link: Cloud Architecture
Cloud Network
Diagram
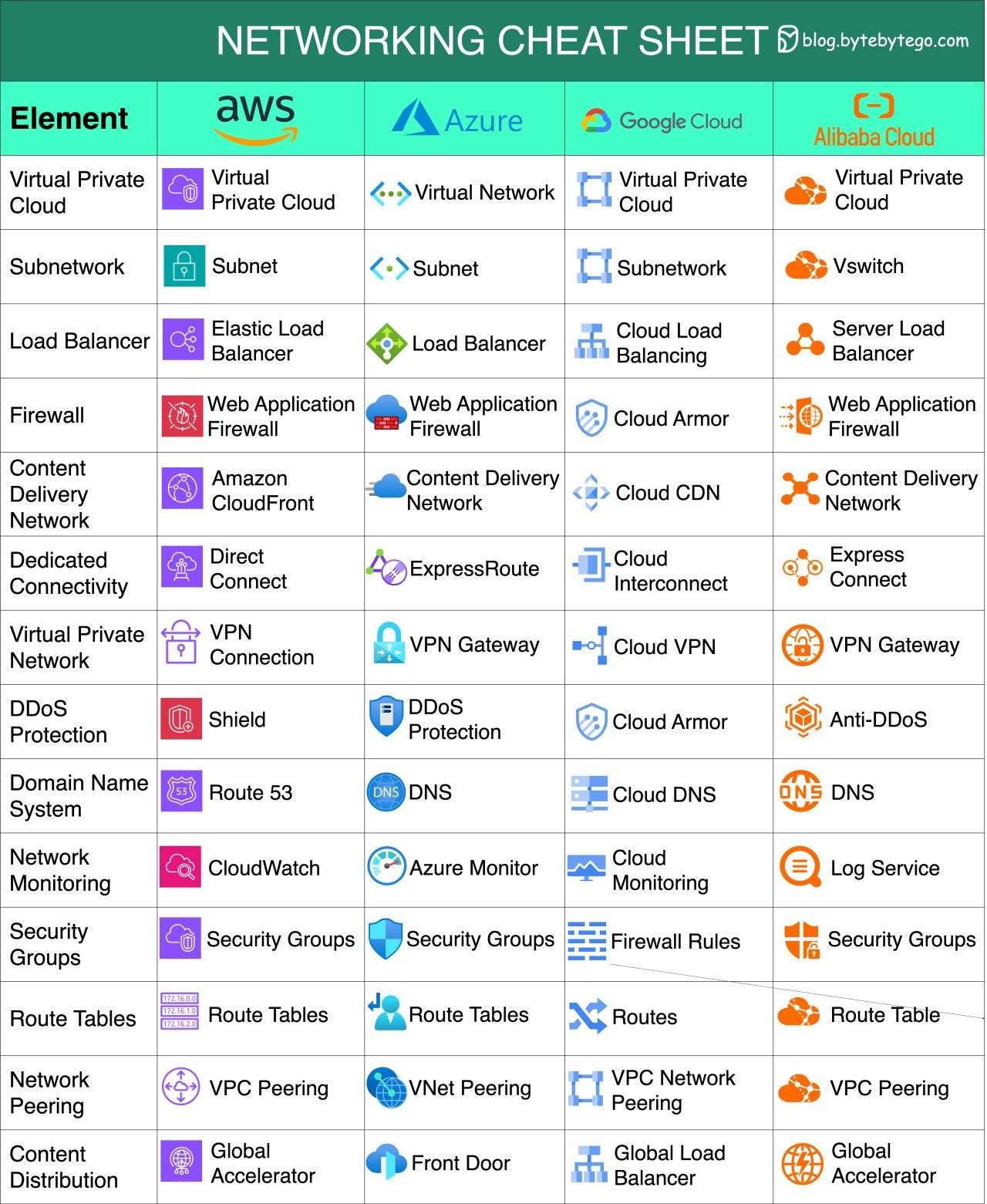
Overview
Cloud solutions provide scalable and flexible computing resources over the internet, enabling businesses to leverage powerful infrastructure, platforms, and services without the need for physical hardware. Major cloud providers like Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud, along with containerization and orchestration tools like Docker and Kubernetes, have revolutionized how applications are developed, deployed, and managed.
Major Cloud Providers
Azure
Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform offering a wide range of services, including computing power, storage, databases, and advanced analytics.
Key Features of Azure
- Virtual Machines: Scalable computing resources for running applications.
- Azure App Service: Managed platform for building, deploying, and scaling web apps and APIs.
- Azure SQL Database: Fully managed relational database service.
- Azure Functions: Serverless computing for event-driven applications.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Managed Kubernetes for containerized applications.
AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud platform providing a vast array of services to build, deploy, and scale applications.
Key Features of AWS
- EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): Scalable virtual servers for running applications.
- S3 (Simple Storage Service): Highly durable object storage.
- RDS (Relational Database Service): Managed relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
- Lambda: Serverless computing for running code in response to events.
- EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service): Managed Kubernetes service.
Google Cloud
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a suite of cloud services for computing, storage, machine learning, and data analytics.
Key Features of Google Cloud
- Compute Engine: Scalable virtual machines for any workload.
- Cloud Storage: Secure and scalable object storage.
- BigQuery: Serverless, highly scalable data warehouse.
- Cloud Functions: Event-driven serverless compute service.
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE): Managed Kubernetes service.
Containerization and Orchestration
Docker
Docker is a platform that enables developers to create, deploy, and run applications in containers. Containers package an application with all its dependencies, ensuring consistent environments across development and production.
Key Features of Docker
- Containerization: Isolates applications and their dependencies into containers.
- Docker Hub: Repository for sharing container images.
- Portability: Ensures that applications run consistently across different environments.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Key Features of Kubernetes
- Automated Deployment: Automates the deployment of containerized applications.
- Scaling: Automatically scales applications based on demand.
- Self-Healing: Automatically replaces and reschedules failed containers.
- Service Discovery and Load Balancing: Distributes traffic across containers and ensures that services are discoverable.
Use Cases
- Web Applications: Deploying and scaling web apps with services like Azure App Service, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, or Google App Engine.
- Data Processing: Leveraging serverless compute services like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions for event-driven data processing.
- Machine Learning: Utilizing cloud-based machine learning services and tools for building and deploying models.
- DevOps: Streamlining development and operations workflows with containerization (Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes).
Summary
Cloud solutions from Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud, combined with containerization and orchestration tools like Docker and Kubernetes, provide robust, scalable, and flexible infrastructure for modern applications. These platforms and tools empower businesses to innovate and scale efficiently while reducing operational overhead and costs.