link: Load Balancing
Load Balancing Algorithms
Diagram
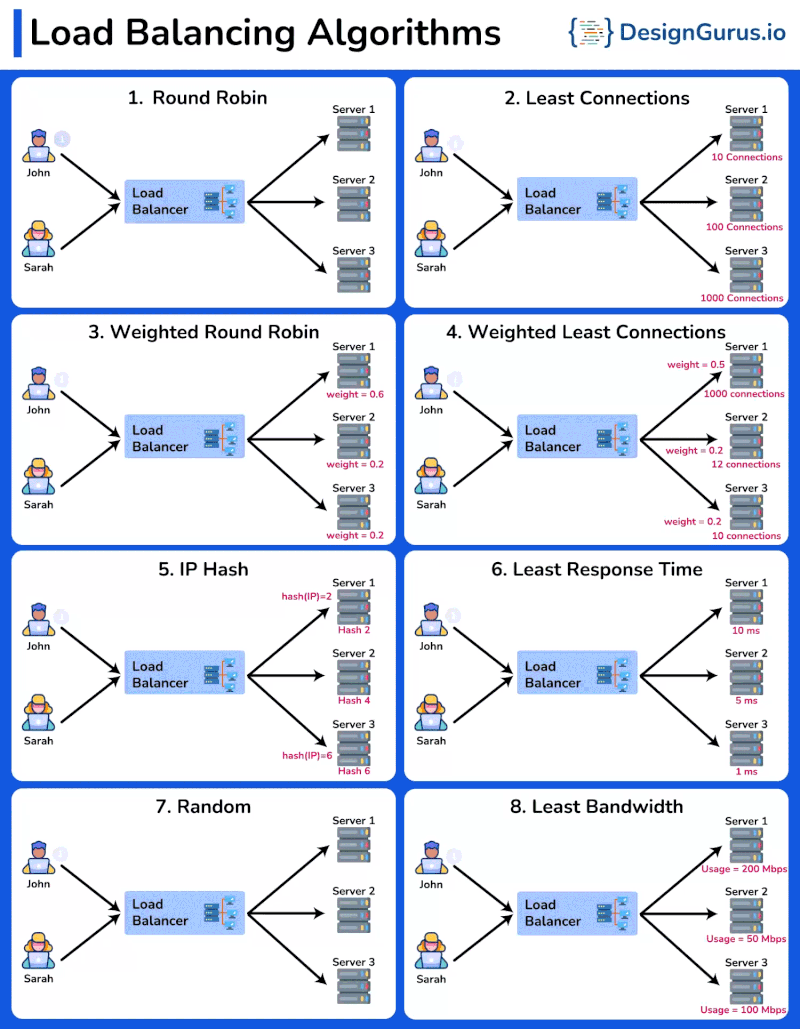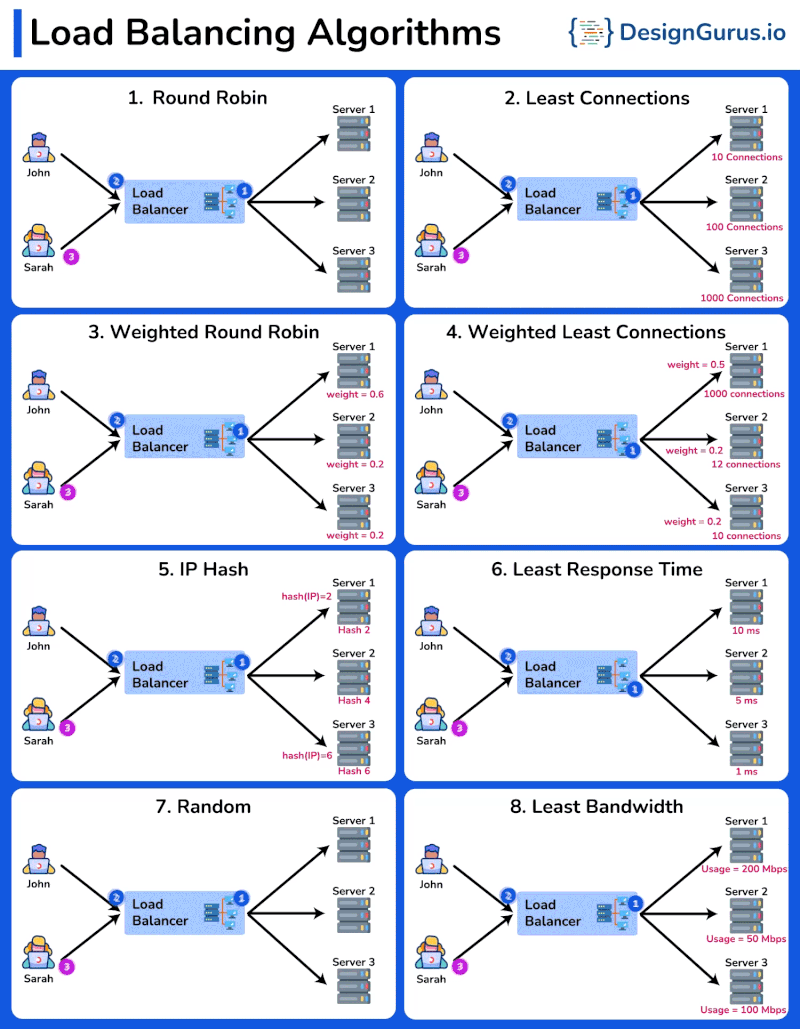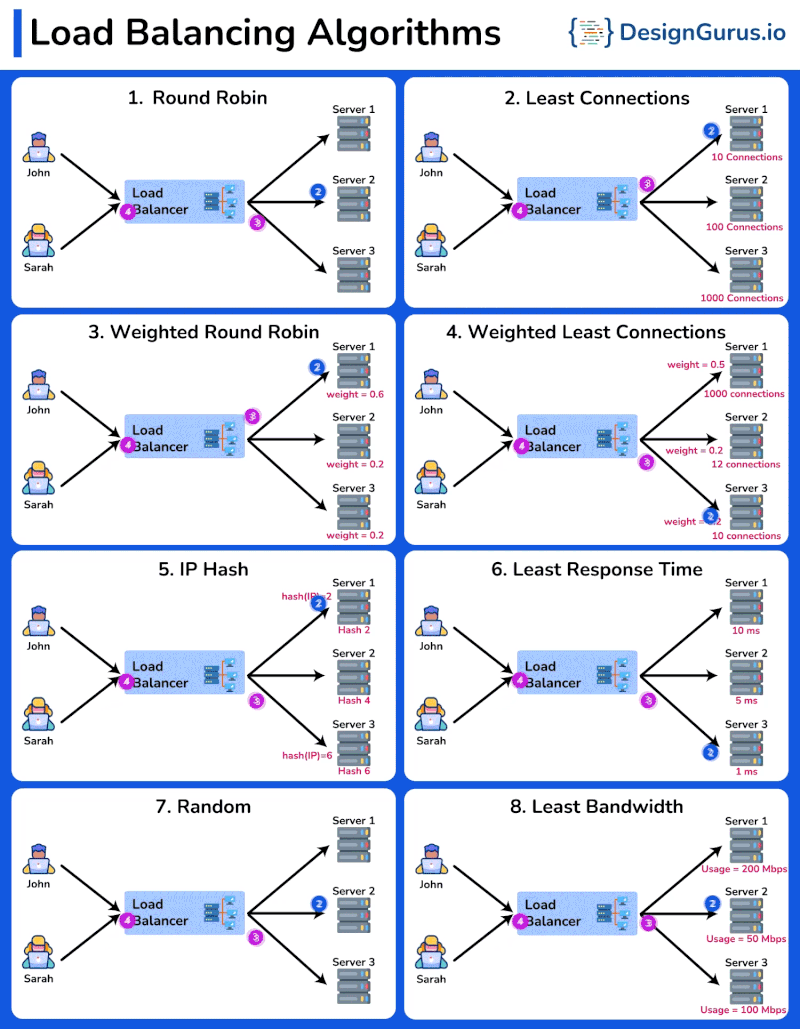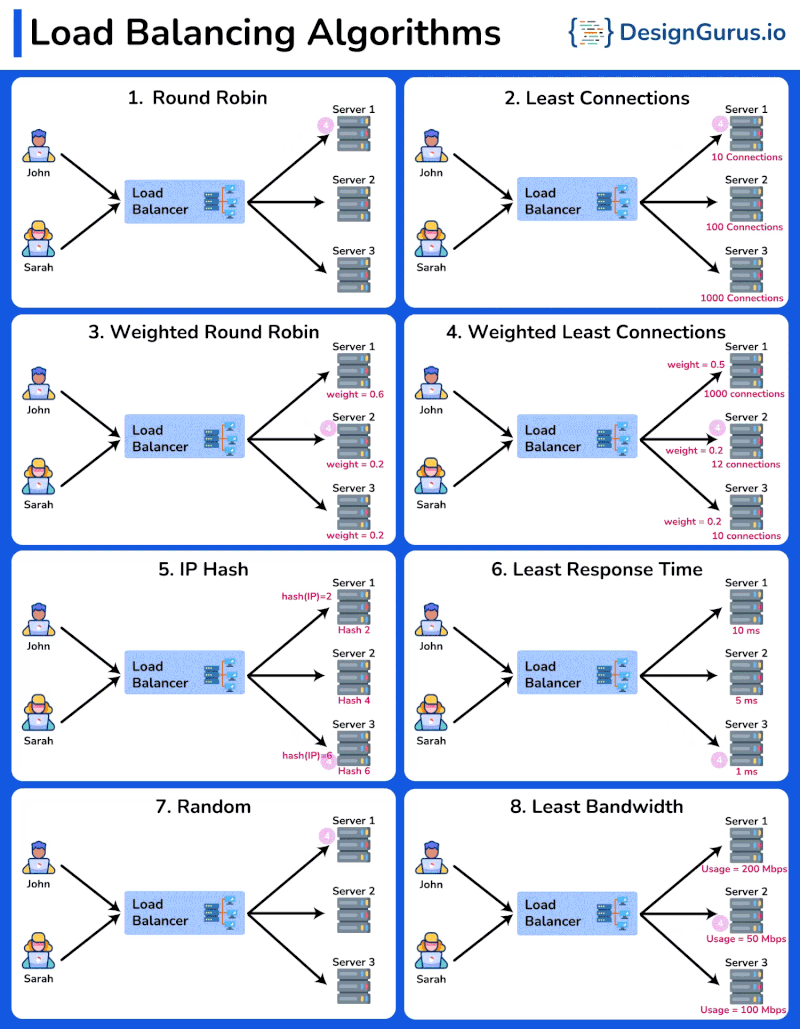
Overview
Load balancing algorithms distribute incoming network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed. By using these algorithms, systems can achieve high availability, scalability, and reliability.
