link: Message brokers, Database
Database Backed Queue
Overview
A database-backed queue leverages a relational or NoSQL database to implement a queuing mechanism. This approach is ideal for applications that already use a database and need a straightforward way to handle asynchronous processing and ensure persistence.
Key Features
Summary
- Asynchronous Processing: Allows for decoupling tasks, enabling systems to handle multiple operations concurrently without blocking.
- Persistence: Ensures that messages are not lost in case of system failures, as they are stored in a durable database.
- Ease of Implementation: Utilizes existing database infrastructure, making it easy to implement without additional message broker tools.
How It Works
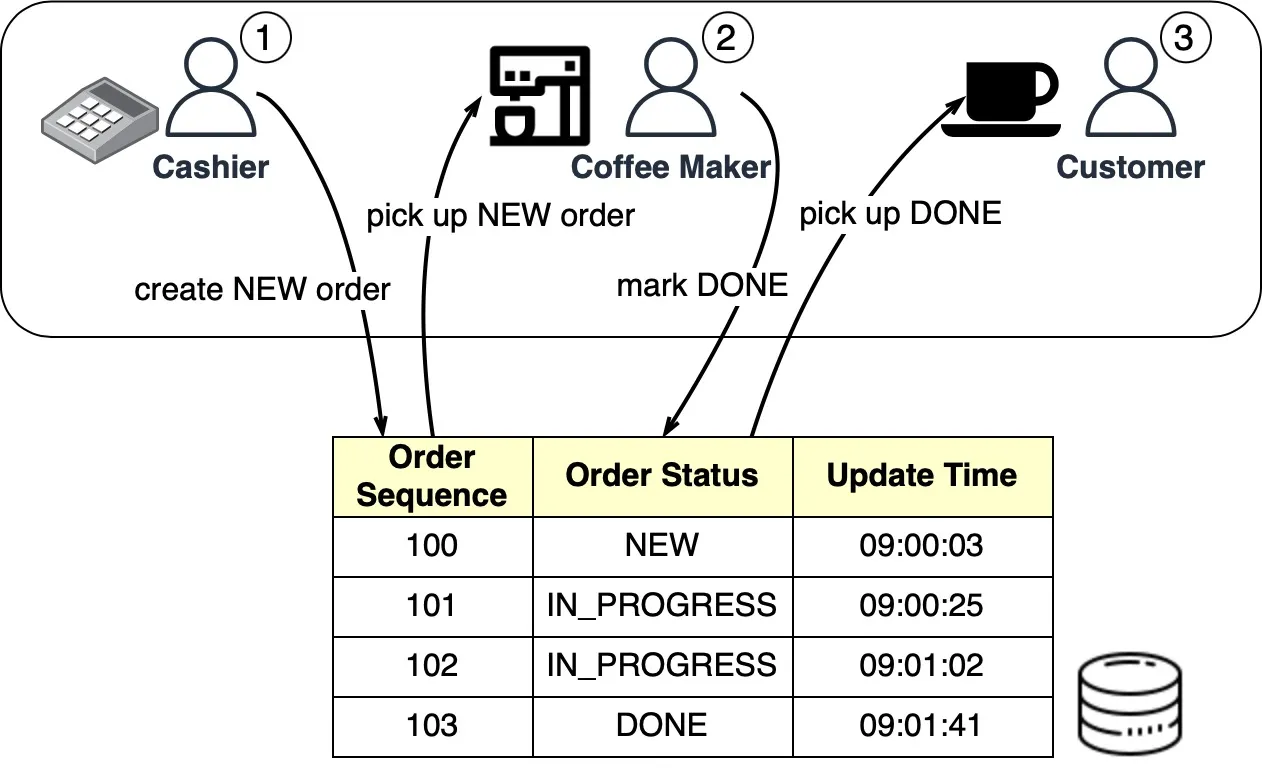
Using a Starbucks example, the two most critical requirements are asynchronous processing and persistence. In this scenario, the process flow is as follows:
- Cashier: Creates a new order in the database-backed queue.
- Coffee Maker: Picks up the new order, updates the state to IN_PROGRESS.
- Coffee Maker Response: Processes the order and updates the status to DONE.
- Customer: Picks up the completed order.
Pros and Cons
Pros
- Simplicity: Easy to implement using existing database infrastructure.
- Durability: Ensures message persistence through database storage.
- Flexibility: Can be adapted to various use cases with minimal setup.
Cons
- Scalability: Not suitable for high-throughput scenarios due to database constraints.
- Performance: Can introduce latency compared to specialized message brokers.
- Maintenance: Requires periodic housekeeping to manage completed messages.