link: Message brokers
Apache Kafka
Overview
Apache Kafka is a distributed event streaming platform capable of handling high-throughput, low-latency data streams. Originally developed by LinkedIn and later open-sourced, Kafka is widely used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications.
Key Concepts
Topics
- Definition: Topics are the categories to which records are sent.
- Structure: A topic is divided into partitions for scalability and parallelism.
- Replication: Each partition can be replicated across multiple nodes for fault tolerance.
Producers
- Role: Send records to Kafka topics.
- Mechanism: Can send data to a specific partition within a topic, allowing for ordered delivery within that partition.
Consumers
- Role: Read records from Kafka topics.
- Consumer Groups: Consumers can be part of a consumer group, enabling load balancing of data consumption.
Brokers
- Definition: Kafka brokers are servers that store data and serve clients.
- Cluster: A Kafka cluster is composed of multiple brokers working together.
Zookeeper
- Role: Manages the Kafka cluster metadata and configurations.
- Coordination: Helps in leader election for partitions and keeping track of brokers.
Models Supported
Important
- Publish-Subscribe Model: Kafka supports a publish-subscribe messaging model where producers publish messages to topics, and multiple consumers can subscribe to those topics to receive the messages.
- Point-to-Point Model: Through the use of consumer groups, Kafka can also support a point-to-point model where each message is processed by only one consumer within a group.
How It Works
Data Flow
- Producers: Send messages to a Kafka topic.
- Broker: Receives the message and stores it in the topic’s partition.
- Consumers: Subscribe to the topic and read messages from the partitions.
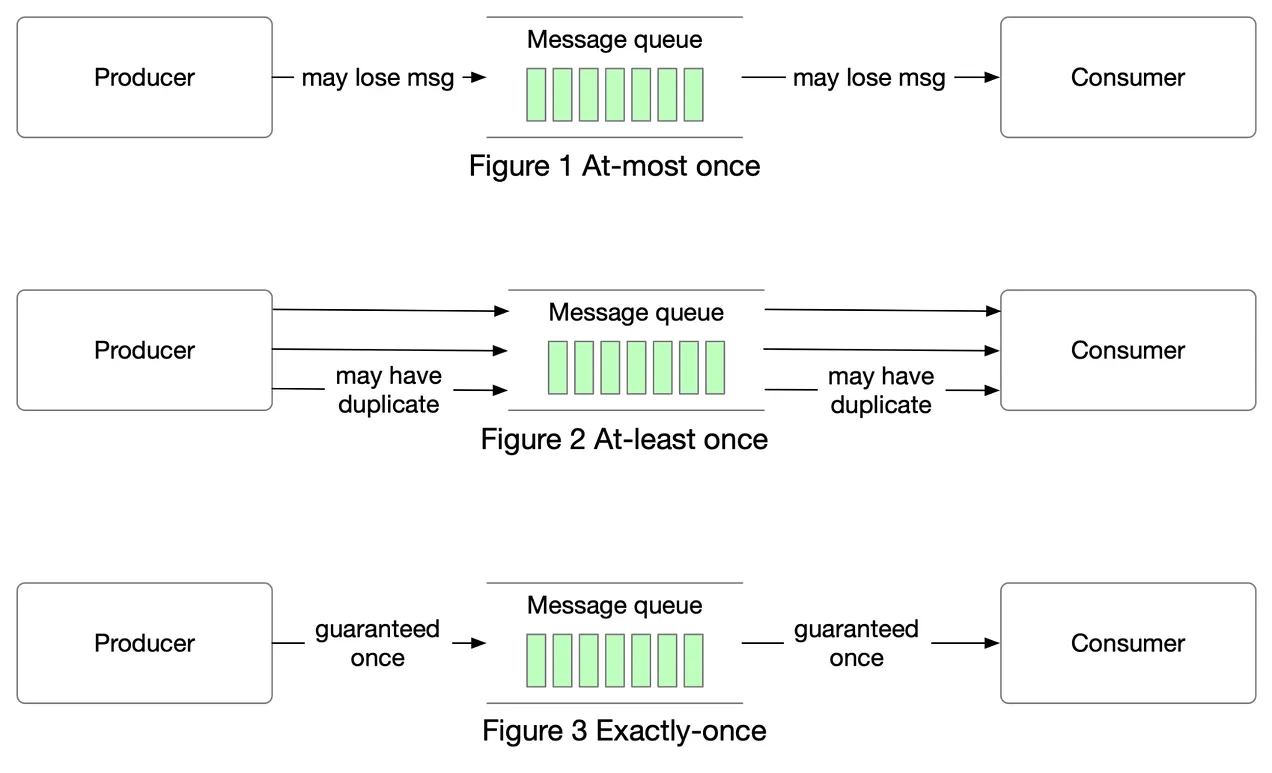
Quality of Service
Supports three Quality Of Service
Diagram
Link to original
Use Cases
- Real-time Data Processing: Processing streams of data in real time, such as log aggregation and monitoring.
- Data Integration: Integrating data across various systems and applications.
- Event Sourcing: Storing state changes as a sequence of events, enabling replay and reconstruction of system state.
Related Topics
References
Cloudflare’s Trillion-Message Kafka Infrastructure: A Deep Dive