Summary of Load Balancing Algorithms
Summary
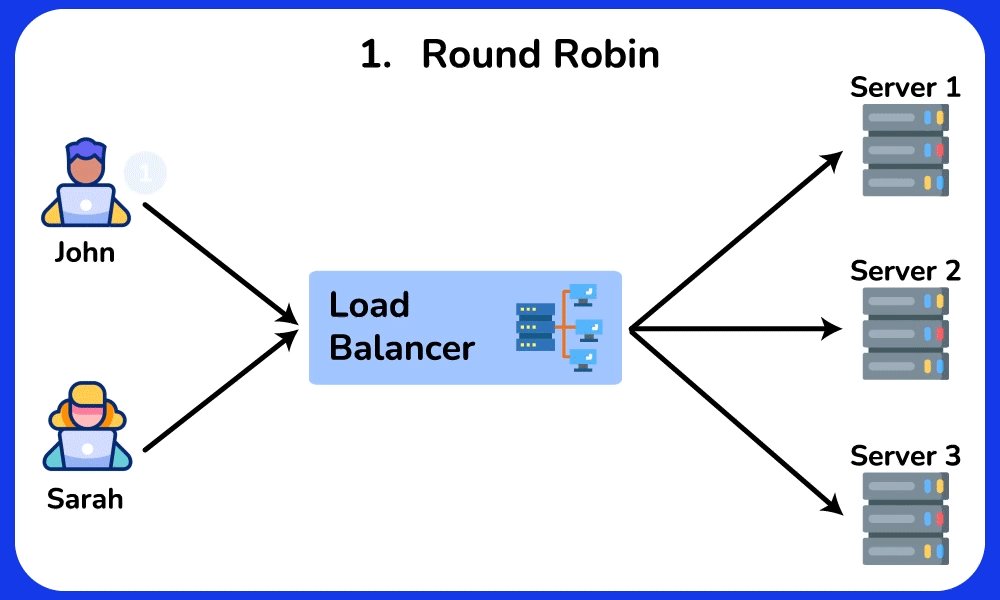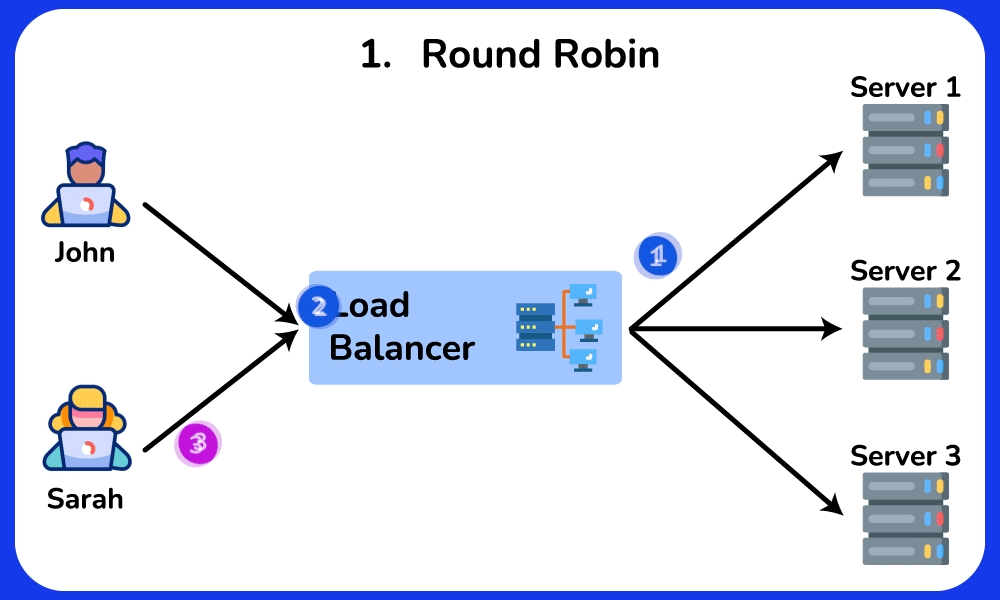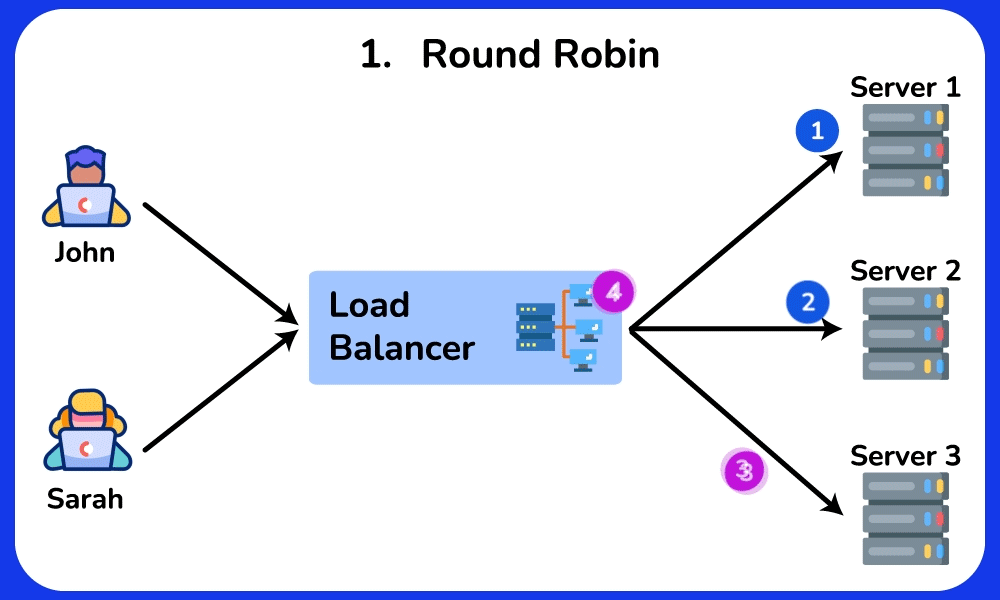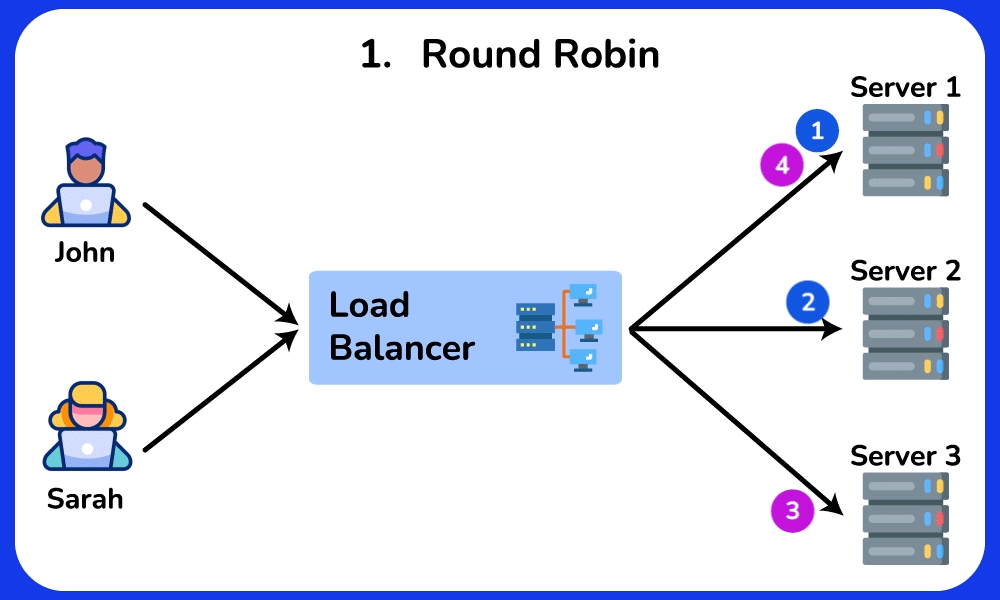
- Round Robin: Distributes requests sequentially among servers.
- Least Connections: Sends requests to the server with the fewest active connections.
- Weighted Round Robin: Similar to Round Robin, but assigns a weight to each server based on its capacity. Servers with higher weights receive more requests.
- Weighted Least Connections: Directs traffic to servers with fewer active connections, considering the weight of each server.
