link: Microservice Architecture
Database per Service
Diagram
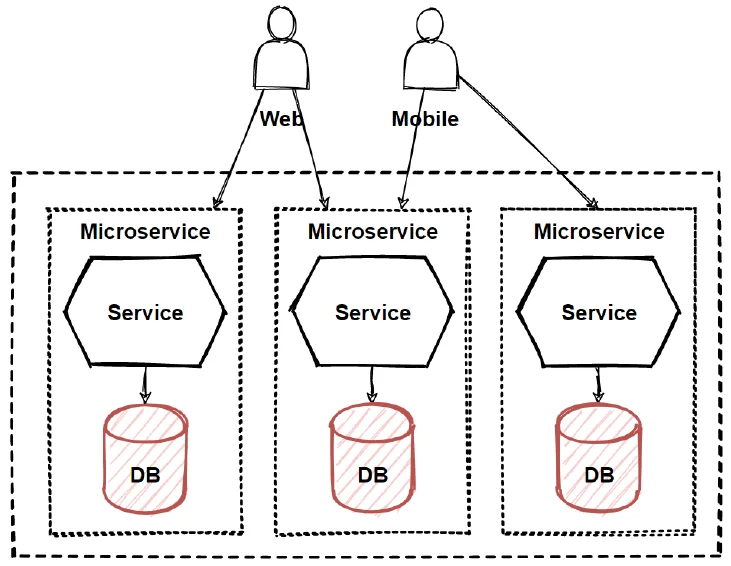
Overview
In Microservices architecture, each microservice managing its own database is a foundational pattern called “Database per Service.” This pattern addresses the challenges of data management in distributed systems by ensuring that each service has exclusive control over its database.
Abstract
The Database per Service pattern enhances the autonomy and scalability of microservices by allowing each service to manage its own database schema and lifecycle independently.
Content
Key Concepts
The Database per Service pattern is critical for achieving true modularity and independence among services in a microservices architecture. Here are the core principles:
Important
- Service Autonomy: Each microservice owns its private database, which can only be accessed directly by the service itself. This encapsulates the database schema and ensures that the data models can evolve without affecting other services.
- Data Decentralization: Unlike monolithic architectures that might use a single database for all components, this pattern decentralizes data storage, which can lead to better performance and scalability.
- Polyglot Persistence: Services can use different types of databases that best fit their needs—SQL for transactional systems, NoSQL for unstructured data, etc., optimizing data handling and storage efficiency.
Implementation Overview
Implementing the Database per Service pattern involves:
- Choosing the Right Database Type: Based on the service’s specific needs, the appropriate type of database (relational, NoSQL, graph, etc.) should be selected.
- Service-specific Schemas: Each service should define and manage its own database schema, including migrations and updates.
- Integration and Communication: Services communicate with each other using APIs instead of direct database access. Data needed by other services must be exposed through service endpoints.
- Data Integrity and Transactions: Careful design is needed to maintain data integrity and manage transactions, especially in operations that span multiple services.
Summary
Summary
The Database per Service pattern is a strategic approach in microservices architecture that promotes service independence and scalability. By allowing each microservice to manage its own database, systems can achieve higher levels of resilience and flexibility, albeit at the cost of increased complexity in data management and inter-service coordination.