeType
{
public override int EmployeeCode
{
get{ return EmployeeType.SALESMAN; }
}
public override int PayAmount(Employee employee)
{
return employee.MonthlySalary + employee.Commission;
}
}
public class Manager: EmployeeType
{
public override int EmployeeCode
{
get{ return EmployeeType.MANAGER; }
}
public override int PayAmount(Employee employee)
{
return employee.MonthlySalary + employee.Bonus;
}
}Introduce Null Object
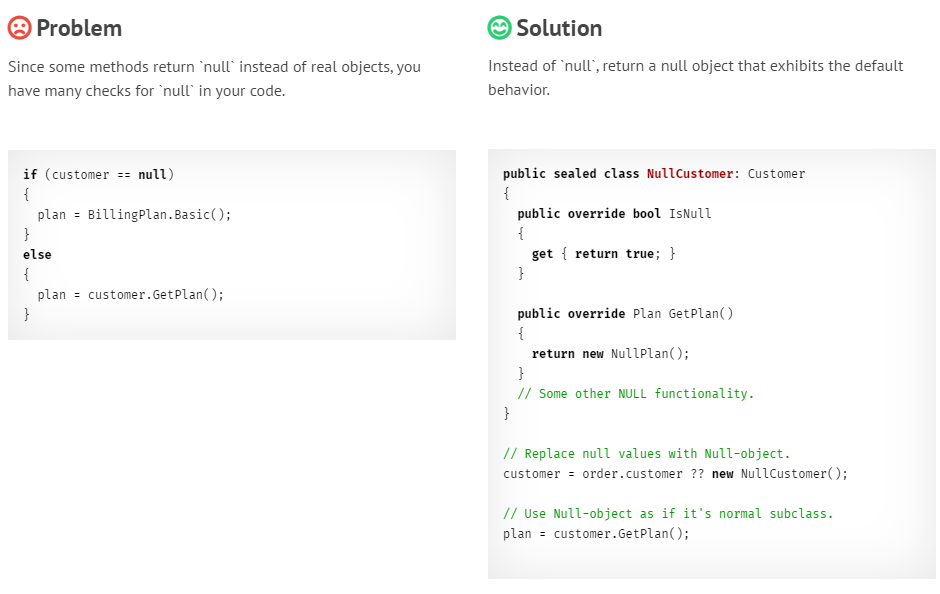
Example:
Before(Wrong):
public class Company
{
//…
private Customer customer;
public Customer Customer
{
get{ return customer; }
}
}
public class Customer
{
public string Name {
//…
}
public BillingPlan GetPlan() {
//…
}
public PaymentHistory GetHistory() {
//…
}
}
public class PaymentHistory
{
public int WeeksDelinquentInLastYear {
//…
}
}
// Somewhere in client code
Customer customer = site.Customer;
string customerName;
if (customer == null)
customerName = "N/A";
else
customerName = customer.Name;
//…
BillingPlan plan;
if (customer == null)
plan = BillingPlan.Basic();
else
plan = customer.GetPlan();
//…
int weeksDelinquent;
if (customer == null)
weeksDelinquent = 0;
else
weeksDelinquent = customer.GetHistory().WeeksDelinquentInLastYear;After(Correct):
public class Company
{
//…
private Customer customer;
public Customer Customer
{
get{ return customer ?? Customer.NewNull(); }
}
}
public class Customer
{
public virtual bool IsNull
{
get{ return false; }
}
public virtual string Name {
//…
}
public static Customer NewNull()
{
return new NullCustomer();
}
public virtual BillingPlan GetPlan() {
//…
}
public virtual PaymentHistory GetHistory() {
//…
}
}
public class NullCustomer: Customer
{
public override bool IsNull
{
get{ return true; }
}
public override string Name
{
get{ return "N/A"; }
}
public override BillingPlan GetPlan()
{
return BillingPlan.Basic();
}
public override PaymentHistory GetHistory()
{
return PaymentHistory.NewNull();
}
}
public class PaymentHistory
{
public virtual bool IsNull
{
get{ return false; }
}
public virtual int WeeksDelinquentInLastYear {
//…
}
public static PaymentHistory NewNull()
{
return new NullPaymentHistory();
}
}
public class NullPaymentHistory: PaymentHistory
{
public override bool IsNull
{
get{ return true; }
}
public override int WeeksDelinquentInLastYear
{
get{ return 0; }
}
}
// Somewhere in client code
Customer customer = site.Customer;
string customerName = customer.Name;
//…
BillingPlan plan = customer.GetPlan();
//…
int weeksDelinquent = customer.GetHistory().WeeksDelinquentInLastYear;
### Refactoring Checklist
## Replace Constructor with Factory Method
## Replace Constructor with Factory Method
## Extract Subclass
## Extract Subclass
### Example
### Example
#### Before(Wrong):
``` C#
public class JobItem
{
private int unitPrice;
public int Quantity
{ get; private set; }
public bool IsLabor
{ get; private set; }
public Employee Employee
{ get; private set; }
public JobItem(int quantity, int unitPrice, bool isLabor, Employee employee)
{
this.Quantity = quantity;
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
this.IsLabor = isLabor;
this.Employee = employee;
}
public int GetTotalPrice()
{
return Quantity * GetUnitPrice();
}
public int GetUnitPrice()
{
return IsLabor ? Employee.Rate : unitPrice;
}
}
public class Employee
{
public int Rate
{ get; private set; }
public Employee(int rate)
{
Rate = rate;
}
}
// Somewhere in client code
Employee kent = new Employee(50);
JobItem j1 = new JobItem(5, 0, true, kent);
JobItem j2 = new JobItem(15, 10, false, null);
int total = j1.GetTotalPrice() + j2.GetTotalPrice();After(Correct):
public abstract class JobItem
{
public int Quantity
{ get; private set; }
protected JobItem(int quantity)
{
this.Quantity = quantity;
}
public int GetTotalPrice()
{
return Quantity * GetUnitPrice();
}
public abstract int GetUnitPrice();
}
public class PartsItem: JobItem
{
private int unitPrice;
public PartsItem(int quantity, int unitPrice): base(quantity)
{
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
}
public override int GetUnitPrice()
{
return unitPrice;
}
}
public class LaborItem: JobItem
{
public Employee Employee
{ get; private set; }
public LaborItem(int quantity, Employee employee): base(quantity)
{
Employee = employee;
}
public override int GetUnitPrice()
{
return Employee.Rate;
}
}
public class Employee
{
public int Rate
{ get; private set; }
public Employee(int rate)
{
Rate = rate;
}
}
// Somewhere in client code
Employee kent = new Employee(50);
JobItem j1 = new LaborItem(5, kent);
JobItem j2 = new PartsItem(15, 10);
### Refactoring Checklist
### Refactoring Checklist
![[Pasted image 20230905142212.png]]