- IP Hash: Distributes requests based on the client IP address, ensuring that the same client is always directed to the same server.
- Least Response Time: Sends requests to the server with the fastest response time.
- Random: Distributes requests to servers randomly, providing a simple way to balance load.
- Least Bandwidth: Directs traffic to the server currently handling the least amount of network traffic.
- Custom Load: Uses custom metrics or algorithms to distribute traffic based on specific needs or conditions.
Details of Load Balancing Algorithms
Round Robin
Details
Description: Distributes requests sequentially among servers.
Use Case: Suitable for evenly distributing load in environments where servers have similar capabilities and performance.
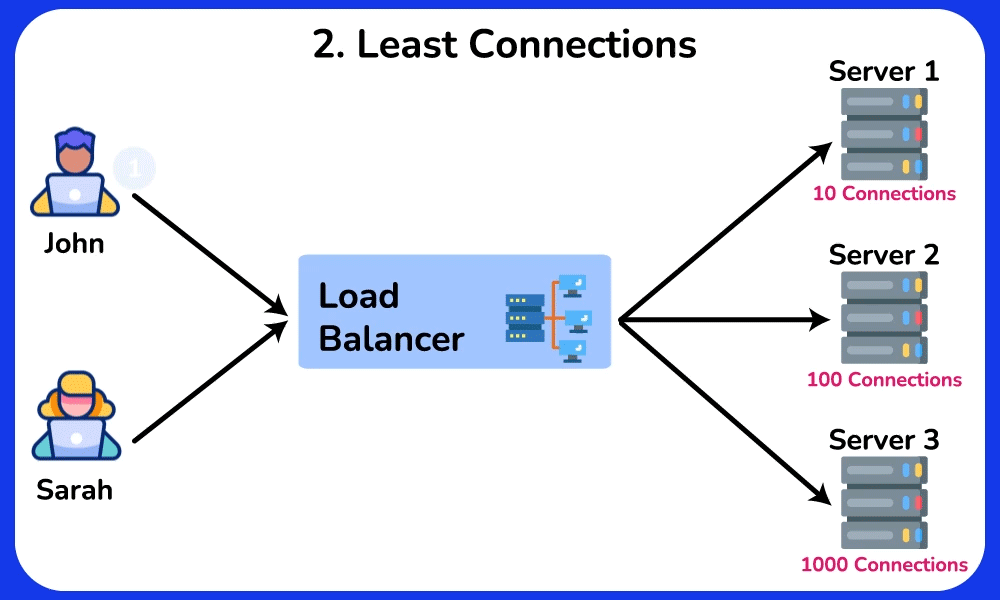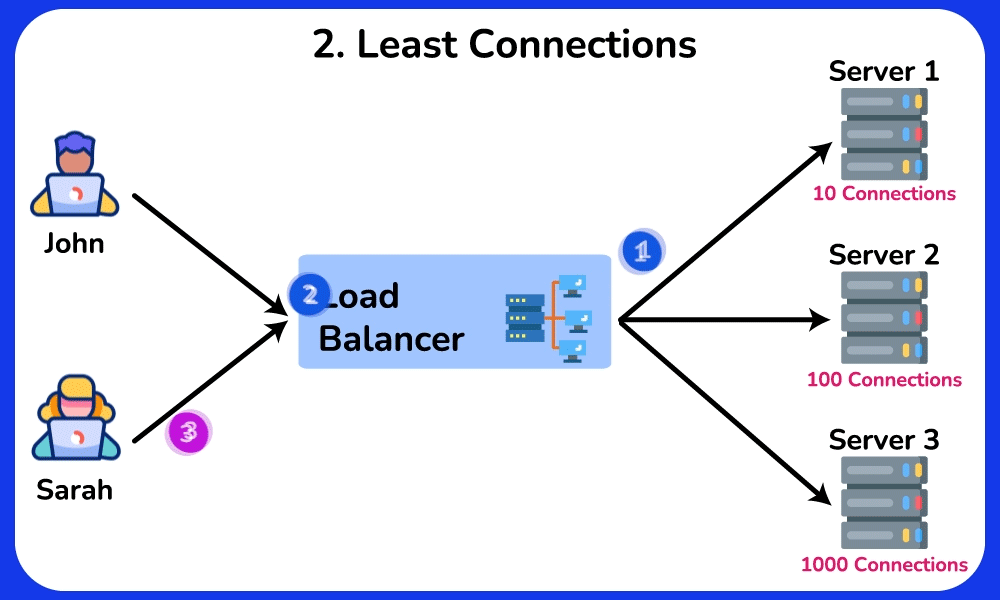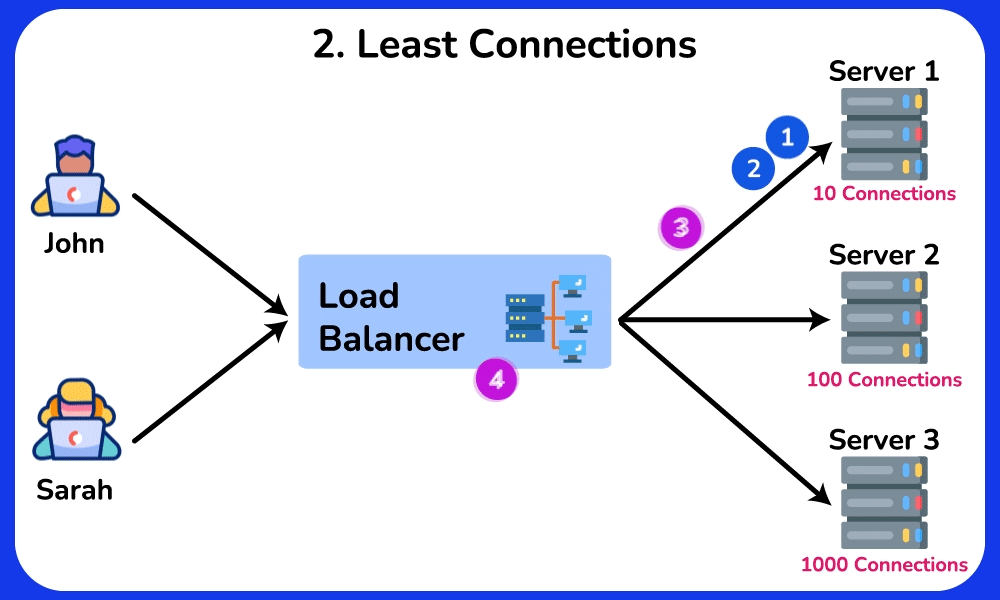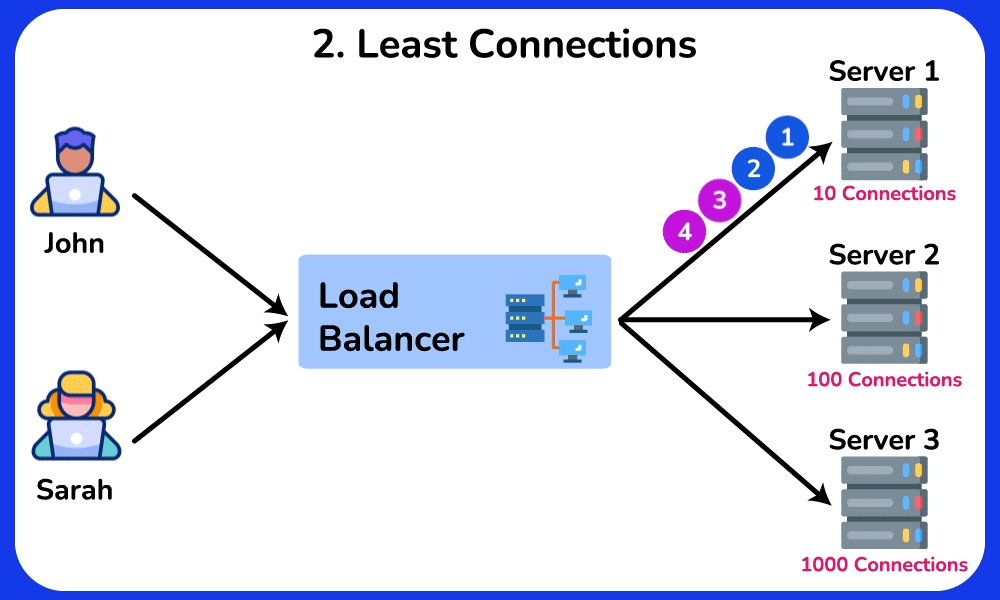
Least Connections
Details
Description: Sends requests to the server with the fewest active connections.
Use Case: Ideal for scenarios where server load varies significantly, ensuring that the least busy server handles new requests.
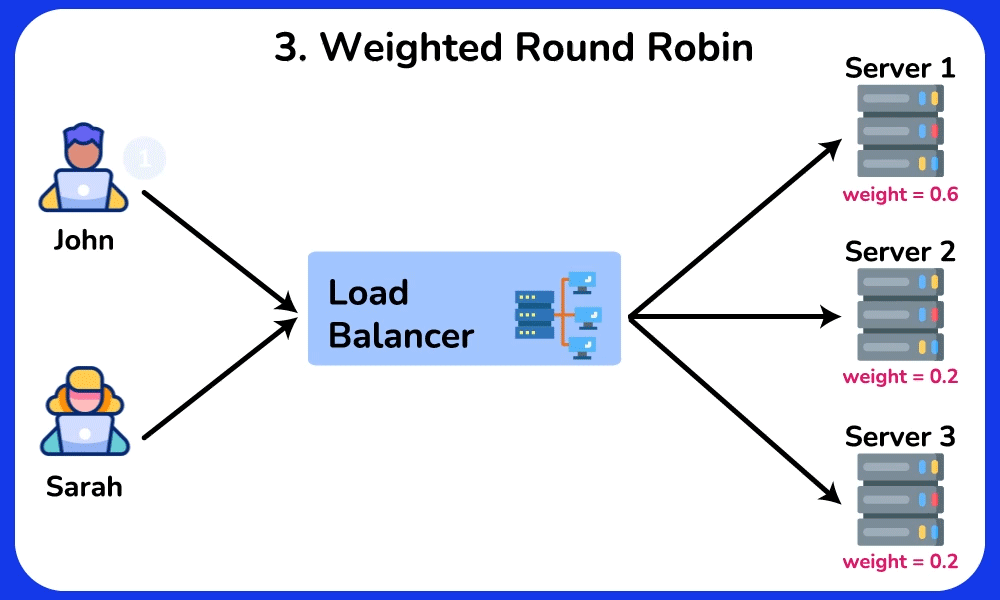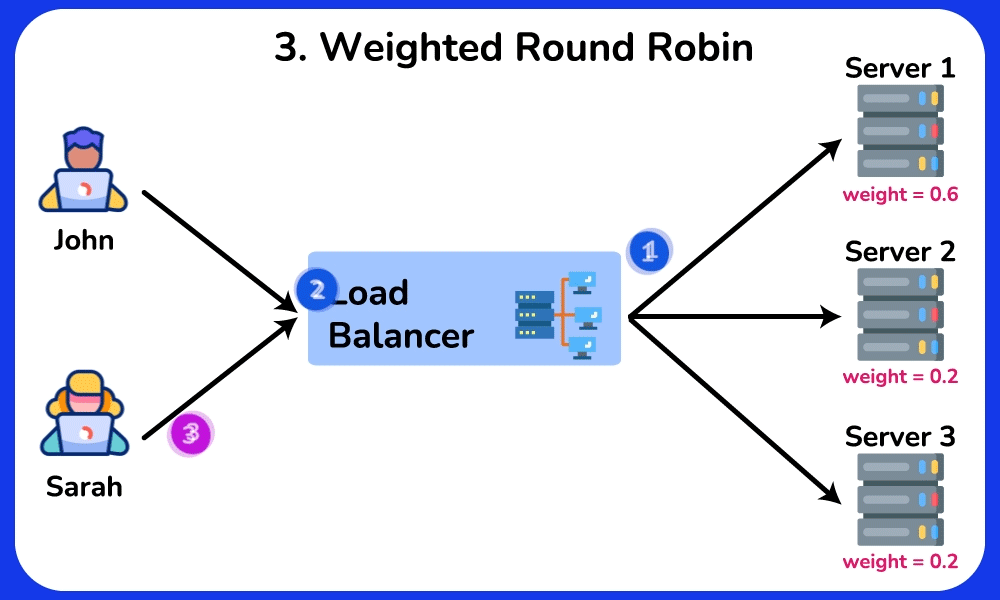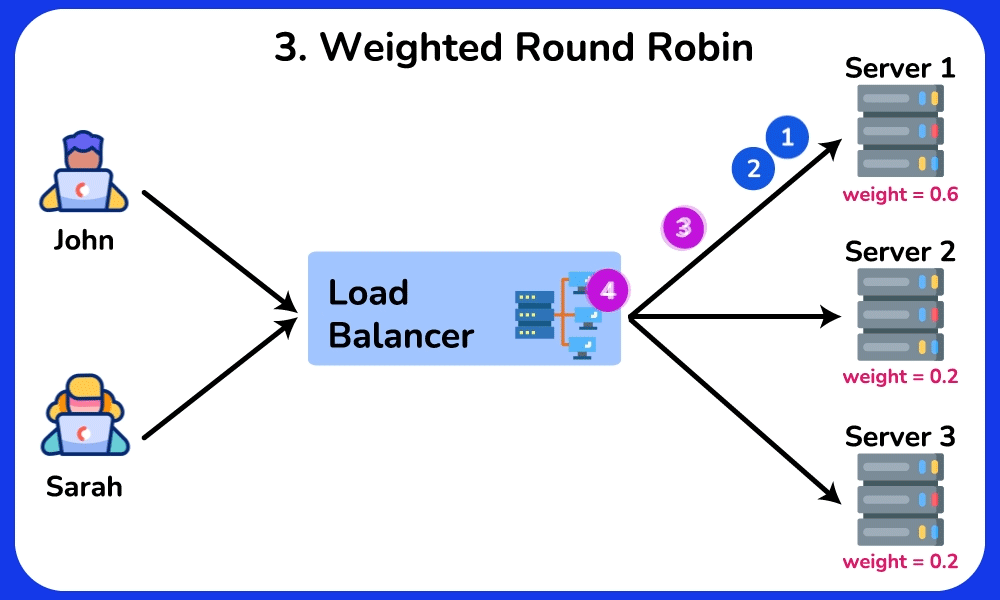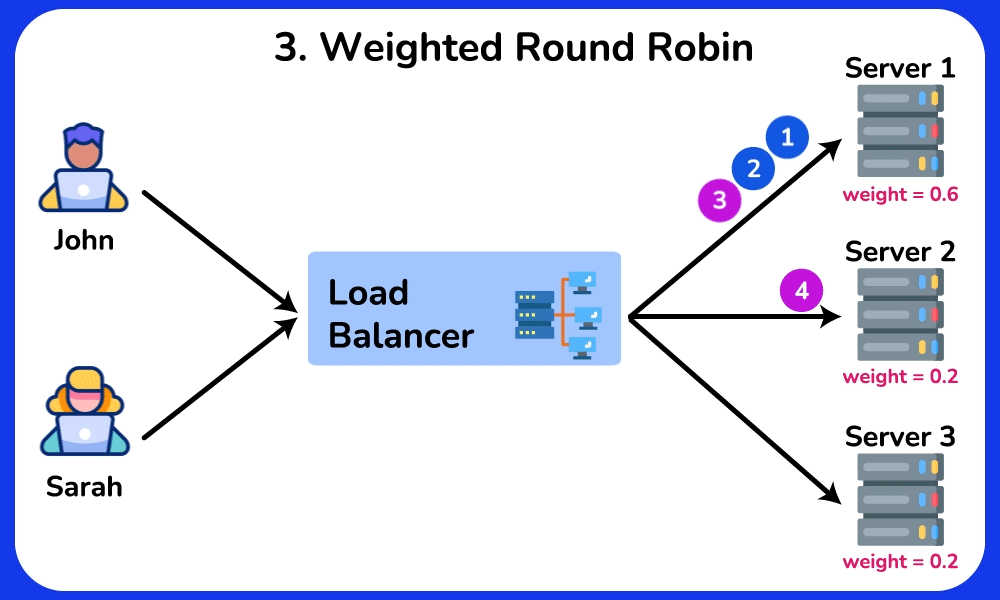
Weighted Round Robin
Details
Description: Similar to Round Robin, but assigns a weight to each server based on its capacity. Servers with higher weights receive more requests.
Use Case: Useful when servers have different processing capacities, ensuring that more powerful servers handle a larger share of the load.
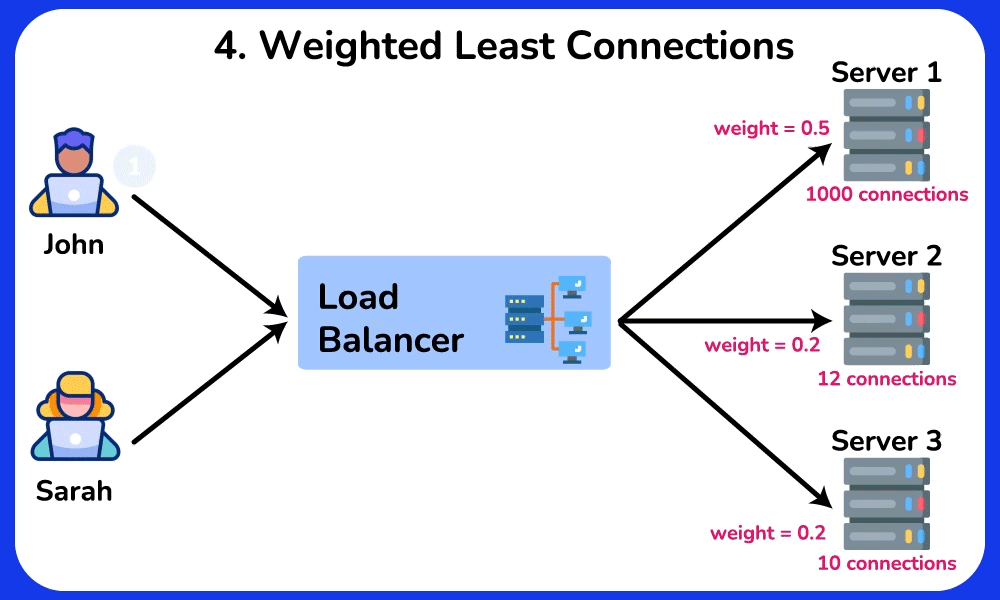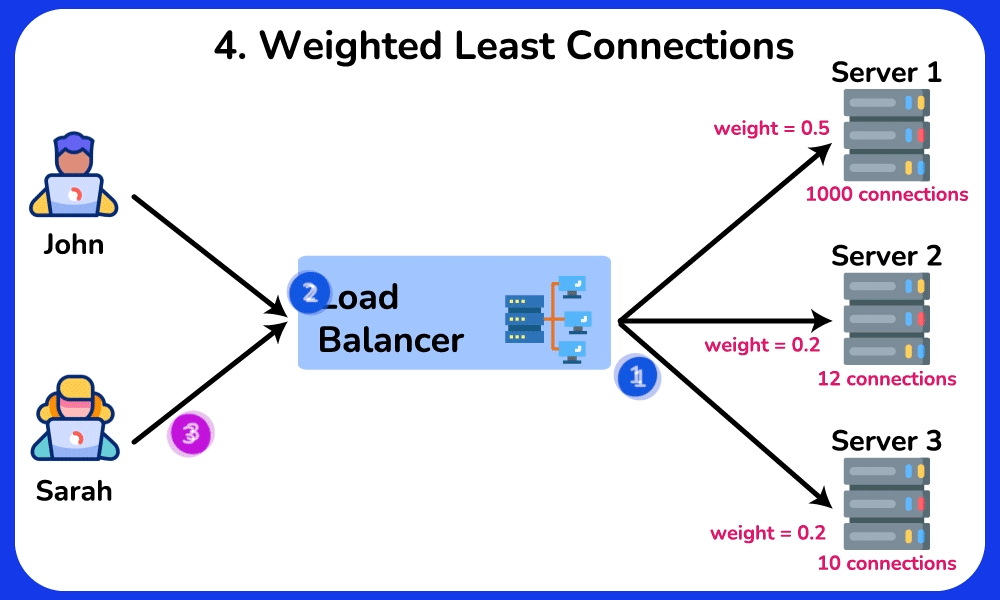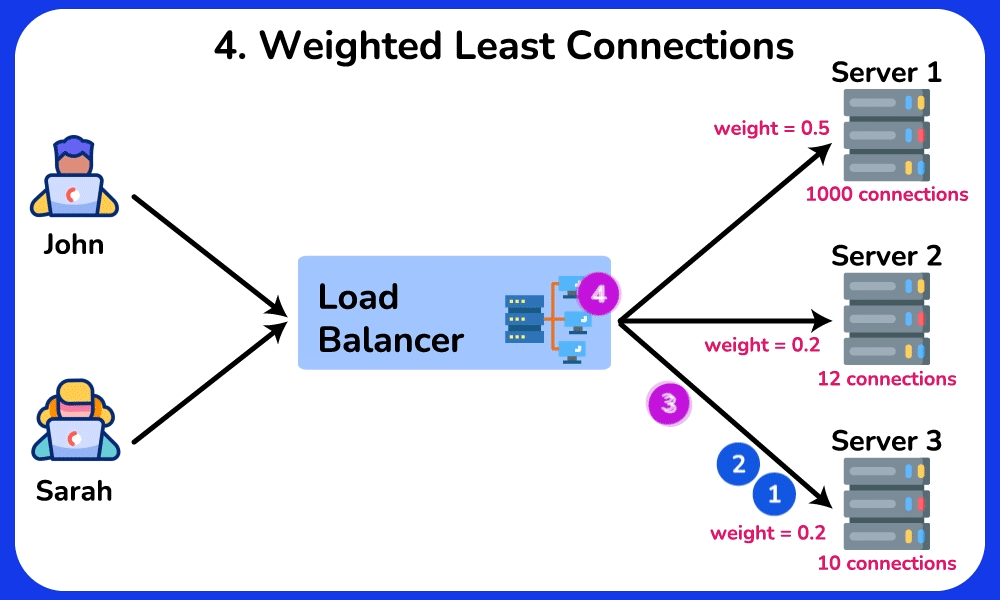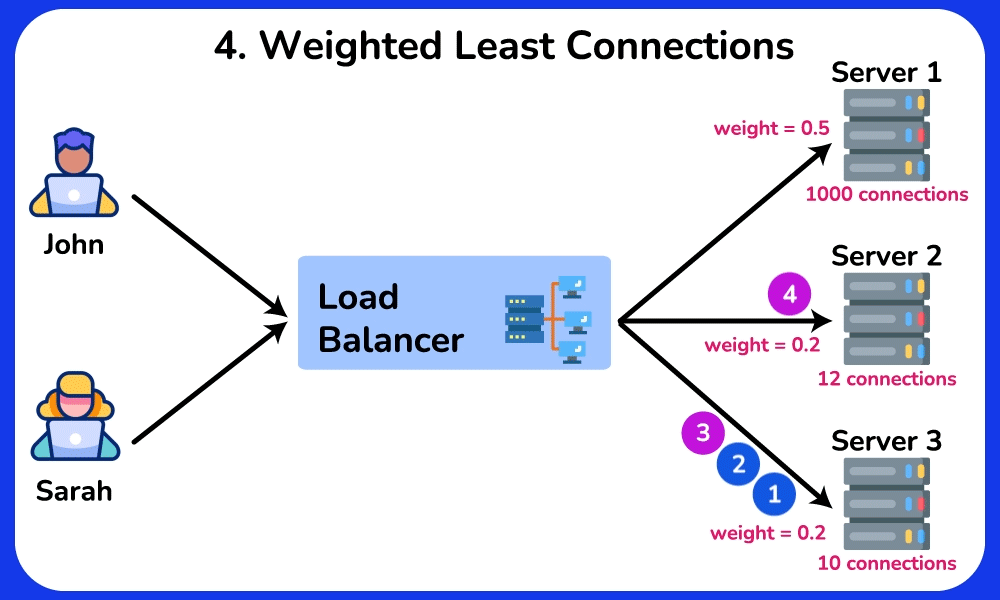
Weighted Least Connections
Details
Description: Directs traffic to servers with fewer active connections, considering the weight of each server.
Use Case: Effective in environments with servers of varying capacities and loads, balancing traffic based on both load and server capability.
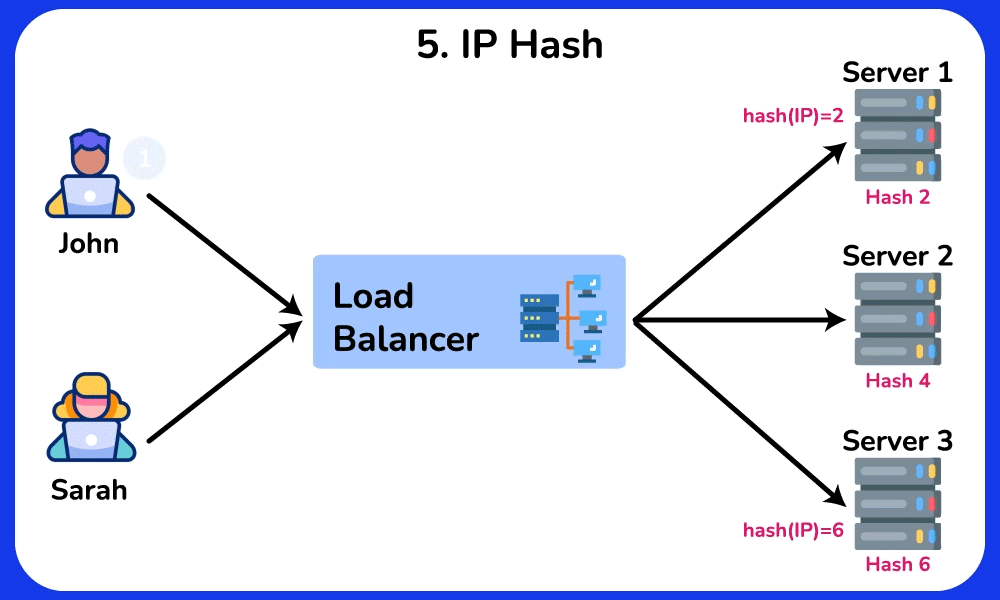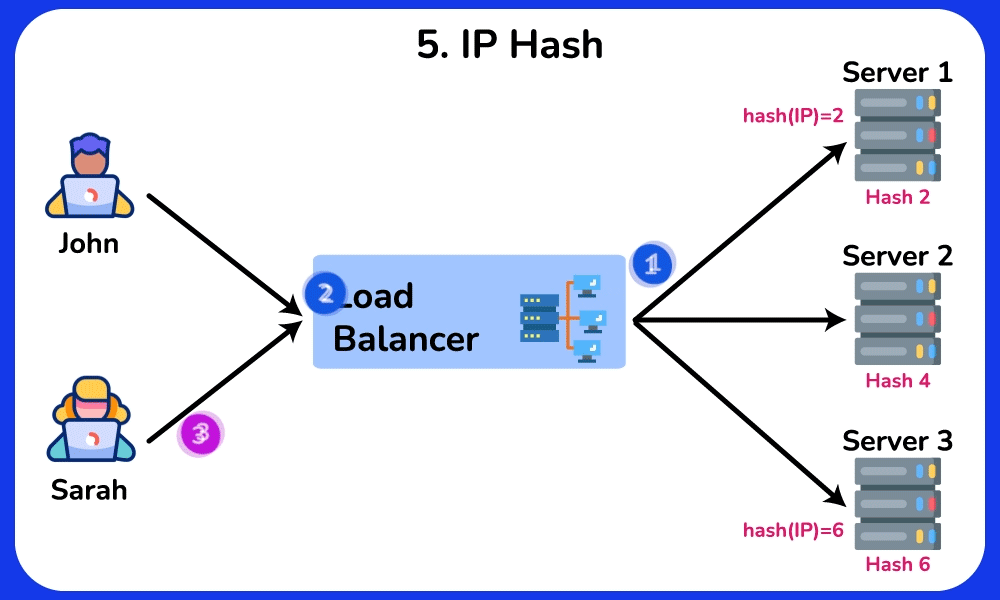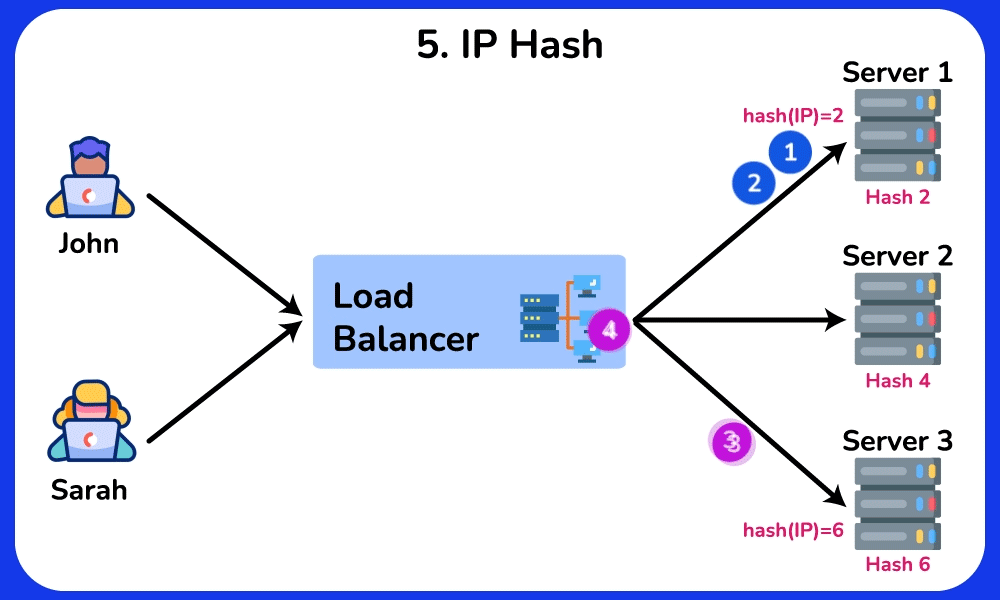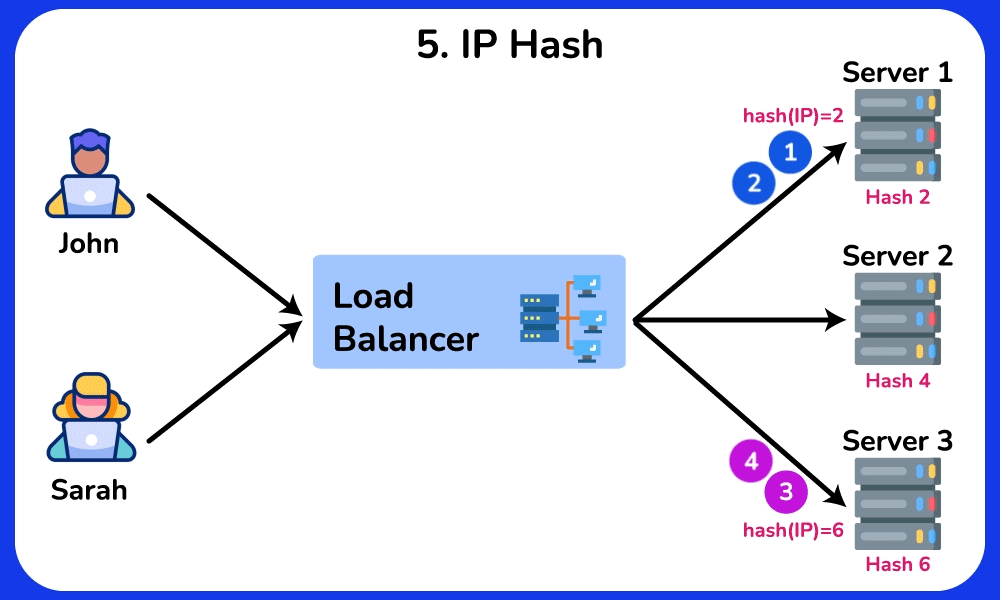
IP Hash
Details
Description: Distributes requests based on the client IP address, ensuring that the same client is always directed to the same server.
Use Case: Suitable for applications that require session persistence, such as e-commerce websites where user sessions need to be maintained.
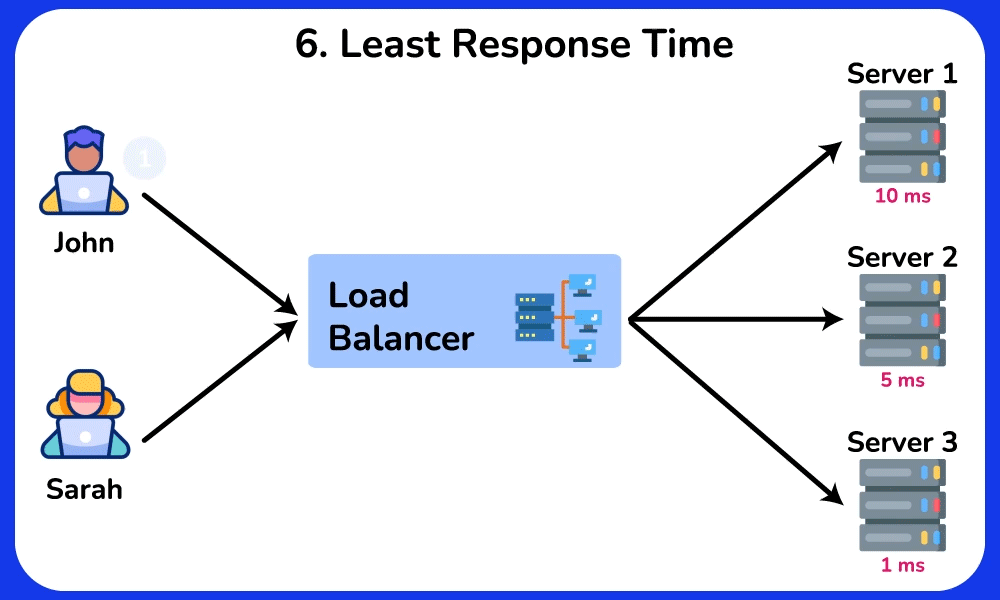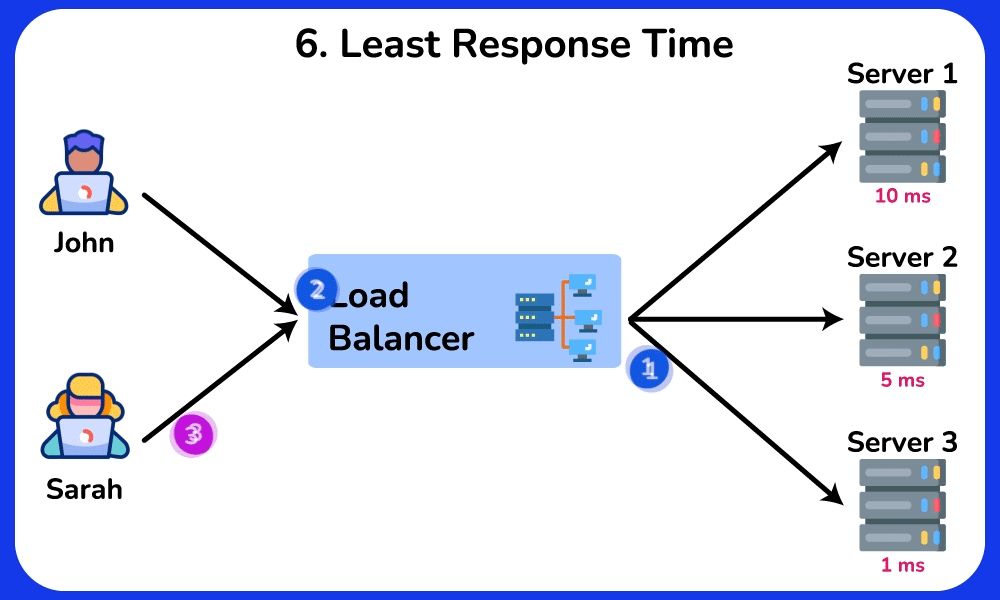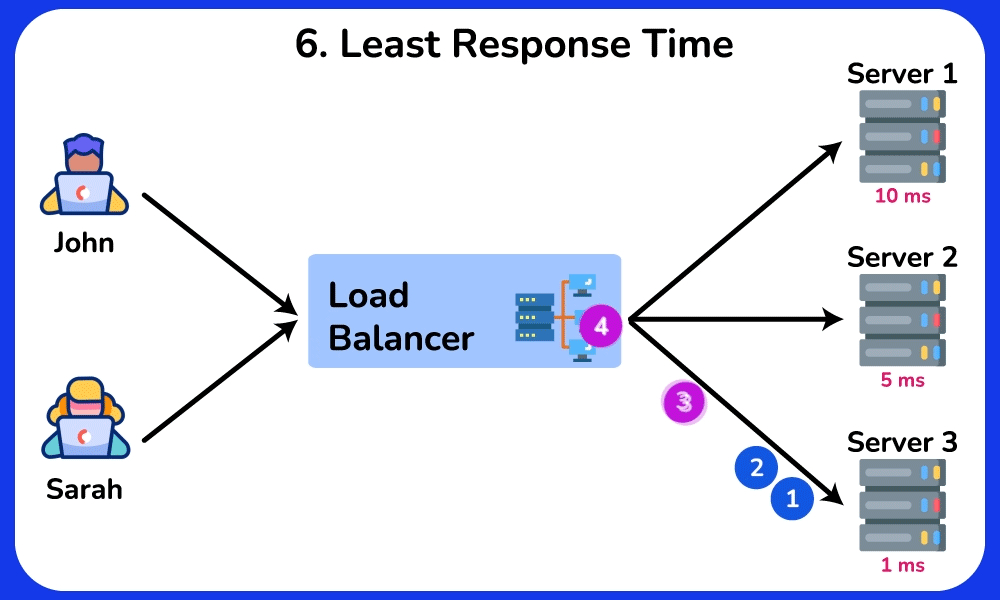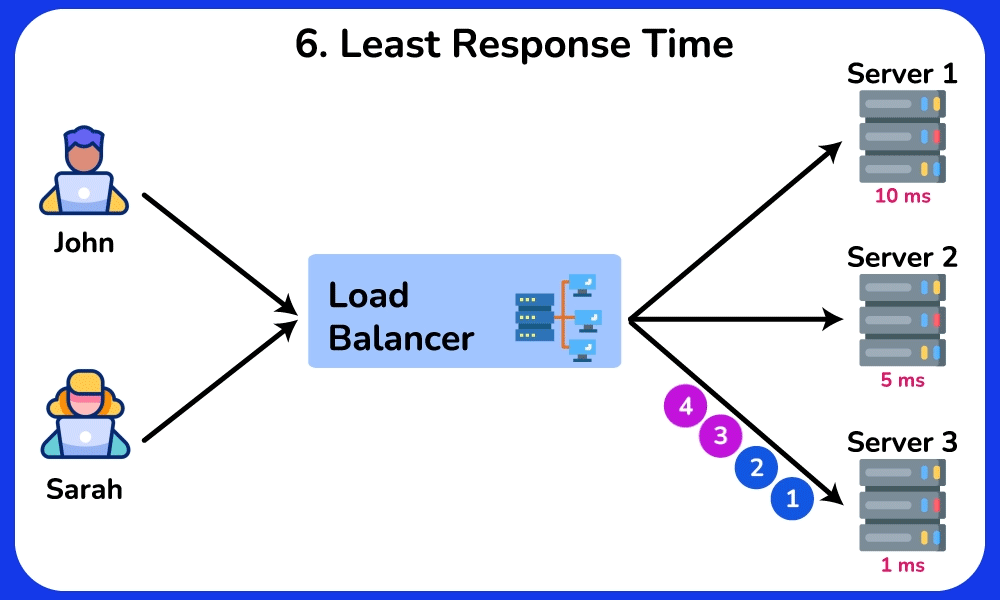
Least Response Time
Details
Description: Sends requests to the server with the fastest response time.
Use Case: Ideal for real-time applications where response time is critical, ensuring that the quickest server handles the requests.
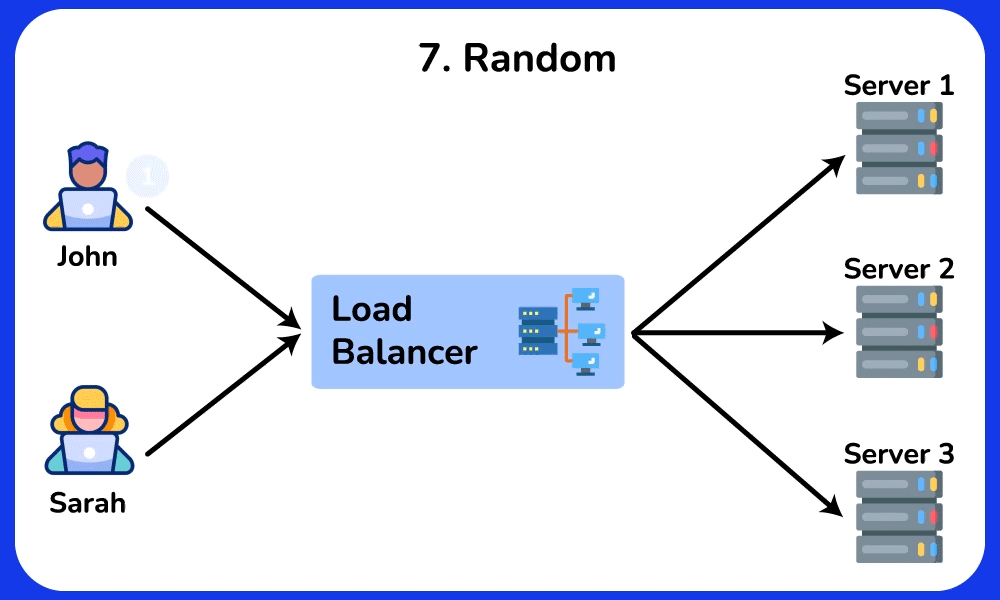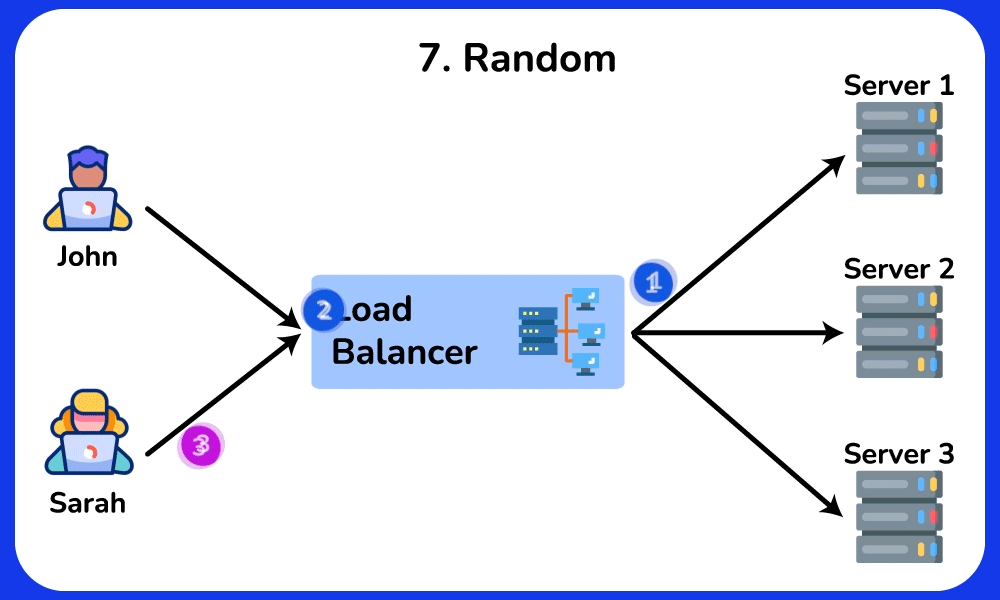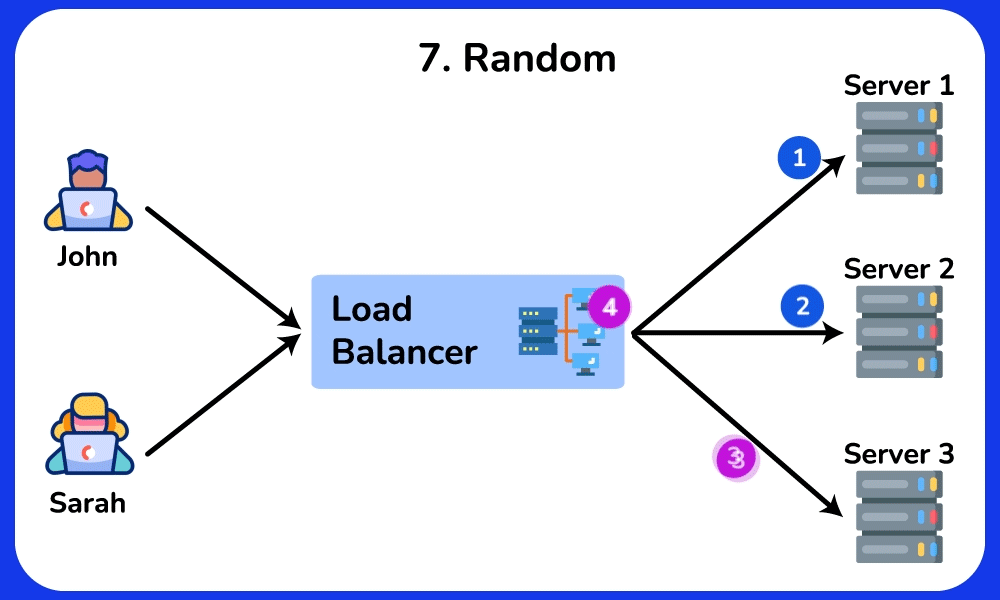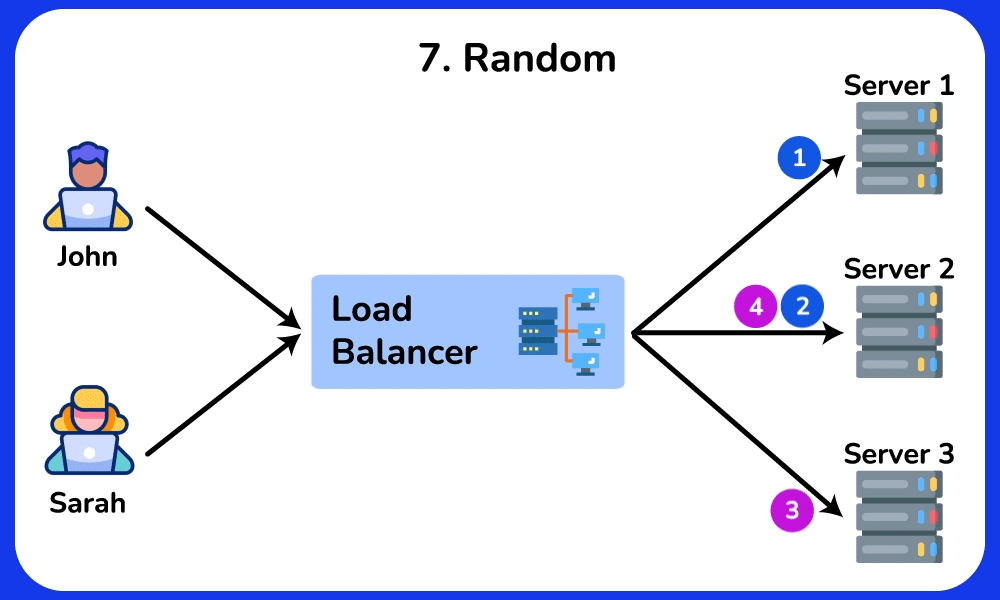
Random
Details
Description: Distributes requests to servers randomly, providing a simple way to balance load.
Use Case: Useful for simple load balancing scenarios where advanced algorithms are not necessary.
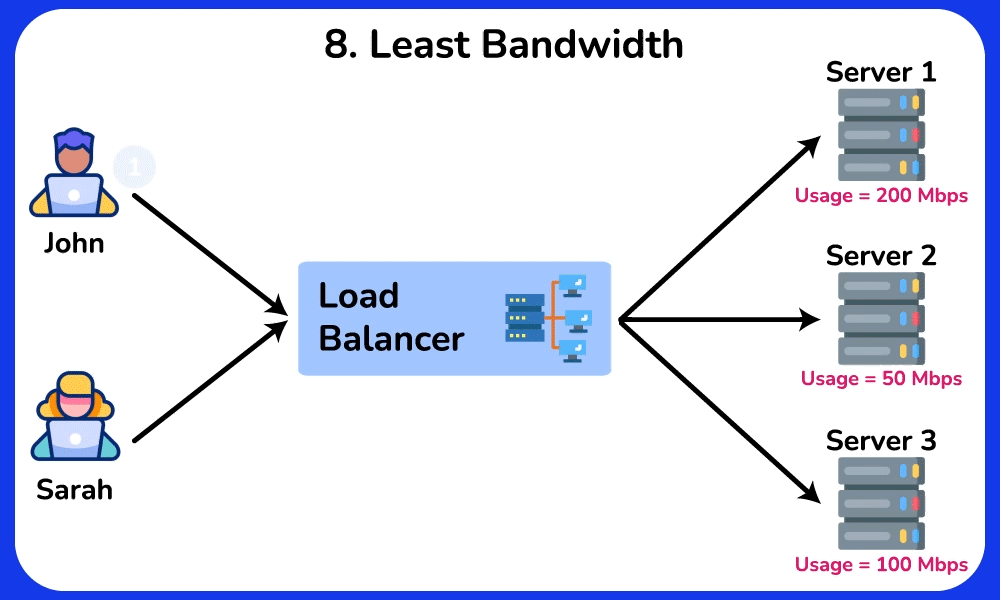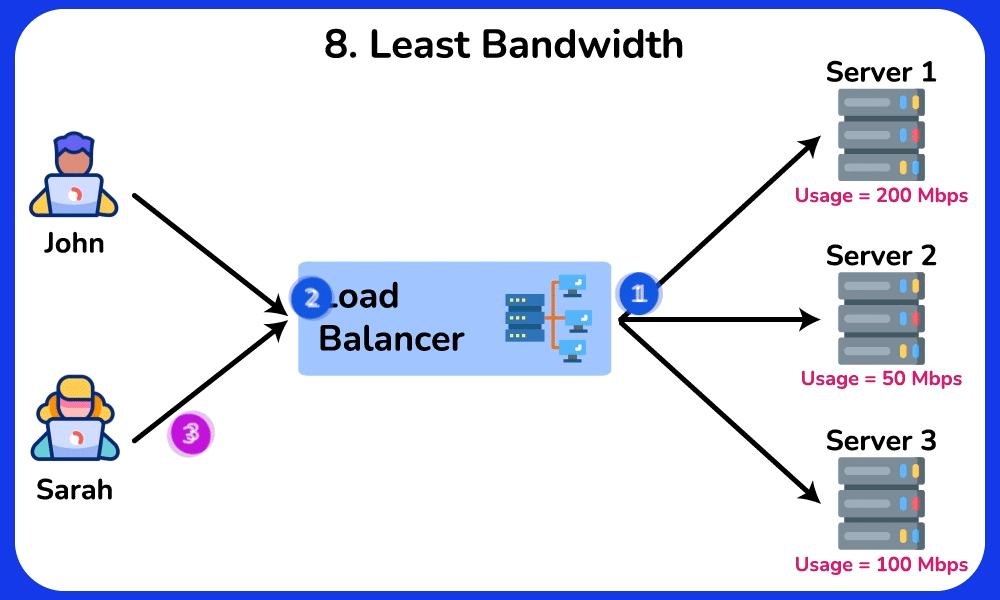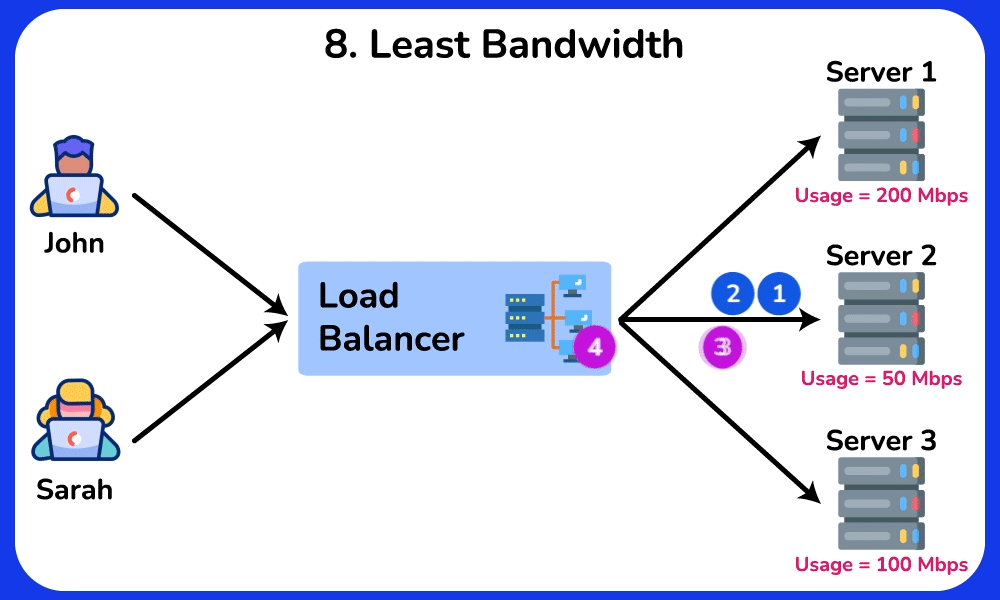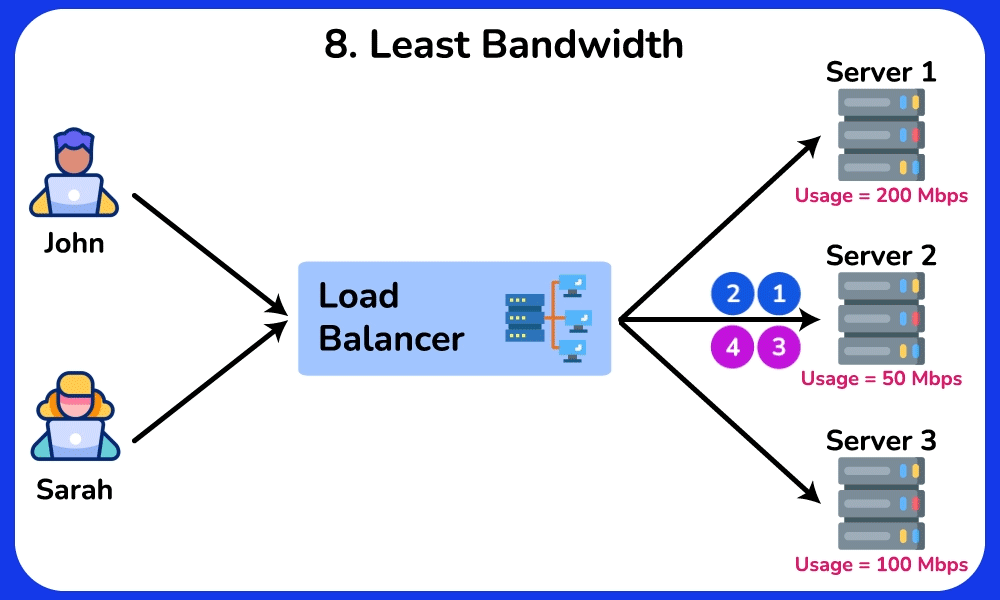
Least Bandwidth
Details
Description: Directs traffic to the server currently handling the least amount of network traffic.
Use Case: Effective for applications where network traffic load is a critical factor, ensuring that the least congested server handles new requests.
Custom Load
Details
Description: Uses custom metrics or algorithms to distribute traffic based on specific needs or conditions.
Use Case: Suitable for specialized environments where standard algorithms do not meet the unique requirements of the application or infrastructure.